Abstract
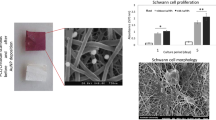
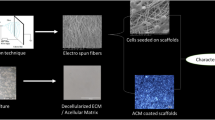
Despite of the pivotal role of Schwann cells (SCs) in peripheral nerve regeneration, lack of an available source has prompted researches for Schwann-like cells transdifferentiation. This study suggests an effective method for tuning the surface of aligned poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanofibers to enhance attachment and proliferation of h-ADSCs on the scaffold through coating of laminin. Following the characterization of biofunctionalized PLGA, brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles (CSNPs), added into laminin solution, and coated on the surface of aligned PLGA scaffold. The release behavior of BDNF and AuNPs from scaffold was evaluated by Bradford assay and inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) technique, respectively. Afterwards, experimental groups were investigated for potential of Schwann cell differentiation using immunocytochemical staining and real-time RT-PCR technique. Results of MTT assay showed the significantly higher proliferation of h-ADSCs on laminin-functionalized scaffold compared to PLGA scaffold (p < 0.05). Additionally, the presence of BDNF and AuNPs on scaffold significantly improved the expression of SCs markers as compared to the control group (p < 0.05). Therefore, use of biofunctionalized PLGA nanofibers can be a promising strategy for inducing the differentiation of h-ADSCs into SCs for nerve tissue engineering.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Arslantunali, T. Dursun, D. Yucel, N. Hasirci, and V. Hasirci (2014). Med. Devices (Auckl). 7, 405.
B. J. Pfister, T. Gordon, J. R. Loverde, A. S. Kochar, S. E. Mackinnon, and D. K. Cullen (2011). Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 39, 2.
A. F. Svennigsen and L. B. Dahlin (2013). Brain Sci. 3, 3.
K. M. Chan, T. Gordon, D. W. Zochodne, and H. A. Power (2014). Exp. Neurol. 261, 82.
A. Faroni, S. A. Mobasseri, P. J. Kingham, and A. J. Reid (2015). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 82–83, 160–167.
T. Tamaki (2014). Neural Regen. Res. 9, 14.
B. Battiston, I. Papalia, P. Tos, and S. Geuna (2009). Int. Rev. Neurobiol 87, 1.
P. Sensharma, G. Madhumathi, R. D. Jayant, and A. K. Jaiswal (2017). Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 77, 13.
H. S. Kim, J. Lee, D. Y. Lee, Y. D. Kim, J. Y. Kim, H. J. Lim, S. Lim, and Y. S. Cho (2017). Stem Cell Rep. 8, 6.
F. M. Chen, L. A. Wu, M. Zhang, R. Zhang, and H. H. Sun (2011). Biomaterials 32, 12.
P. A. Zuk, M. Zhu, P. Ashjian, D. A. De Ugarte, J. I. Huang, H. Mizuno, Z. C. Alfonso, J. K. Fraser, P. Benhaim, and M. H. Hedrick (2002). Mol. Biol. Cell. 13, 12.
W. Liu and Y. L. Cao (2007). Biomaterials 28, 34.
P. X. Ma (2008). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60, 2.
J. L. Wu and Y. Hong (2016). Bioactive Mater. 1, 1.
J. Ai, A. Kiasat-Dolatabadi, S. Ebrahimi-Barough, A. Ai, N. Lotfibakhshaiesh, A. Norouzi-Javidan, H. Saberi, B. Arjmand, and H. R. Aghayan (2014). Neuroscience 1, 1.
L. Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, M. P. Prabhakaran, M. Morshed, M. H. Nasr-Esfahani, and S. Ramakrishna (2010). Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 30, 8.
Z. Meng, Q. Zeng, Z. Sun, X. Xu, Y. Wang, W. Zheng, and Y. Zheng (2012). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 94, 1.
G. Chen, Y. Xia, X. L. Lu, X. F. Zhou, F. M. Zhang, and N. Gu (2013). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 101, 1.
W. M. Yu, Z. L. Chen, A. J. North, and S. Strickland (2009). J. Cell Sci. 122, 7.
A. Bajek, D. Porowińska, and K. Roszkowski (2017). Eur. J. Biol. Res. 7, 3.
J. Y. Zhang, X. G. Luo, C. J. Xian, Z. H. Liu, and X. F. Zhou (2000). Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 12.
A. W. English, W. Meador, and D. Carrasco (2005). Eur J Neurosci. 21, 10.
D. Nevozhay, U. Kańska, R. Budzyńska, and J. Boratyński (2007). Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw.. 61, 1.
A. Bernkop-Schnürch, and S. Dünnhaupt (2012). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 81, 3.
K. Baranes, M. Shevach, O. Shefi, and T. Dvir (2015). Nano lett. 16, 5.
S. Vaezifar, S. Razavi, M. A. Golozar, H. Z. Esfahani, M. Morshed, and S. Karbasi (2015). Int. J. Polym. Mater. Po. 64, 2.
T. Wu, D. Li, Y. Wang, B. Sun, D. Li, Y. Morsi, H. El-Hamshary, S. S. Al-Deyab, and X. Mo (2017). J. Mater. Chem. B. 5, 1.
S. Razavi, M. Mardani, M. Kazemi, E. Esfandiari, M. Narimani, A. Esmaeili, and N. Ahmadi (2013). J. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 33, 2.
S. Razavi, S. Karbasi, M. Morshed, H. Zarkesh Esfahani, M. Golozar, and S. Vaezifar (2015). Cell J. 17, 1.
A. Abdal-Hay, A. Memic, K. H. Hussein, Y. S. Oh, M. Fouad, F. F. Al-Jassir, H. M. Woo, Y. Morsi, X. M. Mo, and S. Ivanovski (2017). Eur. Polym. 96, 6.
E. N. Koukaras, S. A. Papadimitriou, D. Bikiaris, and G. E. Froudakis (2012). Mol. Pharm. 9, 10.
I. Khalin and R. Alyautdin (2016). Drug Deliv. 23, 9.
Y. L. Lin, J. C. Jen, S. Hsu, and I. M. Chiu (2008). Surg. Neurol. 70, 1.
L. Rou (2012). Polytech Univ Turin. 1, 25.
Y. Yang, C. L. Long, H. Pul, Q. Wang, and Z. Yang (2016). Sci. Total Environ. 563, 1.
G. Zarinfard, M. Tadjalli, S. Razavi, and M. Kazemi (2016). J. Mol. Neurosci. 60, 4.
X. J. Wen and P. A. Tresco (2006). Biomaterials. 27, 20.
V. Chiono and C. Tonda-Turo (2015). Prog. Neurobiol. 131, 87.
R. Valentini, P. Aebischer, S. Winn, and P. Galletti (1987). Exp. Neurol. 98, 2.
D. J. Bryan, A. H. Holway, K. K. Wang, A. E. Silva, D. J. Trantolo, D. Wise, and I. C. Summerhayes (2000). Tissue Eng. 6, 2.
G. Keilhoff, A. Goihl, F. Stang, G. Wolf, and H. Fansa (2006). Tissue Eng. 12, 6.
C. Zhao, A. Tan, G. Pastorin, and H. K. Ho (2013). Biotechnol. Adv. 31, 5.
N. J. Schaub (2016). Neural Regen. Res. 11, 12.
J. M. Corey, D. Y. Lin, K. B. Mycek, Q. Chen, S. Samuel, E. L. Feldman, and D. C. Martin (2007). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 83, 3.
F. Yang, R. Murugan, S. Wang, and S. Ramakrishna (2005). Biomaterials. 26, 15.
M. Laura, N. D. Leipzig, and M. S. Shoichet (2008). Mater. Today. 11, 5.
N. E. Zander, J. A. Orlicki, A. M. Rawlett, and T. P. Beebe (2010). Biointerphases. 5, 4.
C. E. Dumont and W. Born (2005). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. 73, 1.
R. Seyedebrahimi, S. Razavi, and J. Varshosaz (2019). J. Clust. Sci. 31, 1.
S. Razavi, R. Seyedebrahimi, and M. Jahromi (2019). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 513, 3.
S. Gurunathan and J. H. Kim (2018). Nanomaterials 8, 6.
S. Das, M. Sharma, D. Saharia, K. K. Sarma, M. G. Sarma, B. B. Borthakur, and U. Bora (2015). Biomaterials. 62, 66–75.
P. G. di Summa, D. F. Kalbermatten, W. Raffoul, G. Terenghi, and P. J. Kingham (2012). Tissue Eng. Part A. 19, 3–4.
A. Faroni, R. J. Smith, L. Lu, and A. J. Reid (2016). Eur. J. Neurosci. 43, 3.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Isfahan University of Medical Sciences for their financial support (Grant no.196052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10876_2020_1822_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 341 kb) Agarose gel electrophoresis image showing PCR product of DNA ladder, 100bp (1), CNTF (2), MBP (3), S100 β (4), NGF (5), GDNF (6), BDNF (7), GFAP (8) genes in PLGB group.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seyedebrahimi, R., Razavi, S., Varshosaz, J. et al. Beneficial effects of biodelivery of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and gold nanoparticles from functionalized electrospun PLGA scaffold for nerve tissue engineering. J Clust Sci 32, 631–642 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01822-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01822-7