Abstract
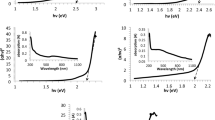
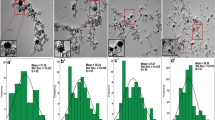
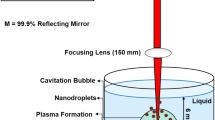
Effects of laser fluence on the characteristics of copper sulfide (CuS) nanoparticles (NPs), produced by laser ablation method have been investigated experimentally. CuS nanoparticles were synthesized by the pulsed laser ablation of a high purity copper bulk in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Pulses of a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser of 1064 nm wavelength at 7 ns pulse width and different fluences were employed to irradiate the Cu solid target in DMSO. The Effects of laser fluence on the size, morphology, and structure of produced nanoparticles have been studied. Results show that the size distribution of the generated CuS nanoparticles was augmented by increasing the laser fluence. The rate of CuS nanoparticles production was increased by increasing the laser fluence. The bandgap energy for CuS nanoparticles was calculated to be 3.77–3.94 eV.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. X. Zhao and C. Burda (2012). Development of plasmonic semiconductor nanomaterials with copper chalcogenides for a future with sustainable energy materials. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, (2), 5564–5576.
H. Lee, S. W. Yoon, E. J. Kim, and J. Park (2007). In-Situ Growth of Copper Sulfide Nanocrystals on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and Their Application as Novel Solar Cell and Amperometric Glucose Sensor Materials. Nano Lett. 7, (3), 778–784.
X. L. Yu, Y. Wang, H. L. W. Chan, and C. B. Cao (2009). Novel gas sensoring materials based on CuS hollow spheres. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 118, (1–3), 423–426.
A. E. Raevskaya, A. L. Stroyuk, S. Y. Kuchmii, and A. I. Kryukov (2004). Catalytic activity of CuS nanoparticles in hydrosulfide ions air oxidation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 212, (1–2), 259–265.
A. M. Malyarevich, et al. (2000). Nonlinear optical properties of CuxS and CuInS2 nanoparticles in sol–gel glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 87, (1), 212–216.
R. S. Mane and C. D. Lokhande (2000). Chemical deposition method for metal chalcogenide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 65, (1), 1–31.
Y. Wang, X. Zhang, P. Chen, H. Liao, and S. Cheng (2012). In situ preparation of CuS cathode with unique stability and high rate performance for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 80, 264–268.
F. Davar, M. R. Loghman-Estarki, M. Salavati-Niasari, and M. Mazaheri (2016). Controllable Synthesis of Covellite Nanoparticles via Thermal Decomposition Method. J. Clust. Sci. 27, (2), 593–602.
M. Salavati-Niasari, S. Alizadeh, M. Mousavi-Kamazani, N. Mir, O. Rezaei, and E. Ahmadi (2013). Surfactant-Free Fabrication of Copper Sulfides (CuS, Cu2S) via Hydrothermal Method. J. Clust. Sci. 24, (4), 1181–1191.
E. Godočíková, P. Baláž, J. M. Criado, C. Real, and E. Gock (2006). Thermal behaviour of mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline CuS. Thermochim. Acta 440, (1), 19–22.
M. Xin, K. Li, and H. Wang (2009). Synthesis of CuS thin films by microwave assisted chemical bath deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, (5), 1436–1442.
C. Wu, et al. (2008). Synthesis and optical properties of CuS nanowires fabricated by electrodeposition with anodic alumina membrane. Mater. Lett. 62, (6–7), 1074–1077.
K.-J. Huang, J.-Z. Zhang, and Y. Fan (2015). One-step solvothermal synthesis of different morphologies CuS nanosheets compared as supercapacitor electrode materials. J. Alloys Compd. 625, 158–163.
K. Y. Niu, J. Yang, S. A. Kulinich, J. Sun, H. Li, and X. W. Du (2010). Morphology Control of Nanostructures via Surface Reaction of Metal Nanodroplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, (28), 9814–9819.
V. Amendola and M. Meneghetti (2009). Laser ablation synthesis in solution and size manipulation of noble metal nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, (20), 3805–3821.
D. Dorranian, S. A. Ahmadi Afshar, N. Tahmasebi, and A. Fotovat Eskandari (2014). Effect of Laser Pulse Energy on the Characteristics of Cu Nanoparticles Produced by Laser Ablation Method in Acetone. J. Clust. Sci. 25, (4), 1147–1156.
V. Amendola and M. Meneghetti (2013). What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, (9), 3027–3046.
K. Y. Niu, J. Yang, S. A. Kulinich, J. Sun, and X. W. Du (2010). Hollow Nanoparticles of Metal Oxides and Sulfides: fast Preparation via Laser Ablation in Liquid. Langmuir 26, (22), 16652–16657.
M. Saranya, et al. (2014). Hydrothermal growth of CuS nanostructures and its photocatalytic properties. Powder Technol. 252, 25–32.
R. Sahraei, S. Noshadi, and A. Goudarzi (2015). Growth of nanocrystalline CuS thin films at room temperature by a facile chemical deposition method. RSC Adv. 5, (94), 77354–77361.
E. Solati, M. Mashayekh, and D. Dorranian (2013). Effects of laser pulse wavelength and laser fluence on the characteristics of silver nanoparticle generated by laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 112, (3), 689–694.
V. S. Vendamani, A. Tripathi, A. P. Pathak, and S. V. Rao, “Laser ablation of natural micas: Synthesis of MgO and Mg (OH) 2 nanoparticles and nanochains,” Mater. Lett., 2017.
C. Chen, Q. Li, Y. Wang, Y. Li, and X. Zhong (2011). Room temperature synthesis of flower-like CuS nanostructures under assistance of ionic liquid. Front. Optoelectron. China 4, (2), 150–155.
M. Anpo (2004). Preparation, Characterization, and Reactivities of Highly Functional Titanium Oxide-Based Photocatalysts Able to Operate under UV–Visible Light Irradiation: approaches in Realizing High Efficiency in the Use of Visible Light. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 77, (8), 1427–1442.
D. Dorranian, E. Solati, and L. Dejam (2012). Photoluminescence of ZnO nanoparticles generated by laser ablation in deionized water. Appl. Phys. A 109, (2), 307–314.
R. Rusdi, A. A. Rahman, N. S. Mohamed, N. Kamarudin, and N. Kamarulzaman (2011). Preparation and band gap energies of ZnO nanotubes, nanorods and spherical nanostructures. Powder Technol. 210, (1), 18–22.
F. Li, J. Wu, Q. Qin, Z. Li, and X. Huang (2010). Controllable synthesis, optical and photocatalytic properties of CuS nanomaterials with hierarchical structures. Powder Technol. 198, (2), 267–274.
K. R. Nemade and S. A. Waghuley (2015). Band gap engineering of CuS nanoparticles for artificial photosynthesis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 39, 781–785.
S. Hamad, et al. (2014). Femtosecond ablation of silicon in acetone: tunable photoluminescence from generated nanoparticles and fabrication of surface nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, (13), 7139–7151.
J. Liqiang, et al. (2006). Review of photoluminescence performance of nano-sized semiconductor materials and its relationships with photocatalytic activity. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, (12), 1773–1787.
J. Zhou, F. Zhao, X. Wang, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, and L. Yang (2006). Template synthesis and luminescent properties of nano-sized YAG: tb phosphors. J. Lumin. 119–120, 237–241.
K. Takase, et al. (2002). Electrical resistivity and photoluminescence spectrum of layered oxysulfide (LaO)CuS. Solid State Commun. 123, (12), 531–534.
A. Awadhia and S. L. Agrawal (2007). Structural, thermal and electrical characterizations of PVA:dMSO:NH4SCN gel electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 178, (13–14), 951–958.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khademian, M., Zandi, M., Amirhoseiny, M. et al. Synthesis of CuS Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation Method in DMSO Media. J Clust Sci 28, 2753–2764 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1257-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1257-2