Abstract
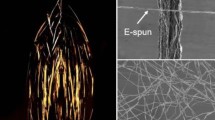
In this research work, crystalline structure, phase transformation, morphology and mean size of titanium dioxide (TiO2) electrospun nanofibers have been tailored by loading with 2.5, 5.0 and 7.5 wt.% of silver (Ag) which was followed by calcination. The as prepared non woven mats of nanofibers were calcinated at 500 °C to allow the reaction moieties to leave the TiO2 matrix and subsequently formation of Ag clusters. The effect of Ag loading and calcination on the transformation of microstructure of these electrospun nanofibers have been characterized by XRD, FESEM, FT-IR and Raman spectroscopy (RS). The mean diameter of Ag loaded nanofibers has been found to decrease upon calcination which was estimated to 70 nm whereas length was in the order of mm range. XRD and RS results have strongly supported the transformation of crystalline phase from rutile (A) to anatase (R) above 2.5 wt.% of Ag loading in TiO2 after calcination. The roughness on the outer surfaces of these nanofibers has been observed to increase with the Ag loading consequent to calcination, which has been attributed to the formation Ag nanoparticles that were found adsorbed at the surfaces. An interesting finding of this study is the existence of 1D nanofibers’ structure even at higher (7.5 wt.%) Ag loading, as observed by the SEM micrographs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. Boyd, L. Greengard, M. Brongersma, M. Y. El-Naggar, and D. G. Goodwin (2006). Nano Lett. 6, 2592–2597.
D. A. H. Hanaor and C. Charles (2011). Sorrell, review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. Mater. Sci. 46, 855–874.
T. B. Ghosh, S. Dhabal, and A. K. Datta (2003). Appl. Phys. 94, 4577.
M. Hirano, N. Nakahara, K. Ota, O. Tanaike, and N. Inagaki (2003). Solid State Chem. 170, 39.
G. Li, L. Li, J. G. Boerio, and B. F. Woodfield (2005). Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 8659.
M. Xu, et al. (2011). Photocatalytic activity of bulk TiO2 anatase and rutile single crystals using infrared absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 138302.
O. Carp, C. L. Huisman, and A. Reller (2004). Prog. Solid State Chem. 32, 33–177.
Y. Dai, C. M. Cobley, J. Zeng, Y. Sun, and Y. Xia (2009). Nano Lett. 9, 2455–2459.
S. J. Doh, C. Kim, S. G. Lee, S. J. Lee, and H. Kim (2008). J. Hazard. Mater. 154, 118–127.
R. Kralchevska, M. Milanova, T. Tišler, A. Pintar, G. Tyuliev, and D. Todorovsky (2012). Mater. Chem. Phys. 133, 1116–1126.
L. Han, Y. Xin, H. Liu, X. Ma, and G. Tang (2010). J. Hazard. Mater. 175, 524–531.
A. Vohra, D. Goswami, D. Deshpande, and S. Block (2006). Appl. Catal. B 64, 57–65.
D. Li and Y. Xia (2003). Nano Lett. 3, 555–560.
R. Chandrasekar, L. Zhang, J. Y. Howe, N. E. Hedin, Y. Zhang, and H. Fong (2009). J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1198–1205.
S. Chuangchote, J. Jitputti, T. Sagawa, and S. Yoshikawa (2009). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 1140–1143.
G. Hongyu, W. Xiaohong, G. Yihang, and S. Changlu (2013). Appl. Surf. Sci. 280, 720–725.
W. Chang, F. Xu, X. Mu, L. Ji, G. Ma, and J. Nie (2013). Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 2661–2668.
H. E. Chao, Y. U. Yun, H. U. Xingfang, and A. Larbot (2003). J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23, 1457–1464.
J. G. Amores, and V. S. Escribano (1994) J. Mater. Chem. 4.
C. Suryanarayana and M. G. Norton X-ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach (Springer, Berlin, 2013).
R. A. Spurr and H. Myers (1957). Anal. Chem. 29, 760–762.
R. E. Bailey, A. M. Smith, and S. Nie (2004). Phys. E 25, 1–12.
N. K. Reddy, K. Ramesh, R. Ganesan, K. R. Reddy, K. Gunasekhar, and E. Gopal (2006). Appl. Phys. A 83, 133–138.
M. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, M. Shokri, and B. Rad (2008). Glob. Nest J. 10, 1–7.
B. M. Reddy, G. K. Reddy, K. N. Rao, I. Ganesh, and J. M. Ferreira (2009). J. Mater. Sci. 44, 4874–4882.
D. Vu, X. Li, Z. Li, and C. Wang (2012). J. Chem. Eng. Data 58, 71–77.
J.-Y. Park, K.-J. Hwang, J.-W. Lee, and I.-H. Lee (2011). J. Mater. Sci. 46, 7240–7246.
T. M. Khan and T. BiBi (2012). Chin. Phys. B 21, 097303.
C. Rath, P. Mohanty, A. Pandey, and N. Mishra (2009). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42, 205101.
H. C. Wu Continuum Mechanics and Plasticity (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2004).
A. Alves, F. Berutti, F. Clemens, T. Graule, and C. Bergmann (2009). Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 312–317.
S. Ray, R. Banerjee, and A. Barua (1980). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 19, 1889.
M. Suwarnkar, R. Dhabbe, A. Kadam, and K. Garadkar (2014). Ceram. Int. 40, 5489–5496.
T. Ohsaka, F. Izumi, and Y. Fujiki (1978). J. Raman Spectrosc. 7, 321–324.
S. Hamaguchi and H. Yoshitake (2009). Electrochemistry 77, 373–378.
A. N. Murashkevich, A. S. Lavitskaya, T. I. Barannikova, and I. M. Zharskii (2008). J. Appl. Spectrosc. 75, 730–734.
X. Feng, X. Wang, X. Chen, and Y. Yue (2011). Acta Mater. 59, 1934–1944.
M. R. Hoffmann, S. T. Martin, W. Choi, and D. W. Bahnemann (1995). Chem. Rev. 95, 69–96.
J. Zhang, M. Li, Z. Feng, J. Chen, and C. Li (2006). J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 927–935.
S. Vlassov, B. Polyakov, M. Vahtrus, M. Mets, M. Antsov, R. Saar, and L. Dorogin (2015). Mater. Charact. 100, 98–103.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the technical support extended by Central Resource Lab, University of Peshawar, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batool, Z., Raffi, M., Zakria, M. et al. Effect of Ag Loading on the Microstructure of TiO2 Electrospun Nanofibers. J Clust Sci 28, 1857–1870 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1187-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1187-z