Abstract
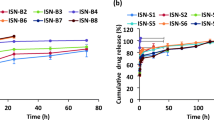
In the present study the effect of process (homogenization speed) and formulation (polymer concentration, surfactant concentration, drug amount, perfluorohexane volume fraction and co-surfactant inclusion) variables on particle size, entrapment efficiency, and drug release kinetics of doxorubicin-loaded alginate stabilized perfluorohexane nanodroplets were evaluated. Particle size and doxorubicin entrapment efficiency were highly affected by formulation and process variables. In vitro release profile of doxorubicin from all formulations was an apparently biphasic release process and 7–13 % of drug released from nanodroplets after 24 h incubation in PBS, pH 7.4, depending on the nanodroplets composition but ultrasound exposure for 10 min resulted in triggered release of 85.95 % of doxorubicin fromoptimal formulation (G). The inclusion of Span 60 (0.15 %), Poloxamer 188 (0.15 %) as co-surfactants reduced the particle size of nanodroplets from 51.8 to 42.3 and 35.6 nm, respectively. The entrapment efficiency decreased for span 60, while it did not changed in the case of Poloxamer 188. Comparison of drug release kinetics demonstrated that drug release was delayed for both Span 60 and Poloxamer 188. Thus, it was concluded that the particle size, entrapment efficiency and the doxorubicin release kinetics could easily be adjusted by taking advantage of process and formulation variables.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Miura, K. Tachibana, T. Okamoto, and K. Saku (2002). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 298, 587.
Y. Ueno, S. Sonoda, R. Suzuki, M. Yokouchi, Y. Kawasoe, K. Tachibana, K. Maruyama, T. Sakamoto, and S. Komiya (2011). Cancer Biol. Ther. 12, 270.
G. A. Husseini, D. Velluto, L. Kherbeck, W. G. Pitt, J. A. Hubbell, and D. A. Christensen (2013). Colloids Surf. B 101, 153.
N. Rapoport, Z. Gao, and A. Kennedy (2007). J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 99, 1095.
S. Mitragotri (2005). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 4, 255.
N. Rapoport, D. A. Christensen, A. M. Kennedy, and K. H. Nam (2010). Ultrasound Med. Biol. 36, 419.
T. O. Matsunaga, P. S. Sheeran, S. Luois, J. E. Streeter, L. B. Mullin, B. Banerjee, and P. A. Dayton (2012). Theranostics 2, 1185.
O. D. Kripfgans, J. B. Fowlkes, D. L. Miller, O. P. Eldevik, and P. L. Carson (2000). Ultrasound Med. Biol. 26, 1177.
P. S. Sheeran and P. A. Dayton (2012). Curr. Pharm. Des. 18, 2152.
S. Hernot and A. L. Klibanov (2008). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60, 1153.
R. Suzuki, T. Takizawa, Y. Negishi, K. Hagisawa, K. Tanaka, K. Sawamura, N. Utoguchi, T. Nishioka, and K. Maruyama (2007). J. Control. Release 117, 130.
N. Reznik, R. Williams, and P. N. Burns (2011). Ultrasound Med. Biol. 37, 1271.
H. Maeda, J. Wu, T. Sawa, Y. Matsumura, and K. Hori (2000). J. Control. Release 65, 271.
C. Chretien and J. C. Chaumeil (2005). Int. J. Pharm. 304, 8.
G. Jiang, S. Min, E. J. Oh, and S. K. Hahn (2007). Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 12, 648.
K. Yong Lee and D. Mooney (2012). Prog. Polym. Sci. 37, 106.
I. Kurt and C. Taylor (2009). J. Food Hydrocoll. 3, 1.
T. L. Bowersock, H. HogenEsch, M. Suckow, R. E. Porter, R. Jackson, and K. Park (1996). J. Control. Release 39, 209.
B. Thu, P. Bruheim, T. Espevik, O. Smidsrød, P. Soon-Shiong, and G. Skjaệk-Brñk (1996). Biomaterials 17, 1031.
A. J. Rebeiro, R. J. Neufeld, A. Philippe, and J. C. Chaumeil (1999). Int. J. Pharm. 187, 115.
B. Sarmento, A. Ribeiro, F. Veiga, R. Neufeld, and D. Ferreira (2005). Revista Portuguesa Farmácia 2, 139.
C. Ouwerx, N. M. Velings, M. M. Mestdagh, and M. A. V. Axelos (1998). Polym. Gels Netw. 6, 393.
G. A. Husseini, G. D. Myrup, W. G. Pitt, D. A. Christensen, and N. Y. Rapoport (2000). J. Control. Release 69, 43.
A. Budhian, S. J. Siegel, and K. I. Winey (2007). Int. J. Pharm. 336, 367.
M. L. Zweers, D. W. Grijpma, and G. H. Engbers (2003). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 66, 559.
T. Gorner, R. Gref, D. Michenot, et al. (1999). J. Control. Release 57, 259.
A. Budhian, S. J. Siegel, and K. I. Winey (2005). J. Microencapsul. 22, 773.
Y. Krishnamachari, P. Madan, and S. Lin (2007). Int. J. Pharm. 338, 238.
D. Quintanar-Guerrero, H. Fessi, E. Allémann, et al. (1996). Int. J. Pharm. 143, 133.
L. S. Wan and P. F. Lee (1974). J. Pharm. Sci. 63, 136.
Y. Y. Yang, T. S. Chung, and N. P. Ng (2001). Biomaterials 22, 231.
S. Mao, Y. Shi, L. Li, et al. (2008). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 68, 214.
G. D. Rosa, R. Iommelli, M. I. La Rotonda, et al. (2000). J. Control. Release 69, 283.
F. Yan, C. Zhang, Y. Zheng, et al. (2010). Nanomedicine 6, 170.
Sh Song, Zh Wang, Y. Qian, L. Zhang, and E. Luo (2012). J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 4388.
L. Mu and S. S. Feng (2003). J. Control. Release 86, 33.
M. J. Santander-Ortega, A. B. Jodar-Reyes, N. Csaba, et al. (2006). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 302, 522.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baghbani, F., Moztarzadeh, F., Mohandesi, J.A. et al. Optimization of Formulation and Process Variables for the Preparation of Novel Doxorubicin-Loaded Sonosensitive Nanodroplets. J Clust Sci 27, 1519–1536 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-1020-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-1020-0