Abstract
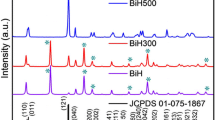
A novel chrysanthemum-shaped monocline ZnWO4 photocatalyst was synthesized by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method with Na2WO4·2H2O and Zn(NO3)2·6H2O as raw materials at different reaction temperatures. The prepared ZnWO4 photocatalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), Transmission electron microscopy, Photoluminescence spectrum (PL) and UV–Vis absorption spectrum (UV–Vis). The photocatalytic property of the prepared chrysanthemum-shaped monocline ZnWO4 photocatalyst was evaluated by the degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) in aqueous solution. The effects of reaction temperature on the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of RhB were investigated. The results indicated that the chrysanthemum-shaped monocline ZnWO4 photocatalyst is prepared by foliated powders with the sizes of about 30 nm and 500 nm respectively at 160 and 220 °C. The PL relative intensity of prepared ZnWO4 photocatalyst is apparently intensifying with increasing temperature. The photocatalytic property decreases with the increasing recombination probability of the excited electrons and holes. The chrysanthemum-shaped monocline ZnWO4 photocatalyst prepared at 160 °C possesses the best photocatalytic property, and the degradation efficiency of RhB at 180 min UV-light irradiation is achieved 75 %. The ZnWO4 has good reusability property on degradation of RhB and the degradation rate is still higher than 65 % after three cycles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Wang, F. D. Medina, D. D. Liu, and Y. D. Zhou (1994). J. Phys Con-dens Matter 6, 5373.
S. H. Yu, B. Liu, M. S. Mo, J. H. Huang, X. M. Liu, and Y. T. Qian (2003). Adv. Funct. Mater. 13, 639.
X. C. Song, E. Yang, Y. F. Zheng, and Y. Wang (2007). Acta. Phys. Chim. Sin. 23, 1123.
J. D. Vergados (2002). Phys. Rep. 361, 1.
Z. D. Lou, J. H. Hao, and M. Cocivera (2002). J. Lumin. 99, 349.
C. L. Yu and J. C. Yu (2009). Sci. Eng. B. 164, 16.
H. B. Fu, J. Lin, L. W. Zhang, and Y. F. Zhu (2006). Appl. Catal. A306, 58.
X. Zhao and Y. F. Zhu (2006). Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 336.
G. B. Kumar, K. Sivaiah, and S. Buddhudu (2010). Ceram. Int. 36, 99.
G. L. Huang, C. Zhang, and Y. F. Zhu (2007). J. Alloys Comd. 432, 269.
X. Zhao, W. Q. Yao, and Y. Wu (2006). J. Solid State Chem. 179, 2562.
F. S. Wen, X. Zhao, H. Huo, J. S. Chen, E. S. Lin, and J. H. Zhang (2002). Mater. Lett. 55, 152.
J. H. Ryu, C. S. Lim, and K. H. Auh (2003). Mater. Lett. 57, 1550.
J. C. Sczancoski, L. S. Cavalcante, M. R. Joy, J. A. Varela, P. S. Pizani, and E. Longo (2008). J. Chem. Eng. 140, 632.
T. Watanabe, T. Takizawa, and K. Honda (1977). J. Phys. Chem. 81, 1845.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51172135); the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51002092); Research and special projects of the Education Department of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 12JK0445); the Graduate Innovation Found of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (SUST-A04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Tan, GQ., Zhang, W. et al. Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Preparation, Characterization and Photocatalytic Properties of a Chrysanthemum-Shaped ZnWO4 Photocatalyst. J Clust Sci 24, 315–325 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-013-0560-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-013-0560-9