Abstract
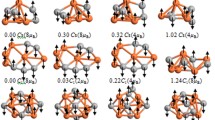
The geometries, stabilities, electronic, and magnetic properties of MB n (M = Y, Zr, Nb, Mo, Tc, Ru, n ≤ 8) clusters have been systematically investigated by density functional theory. It is shown that the lowest energy structures of MB n (n ≤ 3) clusters can be obtained by substituting one B atom in the lowest energy structures of B n+1 clusters in most cases. After n ≥ 8, the 3D configurations prevail and become the lowest-energy structures. The second-order energy difference and the dissociation energy show YB7, ZrB7, NbB6, MoB6, TcB6, RuB6 clusters possess relatively higher stabilities. The doped-M atoms improve the chemical activity of the host clusters in most cases; but different M atom has different effect on B atom’s electronic structure. The binding strengths are strong between M and B n , which plays an important role in the M–B growth mechanisms. It is interesting that the relative orientation between the magnetic moments of the M (M = Zr, Nb, Mo, Tc, Ru) atoms and those of its neighboring B atoms exhibits ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic alignment in contrast to the ferromagnetic alignment of YB n .





Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. J. F. Harris (ed.) Carbon Nanotubes and Related Structures: New Materials for the Twenty First Century (University of Ontario Press, Cambridge, 1999).
S. Ciraci, S. Dag, T. Yildirim, O. Gulseren, and R. T. Senger (2004). J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 16, R901.
G. S. Zakharova, V. L. Volkov, V. V. Ivanovskaya, and A. L. Ivanovskii (2005). Usp. Khim. 74, 651.
E. Durgun, S. Dag, V. M. K. Bagci, O. Gulseren, T. Yildirim, and S. Ciraci (2003). Phys. Rev. B 67, R201401.
C. Cuerretpiecourt, Y. Lebouar, A. Loiseau, and H. Pascard (1994). Nature 372, 761.
N. Grobert, W. K. Hsu, Y. Q. Zhu, J. P. Hare, H. W. Kroto, D. R. M. Walton, M. Terrones, H. Terrones, Ph. Redlich, M. Rühle, R. Escudero, and F. Morales (1999). Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 3363.
A. Leonhardt, A. Ritschel, R. Kozhuharova, A. Graff, T. Mühl, R. Huhle, I. Mönch, D. Elefant, and C. M. Schneider (2003). Diamond Relat. Mater. 12, 790.
N. Grobert, M. Terrones, A. J. Osborne, H. Terrones, W. K. Hsu, S. Trasobares, Y. Q. Zhu, J. P. Hare, H. W. Kroto, and D. R. M. Walton (1998). Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 67, 595.
V. V. Ivanovskaya, C. KÄohler, and G. Seifert (2007). Phys. Rev. B 75, 075410.
X. B. Yang, Y. Ding, and J. Ni (2008) Phys. Rev. B 77, 041402(R).
X. Liu, G. F. Zhao, L. J. Guo, Q. Jing, and Y. H. Luo (2007). Phys. Rev. A 75, 063201.
Z. Yang, Y. L. Yan, W. J. Zhao, X. L. Lei, G. X. Ge, and Y. H. Luo (2007). Acta Phys. Sin 56, (5), 2590.
Z. G. Fang and H. Z. Hu (2006). Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 22, 598.
M. Deshpande, D. G. Kanhere, and R. Pandey (2005). Phys. Rev. A 71, 063202.
Q. Sun, X. G. Gong, Q. Q. Zheng, and G. H. Wang (1996). Acta Phys. Sin. 45, 1146.
J. Teyssier, A. B. Kuzmenko, D. van der Marel, and F. Marsiglio (2007). Phys. Rev. B 75, 134503.
B. Delley (1990). J. Chem. Phys. 92, 508.
C. Lee, W. Yang, and R. G. Parr (1988). Phys. Rev. B 37, 785.
R. S. Mulliken (1955). J. Chem. Phys. 23, 1841.
J. R. Lombardi and B. Davis (2002). Chem. Rev. 102, 2431.
Z. J. Wu (2004). Chem. Phys. Lett. 383, 251.
D. R. Lide (ed),CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 79th (CRC Press, NY, 1998) pp. 9–80.
P. J. Bruna and J. S. Wright (1990). J. Phys. Chem. 94, 1774.
A. Abdurahman, A. Skukla, and G. Seifert (2002). Phys. Rev. B 66, 155423.
I. Boustani (1997). Phys. Rev. B 55, 16426.
J. G. Yao, X. W. Wang, and Y. X. Wang (2008). Chem. Phys. 351, 1.
B. I. Dunlap (1990). Phys. Rev. A 41, 5691.
Z. Q. Li and B. L. Gu (1993). Phys. Rev. A 47, 13611.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge computational support from the institute of theoretical physics of Henan University. Project supported by foundation start up for high level talents of shihezi university, china (Grant No: RCZX200747).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Gx., Jing, Q., Cao, Hb. et al. Structural, Electronic, and Magnetic Properties of MB n (M = Y, Zr, Nb, Mo, Tc, Ru, n ≤ 8) Clusters. J Clust Sci 23, 189–202 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-011-0419-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-011-0419-x