Abstract
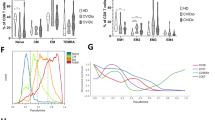
Routine T cells phenotyping occasionally reveals a CD4+CD8dim T cell subset with an apparently homogeneous dot plot. The aim of this study was to elucidate their immunological significance from analysis of 31 healthy donors, 21 elderly and 220 immune deficient patients. CD4+CD8dim T cells expressed reduced levels of CD8 (11–17,000 compared to 96–128,000 mol/cell on CD8+ T Cells). CD4 was expressed at the same level as on CD4+ T cells. The occurrence of raised CD4+CD8dim T cells (> 20 cells/μL) was similar in kidney transplant recipients (28.4%) and healthy donors (26%). It was somewhat lower in HIV+ patients (19.7%) possibly due to virally induced CD4+ T lymphopenia. However, an age effect is possible because the occurrence was raised (33.3%) in 70 volunteers (chi2 test NS). On the other hand, the size of the CD4+CD8dim subset was not correlated with age. CD4+CD8dim T cells did not express the activation markers CD69 (n = 220) or CD25 (n = 10) and expressed the homodimeric (αα) isoform of CD8, suggesting they are related to mucosal immunity (MALT). We selected 29 patients with unambiguous dot plots. In 26 of them one predominant TCR Vβ clonotype was expressed on 18 to 94% of CD4+CD8dim T cells and never on more than 10% of conventional T cells. The predominant clonotypes were Vβ8 (n = 5), Vβ2 (n = 4), Vβ13.1 and Vβ 21 (n = 3 each). Whether this reveals a chronic stimulation or an emerging lymphoproliferative disorder must be elucidated. We propose to name this entity: “Oligoclonal Clonopathy of Undetermined Significance (OCUS).”
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FCM:
-
flow cytometry
- MdFI:
-
median fluorescence intensity
- TCR:
-
T cell receptor
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein Iso Thiocyanate
- EDTA:
-
ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid
- PE:
-
phyco-erythrin
- PE-TR:
-
PE-Texas Red
- PE-Cy5:
-
CD3-PE-cyanine 5
- MALT:
-
mucosal associated lymphoid tissue
- CD4+CD8dim:
-
CD4brightCD8 dimmed CD3+ T lymphocytes
References
Ortolani C, Forti E, Radin E, Cibin R, Ossarizza A: Cytofluorimetric identification of two populations of double positive (CD4+,CD8+) T lymphocytes in human peripheral blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 191:601–609, 1993
Warrington KJ, Takemura S, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM: CD4+,CD28- T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients combine features of the innate and adaptive immune systems. Arthritis Rheum 44:13–20, 2001
Prince HE, Golding J, York J: Characterization of circulating CD4+ CD8+ lymphocytes in healthy individuals prompted by identification of a blood donor with a markedly elevated level of CD4+ CD8+ lymphocytes. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 1:597–605, 1994
Zuckermann FA: Extrathymic CD4/CD8 double positive T cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 72:55–66, 1999
Imhof BA, Dunon D, Courtois D, Luhtala M, Vainio O: Intestinal CD8alphaalpha and CD8alphass intraepithelial lymphocytes are thymus derived and exhibit subtle differences in TCR repertoires. J Immunol 165:6716–6722, 2000
Yamada K, Kimura Y, Nishimura H, Namii Y, Murase M, Yoshikai Y: Characterization of CD4+ CD8alphaalpha+ and CD4-CD8alphaalpha+ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in rats. Int Immunol 11:21–28, 1999
Helgeland L, Johansen FE, Utgaard JO, Vaage JT, Brandtzaeg P: Oligoclonality of rat intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes: Overlapping TCR beta-chain repertoires in the CD4 single-positive and CD4/CD8 double-positive subsets. J Immunol 162:2683–2692, 1999
Airo P, Rossi G, Facchetti F, Marocolo D, Garza L, Lanfranchi A, Prati E, Brugnoni D, Malacarne F, Cattaneo R: Monoclonal expansion of large granular lymphocytes with a CD4+ CD8dim ± phenotype associated with hairy cell leukemia. Haematologica 80:146–149, 1995
Richards SJ, Sivakumaran M, Parapia LA, Balfour I, Norfolk DR, Kaeda J, Scott CS: A distinct large granular lymphocyte (LGL)/NK-associated (NKa) abnormality characterized by membrane CD4 and CD8 coexpression. The Yorkshire Leukaemia Group. Br J Haematol 82:494–501, 1992
Sala P, Tonutti E, Feruglio C, Florian F, Colombatti A: Persistent expansions of CD4+ CD8+ peripheral blood T cells. Blood 82:1546–1552, 1993
Tonutti E, Sala P, Feruglio C, Yin Z, Colombatti Z: Phenotypic heterogeneity of persistent expansions of CD4+ CD8+ T cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 73:312–320, 1994
Suni MA, Ghanekar SA, Houck DW, Maecker HT, Wormsley SB, Picker LJ, Moss RB, Maino VC: CD4(+)CD8(dim) T lymphocytes exhibit enhanced cytokine expression, proliferation and cytotoxic activity in response to HCMV and HIV-1 antigens. Eur J Immunol 31:2512–2520, 2001
Bagot M, Echchakir H, Mami-Chouaib F, Delfau-Larue MH, Charue D, Bernheim A, Chouaib S, Boumsell L, Bensussan A: Isolation of tumor-specific cytotoxic CD4+ and CD4+CD8dim+ T-cell clones infiltrating a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 91:4331–4341, 1998
Weiss L, Roux A, Garcia S, Demouchy D, Haeffner-Cavaillon N, Kazatchkine MD, Gougeon ML: Persistent expansion, in a human immunodeficiency virus-infected person, of V beta-restricted CD4+CD8+ T lymphocytes that express cytotoxicity-associated molecules and are committed to produce interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Infect Dis 178:1158–1162, 1998
Matsui M, Fukuyama H, Akiguchi I, Kameyama M: Circulating CD4+CD8+ cells in myasthenia gravis: Supplementary immunological parameter for long-term prognosis. J Neurol 236:329–335, 1989
Douek DC, Koup RA: Evidence for thymic function in the elderly. Vaccine 18:1638–1641, 2000
Carrasco YR, Trigueros C, Ramiro AR, de Yebenes VG, Toribio ML: Beta-selection is associated with the onset of CD8beta chain expression on CD4(+)CD8alphaalpha(+) pre-T cells during human intrathymic development. Blood 94:3491–3498, 1999
Leishman AJ, Gapin L, Capone M, Palmer E, MacDonald HR, Kronenberg M, Cheroutre H: Precursors of functional MHC class I- or class II-restricted CD8alphaalpha(+) T cells are positively selected in the thymus by agonist self-peptides. Immunity 16:355–64, 2002
Beagley KW, Husband AJ: Intraepithelial lymphocytes: Origins, distribution, and function. Crit Rev Immunol 18:237–254, 1998
Bagriacik EU, Okabe M, Klein JR: Origins of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes: Direct evidence for a thymus-derived gamma delta T cell component. Immunol Lett 75:77–83, 2000
Guy-Grand D, Cerf-Bensussan N, Malissen B, Malassi-Seris M, Briottet C, Vassali P: Two gut intraepithelial CD8+ lymphocyte populations with different T cell receptors : A role for the gut epithelium in T cell differentiation. J Exp Med 173:471–481, 1991.
Oida T, Suzuki K, Nanno M, Kanamori Y, Saito H, Kubota E, Kato S, Itoh M, Kaminogawa S, Ishikawa H: Role of gut cryptopatches in early extrathymic maturation of intestinal intraepithelial T cells. J Immunol 164:3616–3626, 2000
Luhtala M, Lassila O, Toivanen P, Vainio O: A novel peripheral CD4+ CD8+ T cell population: Inheritance of CD8alpha expression on CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol 27:189–193, 1997
Pittet MJ, Speiser DE, Valmori D, Cerottini JC, Romero P: Cytolytic effector function in human circulating CD8+ T cells closely correlates with CD56 surface expression. J Immunol 164:1148–1152, 2000
Garcia KC, Scott CA, Brunmark A, Carbone FR, Peterson PA, Wilson IA, Teyton L: CD8 enhances formation of stable T-cell receptor/MHC class I molecule complexes. Nature 384:577–581, 1996
Sun J, Kavathas PB: Comparison of the roles of CD8 alpha alpha and CD8 alpha beta in interaction with MHC class I: J Immunol 159:6077–6082, 1997
Renard V, Romero P, Vivier E, Malissen B, Luescher LF: CD8 beta increases CD8 coreceptor function and participation in TCR-ligand binding. J Exp Med 184:2439–2444, 1996
Das G, Janeway CA: Development of CD8alpha/alpha and CD8alpha/beta T cells in major histocompatibility complex class I-deficient mice. J Exp Med 190:881–884, 1999
Park SH, Guy-Grand D, Lemonnier FA, Wang CR, Bendelac A, Jabri B: Selection and expansion of CD8alpha/alpha(1) T cell receptor alpha/beta(1) intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in the absence of both classical major histocompatibility complex class I and nonclassical CD1 molecules. J Exp Med 190:885–890, 1999
Yoshikai Y: The interaction of intestinal epithelial cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes in host defense. Immunol Res 20:219–235, 1999
Heinrichs H, Orr HT: HLA non-A,B,C class I genes: Their structure and expression. Immunol Res 9:265–274, 1990
Padovan E, Casorati G, Dellabona P, Giachino C, Lanzavecchia A: Dual receptor T-cells. Implications for alloreactivity and autoimmunity. Ann NY Acad Sci 756:66–70, 1995
Arcaro A, Gregoire C, Bakker TR, Baldi L, Jordan M, Goffin L, Boucheron N, Wurm F, van der Merwe PA, Malissen B, Luescher IF: CD8beta endows CD8 with efficient co-receptor function by coupling T cell receptor/CD3 to raft-associated CD8/p56(lck) complexes. J Exp Med 194:1485–1495, 2001
Iezzi G, Scotet E, Scheidegger D, Lanzavecchia A: The interplay between the duration of TCR and cytokine signaling determines T cell polarization. Eur J Immunol 29:4092–4101, 1999
Bosselut R, Guinter TI, Sharrow SO, Singer A: 2003. Unraveling a revealing paradox: Why major histocompatibility complex I-signaled thymocytes “paradoxically” appear as CD4+8lo transitional cells during positive selection of CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 197:1709–1719, 2003
Sala P, Tonutti E, Feruglio C, Florian F, Colombatti A: Persistent expansions of CD4+ CD8+ peripheral blood T cells. Blood 82:1546–1552, 1993
Cruz D, Sydora BC, Hetzel K, Yakoub G, Kronenberg M, Cheroutre H: An opposite pattern of selection of a single T cell antigen receptor in the thymus and among intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Exp Med 188:255–265, 1998
Callan MF, Steven N, Krausa P, Wilson JD, Moss PA, Gillespie GM, Bell JI, Rickinson AB, McMichael AJ: Large clonal expansions of CD8+ T cells in acute infectious mononucleosis. Nat Med 2:906–911, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available athttp://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9015-5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Claude, L., Mohammad, I., Cristina, I. et al. Significance of Unconventional Peripheral CD4+CD8dim T Cell Subsets. J Clin Immunol 25, 418–427 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-5257-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-5257-x