Abstract
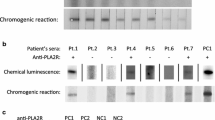
The pathogenetic mechanisms of lupus nephritis (LN) remain to be elucidated. In our previous study, autoantibodies against human glomerular mesangial cells (HMC) were identified in sera of most patients with lupus nephritis. The current study is to investigate the binding characteristics of anti-mesangial cell antibodies to human mesangial cell membrane. Serum samples were collected from 54 patients with renal biopsy proven lupus nephritis, 12 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus without clinical renal involvement, and 15 healthy subjects. Membrane proteins were obtained from in vitro cultured HMC by sonication and sequential centrifugation. DNase I were employed to remove DNA fragments in sera and membrane protein preperation and IgG F(ab′)2 was obtained by pepsin digestion. Western Blot analysis was used to characterize the antibody and antigen interaction. In results, 25 of 54 (46.3%) sera from patients with lupus nephritis had anti-mesangial cell antibodies targeted at 74 kDa, 63 kDa, 52 kDa and 42 kDa protein bands of HMC membrane. Only four of 12 (33.3%) sera from patients without renal involovement recognized the protein bands at 74 kDa and 63 kDa, but not 52 kDa and 42 kDa. DNase treatment of the HMC membrane and the sera did not affect the binding. IgG F(ab′)2 from sera of 10 patients with positive anti-mesangial cell antibodies could still bind the 63 kDa protein. In conclusion, anti-mesangial cell antibodies from sera of patients with lupus nephritis could bind membrane proteins of HMC directly without a DNA bridge and the binding was through antigen–antibody interation. Anti-mesangial cell antibodies might play some role in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis(LN).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mok C, Lau CS: Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Pathol 56:481–490, 2003
Golbus J, McCune WJ: Lupus nephritis: Classification, prognosis, immunopathogenesis, and treatment. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 20(1):213–242, Feb 1994
Chen M, Wang YY, Zhao MM: Anti-mesangial cell autoantibodies and their target antigens in lupus nephritis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 42(12):851–853, Dec 2003, (in Chinese)
Pei F, Zhao MH, Wang YY, Zhang Y, Wang HY: Characterization of target antigens of the novel anti-mesangial cell antibodies in sera from patients with lupus nephritis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 84(3):194–198, Feb 2, 2004, (in Chinese)
Hochberg MC: Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus [letter]. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725, 1997
Wang Y, Zhao MH, Zhang YK, Li XM, Wang HY: Binding capacity and pathophysiological effects of IgA1 from patients with IgA nephropathy on human glomerular mesangial cells.Clin Exp Immunol 136(1):168–175, Apr 2004
Striker GE, Killen PD, Farin FM: Human glomerular cells in vitro: isolation and characterization.Transplant Proc. 12(3 Suppl 1):88–99, Sep 1980
Puccetti A, Madaio MP, Bellese G, Migliorini P: Anti-DNA antibodies bind to DNase I. J Exp Med 181(5):1797–1804, May 1, 1995
Gastinel LN, Pleau JM, Dardenne M, Sasaki A, Bricas E, Morgat JL, Bach JF: High affinity binding sites on plasma membrane obtained from the lymphoblastoid cultured 1301 cell line for highly radioactive serum thymic factor. Biochim Biophys Acta 684(1):117–126, Jan 4, 1982
Williams WM, Isenberg DA: Naturally occurring anti-idiotypic antibodies reactive with anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 7(3):164–175, 1998
Chen C, Nagy Z, Radic MZ, Hardy RR, Huszar D, Camper SA, Weigert M: The site and stage of anti-DNA B cell deletion. Nature 373:252–255, 1995
Westhoff CM, Whittier A, Kathol S, McHugh J, Zajicek C, Shultz LD, Wylie DE: DNA-binding antibodies from viable motheaten mutant mice:implications for B cell tolerance. J Immunol 159:3024–3033, 1997
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ: The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25(11):1271–1277, Nov 1982
Lefkowith JB, Gilkeson GS: Nephritogenic autoantibodies in lupus: current concepts and continuing controversies. Arthritis Rheum 39(6):894–903, Jun 1996
Berden JH, Licht R, Van Bruggen MC, Tax WJ: Role of nucleosomes for induction and glomerular binding of autoantibodies in lupus nephritis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 8(3):299–306, May 1999
Lefkowith JB, Kiehl M, Rubenstein J, Divalerio R, Bernstein K, Kahl L, Rubin RL, Gourley M: Heterogeneity and clinical significance of glomerular-binding antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 98(6):1373–1380, Sep 15, 1996
Raz E, Ben Bassat H, Davidi T, Schlomai Z, Eilat D: Cross-reactions of anti-DNA autoantibodies with cell surface proteins. Eur J Immunol 23(2):383–390, Feb 1993
Raz E, Brezis M, Rosenmann E, Eilat D: Anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to renal antigens and induce kidney dysfunction in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Immunol 142(9):3076–3082, May 1, 1989
D’Andrea DM, Coupaye Gerard B, Kleyman TR, Foster MH, Madaio MP: Lupus autoantibodies interact directly with distinct glomerular and vascular cell surface antigens. Kidney Int 49(5): 1214–1221, May 1996
Chan TM, Leung JKH, Ho SKN, Yung S: Mesangial Cell-Binding Anti-DNA antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol 13(5):1219–1229, 2002
Jordan SC. Intravenous gamma-globulin therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus and immune complex disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 53(2 Pt 2):S164–S169, Nov 1989
Pratesi F, Moscato S, Sabbatini A, Chimenti D, Bombardieri S, Migliorini P: Autoantibodies specific for α-enolase in systemic autoimmune disorders. J Rheumatol 27(1):109–115, 2002
Moodie FDL, Leaker B, Cambridge G, Totty NF, Segal AW: Alpha-enolase: a novel cytosolic autoantigen in ANCA positive vasculitis. Kidney Int 43:675–681, 1993
Pancholi V: Multifunctional alpha-enolase: its role in disease. Cell. Mol Life Sci 58(7):902–920, 2001
Moscato S, Pratesi F, Sabbatini A, Chimenti D, Scavuzzo M, Passatino R, Bombardieri S, Giallongo A, Migliorini P: Surface expression of a glycolytic enzyme, alpha-enolase, recognized by autoantibodies in connective tissue disorders. Eur J Immunol 30(12):3575–3584, Dec 2000
Miles LA, Dahlberg CM, Plescia J, Felez J, Kato K, Plow EJ: Role of cell-surface lysines in plasminogen binding to cells: identification of alpha-enolase as a candidate plasminogen receptor. Biochemistry 30(6):1682–1691, Feb 12 1991
Plow EF, Herren T, Redlitz A, Miles LA, Hoover-Plow JL: The cell biology of the plasminogen system. FASEB J 9:939–945, 1995
Deocharan B, Qing X, Lichauco J, Putterman C: Alpha-actinin is a cross-reactive renal target for pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies. J Immunol 168(6):3072–3078, Mar 15 2002
Chan TM: Clinical and Basic Research in systemic lupus erythematosus. Abstract 2004, ISN
Ballardie FW, Brenchley PE, Williams S, O’Donoghue DJ: Autoimmunity in IgA nephropathy. Lancet 2(8611):588–592, Sep 10, 1988
O’Donoghue DJ, Darvill A, Ballardie FW: Mesangial cell autoantigens in immunoglobulin A nephropathy and Henoch-Schonlein purpura. J Clin Invest 88(5):1522–1530, Nov 1991
Fornasieri A, Pinerolo C, Bernasconi P, Li M, Armelloni S, Gibelli A, D’Amico G: Anti-mesangial and anti-endothelial cell antibodies in IgA mesangial nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 44(2):71–79, Aug 1995
Hanna E: Abboud Resident Glomerular Cells in Glomerular Injury: Mesangial Cells. Semin Nephrol 11(3):304–310, 1991
Chang-Youh Tsai, Tsai-Hung Wu, Huang-Hui Sun, Chia-Li Yu: Effects of antibodies to double stranded DNA, Purified from serum samples of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus, on the glomerular mesangial cells. Ann Rheum Dis 51:162–167, 1992
Yamamoto T, Wilson CB: Quantitative and qualitative studies of antibody-induced mesangial cell damage in the rat. Kidney Int 32(4):514–525, Oct 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, H., Chen, M., Zhang, Y. et al. Characterization of Anti-Mesangial Cell Antibodies and Their Target Antigens in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. J Clin Immunol 25, 281–287 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-4082-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-4082-6