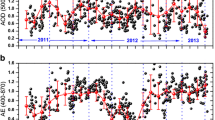
Abstract
The properties of the atmospheric aerosols depend on the source region and on the modifications that occur during their transport in the air. We have studied physical and chemical properties of aerosols along with their sink mechanism over two locations in southwest India, an urban site (Pune) and well-established climate observatory at Sinhagad (SINH), which represents rural and high altitude site. The ground-based measurements of aerosols, together with their radiative properties in this study have provided means to understand the observed variability and the impact on the aerosol radiative properties effectively over this region. The annual mean elemental carbon concentration (3.4 µg m− 3) at Pune was observed about three times higher compared to SINH (1.3 µg m− 3), indicating strong emissions of carbon-rich aerosols at the urban location. Aerosol optical properties were derived using the OPAC model which were used to compute the Aerosol radiative forcing (ARF) over both stations calculated using SBDART (Santa Barbara DISORT Atmospheric Radiative Transfer) model shows pronounced seasonal variations due to changes in aerosol optical depth and single scattering albedo at both locations. The year-round ARF was 4–5 times higher over Pune (31.4 ± 3.5 Wm− 2) compared to SINH (7.2 ± 1.1 Wm− 2). The atmospheric heating rate due to aerosols shows a similar pattern as ARF for these locations. The heating was higher in the wintertime, ~ 0.9–1.6 K day− 1 at Pune, and ~ 0.3–0.6 K day− 1 at SINH. The estimated scavenging ratio was found high for NO3− and Ca.2+. The wet deposition fluxes of Cl−, SO42−, Na+, Mg2+ were observed higher for SINH as compared to Pune, due to the high amount of rain received at SINH.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, K., Trautmann, T., Blaschke, T., Majid, H.: Aerosol optical and radiative properties during summer and winter seasons over Lahore and Karachi. Atmos. Environ. 50, 234–245 (2012)
Ali, K., Budhavant, K.B., Safai, P.D., Rao, P.S.P.: Seasonal factors influencing in chemical composition of total suspended particles at Pune, India. Sci. Total Environ. 414, 257–267 (2012)
Begum, B.A., Hossain, A., Nahar, N., Markwitz, A., Hopke, P.K.: Organic and black carbon in PM2.5 at an urban site at dhaka, Bangladesh. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 12, 1062–1072 (2012)
Birch, M.E., Cary, R.A.: Elemental carbon-based method for monitoring occupational exposures to particulate diesel exhaust. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 25, 221–241 (1996)
Bollasina, M.A., Ming, Y., Ramaswamy, V.: Anthropogenic aerosols and the weakening of the South Asian summer monsoon. Science 80, 502–505 (2011)
Bond, T.C., Doherty, S.J., Fahey, D.W., Forster, P.M., Berntsen, T., Deangelo, B.J., Flanner, M.G., Ghan, S., Kärcher, B., Koch, D., Kinne, S., Kondo, Y., Quinn, P.K., Sarofim, M.C., Schultz, M.G., Schulz, M., Venkataraman, C., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Bellouin, N., Guttikunda, S.K., Hopke, P.K., Jacobson, M.Z., Kaiser, J.W., Klimont, Z., Lohmann, U., Schwarz, J.P., Shindell, D., Storelvmo, T., Warren, S.G., Zender, C.S.: Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118, 5380–5552 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50171
Budhavant, K.B., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Ah, K.: Chemistry of monsoon and post-monsoon rains at a high altitude location, Sinhagad, India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 9, 65–79 (2009). https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2008.07.0033
Budhavant, K.B., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Gawhane, R.D., Raju, M.P.: Chemistry of rainwater and aerosols over Bay of Bengal during CTCZ program. J. Atmos. Chem. 65, 171–183 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-011-9187-0
Budhavant, K.B., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Ali, K.: Influence of local sources on rainwater chemistry over Pune region, India. Atmos. Res. 100, 121–131 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.01.004
Budhavant, K.B., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Gawhane, R.D., Raju, M.P., Mahajan, C.M., Satsangi, P.G.: Atmospheric wet and dry depositions of ions over an urban location in South-West India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 12, 561–570 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2011.12.0233
Budhavant, K.B., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Granat, L., Rodhe, H.: Chemical composition of the inorganic fraction of cloud-water at a high-altitude station in West India. Atmos. Environ. 88, 59–65 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.01.039
Budhavant, K., Andersson, A., Bosch, C., Kruså, M., Murthaza, A., Zahid, Gustafsson, Ö.: Apportioned contributions of PM fine aerosol particles over the Maldives (northern Indian Ocean) from local sources vs long-range transport. Sci. Total Environ. 536, 72–78 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.059
Budhavant, K.B., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Leck, C., Rodhe, H.: Black carbon in cloud-water and rain water during monsoon season at a high altitude station in India. Atmos. Environ. 129, 256–264 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.01.028
Budhavant, K., Bikkina, S., Andersson, A., Asmi, E., Backman, J., Kesti, J., Zahid, H., Satheesh, S.K., Gustafsson, Ö.: Anthropogenic fine aerosols dominate the wintertime regime over the northern Indian Ocean. Tellus, Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 70, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/16000889.2018a.1464871
Budhavant, K.B., Andersson, A., Holmstrand, H., Bikkina, P., Bikkina, S., Satheesh, S.K., Gustafsson, Ö.: Enhanced light-absorption of black carbon in rain over the northern Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 125, e2019JD031246 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031246
Cadle, S.H., Vandekopple, R., Mulawa, P.A., Dasch, J.M.: Ambient concentrations, scavenging ratios and sources regions of acid related compounds and trace metals during winter in Northern Michigan.. Atmos. Environ. 24A(12), 2981–2989 (1990)
Dasari, S., Andersson, A., Bikkina, S., Holmstrand, H., Budhavant, K., Satheesh, S., Asmi, E., Kesti, J., Backman, J., Salam, A., Bisht, D.S., Tiwari, S., Hameed, Z., Gustafsson, Ö: Photochemical degradation affects the light absorption of water-soluble brown carbon in the South Asian outflow. 1–11 (2019)
Dey, S., Tripathi, S.N., Singh, R.P., Holben, B.N.: Influence of dust storms on the aerosol optical properties over the Indo-Gangetic basin. J. Geophys. Res. 109, D20211 (2004)
Gawhane, R.D., Rao, P.S.P., Budhavant, K.B., Waghmare, V., Meshram, D.C., Safai, P.D.: Seasonal variation of chemical composition and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Pune, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24, 21065–21072 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9761-3
Gawhane, R.D., Rao, P.S.P., Budhavant, K., Meshram, D.C., Safai, P.D.: Anthropogenic fine aerosols dominate over the Pune region, Southwest India. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 131, 1497–1508 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-018-0653-y
Gustafsson, O., Krusa, M., Zencak, Z., Sheesley, R.J., Granat, L., Engstrom, E., Praveen, P.S., Rao, P.S.P., Leck, C., Rodhe, H.: Brown clouds over South Asia: biomass or fossil fuel combustion? Science (80-.). 323, 495–498 (2009)
Hess, M., Koepke, P., Schu, I.: Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: The software package OPAC. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 79, 831–844 (1998)
IPCC: Fifth Assessment Report: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, edited by: Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Doschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., and Midgley, P.M. Cambridge University Press (2013). https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.016
Jaffrezo, J.L., Colin, J.L.: Rain-aerosol coupling in urban area: Scavenging ratios measurements and identification of some transfer processes. Atmos. Environ. 22 (5), 929–935 (1988)
Kaskaoutis, D.G., Sinha, P.R., Vinoj, V., Kosmopoulos, P.G., Tripathi, S.N., Misra, A., Sharma, M., Singh, R.P.: Aerosol properties and radiative forcing over Kanpur during severe aerosol loading conditions. Atmos. Environ. 79,7–19 (2013)
Keene, W.C., Pszenny, A.A.P., Galloway, J.N., Hawley, M.E.: Sea-salt corrections and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 6647 (1986)
Lawrence, M.G., Lelieveld, J.: Atmospheric pollutant outflow from southern Asia: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10, 11017–11096 (2010). https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-11017-2010
Martins, C.S., Wesolows, J.J., Harriss, R.C., Kaifer, R.: Chlorine loss from Puerto Rican and San Francisco Bay area marine aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 78(36), 8778–8792 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1029/JC078i036p08778
Mayol-Bracero, O.L., Guyon, P., Graham, B., Andreae, M.O., Decesari, S., Facchini, M.C., Fuzzi, S., Artaxo, P.: Water-soluble organic compounds in biomass burning aerosols over Amazonia, 2 Apportionment of the chemical composition and importance of the polyacidic fraction. J. Geophys. Res. 107(D20), 8091 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JD000522
Menon, S., Koch, D., Beig, G., Sahu, S., Fasullo, J., Orlikowski, D.: Black carbon aerosols and the third polar ice cap. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10, 4559–4571 (2010). https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-4559-2010
Momin GA, Ali K, Rao PSP, Safai PD, Chate DM, Praveen PS, Rodhe H, Granat L (2005) Study of chemical composition of rainwater at an urban (Pune) and a rural (Sinhagad) location in India. J. Geophys. Res. 110:D08302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD004789
Nair, V.S., Babu, S.S., Manoj, M.R., Mooorthy, K.K., Chin, M.: Direct radiative effects of aerosols over South Asia from observations and modeling. Clim. Dyn. 49, 1411–1428 (2017)
Pandithurai, G., Dipu, S., Dani, K.K., Tiwari, S., Bisht, D.S., Devara, P.C.S., Pinker, R.T.: Aerosol radiative forcing during dust events over New Delhi, India. J. Geophys. Res. 113, D13209 (2008)
Pant, P., Shukla, A., Kohl, S.D., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Harrison, R.M.: Characterization of ambient PM2.5 at a pollution hotspot in New Delhi, India and inference of sources. Atmos. Environ. 109, 178–189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.074
Pavuluri, C.M., Kawamura, K., Aggarwal, S.G., Swaminathan, T.: Characteristics, seasonality and sources of carbonaceous and ionic components in the tropical aerosols from Indian region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 11, 8215–8230 (2011)
Raju, M.P., Safai, P.D., Vijayakumar, K., Devara, P.C.S., Naidu, C.V., Rao, P.S.P., Pandithurai, G.: Atmospheric abundances of black carbon aerosols and their radiative impact over an urban and arural site in SW India. Atmos. Environ. 125, 429–436 (2016)
Ram, K., Tripathi, S.N., Sarin, M.M., Bhattu, D.: Primary and secondary aerosols from an urban site (Kanpur) in the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Impact on CCN, CN concentrations and optical properties. Atmos. Environ. 89, 655–663 (2014)
Ramanathan, V., Ramana, M.V., Roberts, G., Kim, D., Corrigan, C., Chung, C., Winker, D.: Warming trends in Asia amplified by brown cloud solar absorption. Nature. 448, 575–578 (2007)
Ricchiazzi, P., Yang, S., Gautier, C., Sowle, D.: SBDART: A research and Teaching software tool for plane-parallel radiative transfer in the Earth’s atmosphere, Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 79, 2101–2114 (1998)
Safai, P.D., Raju, M.P., Budhavant, K.B., Rao, P.S.P., Devara, P.C.S.: Long term studies on characteristics of black carbon aerosols over a tropical urban station Pune, India. Atmos. Res. 132–133, 173–184 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.05.002
Safai, P.D., Devara, P.C.S., Raju, M.P., Vijayakumar, K., Rao, P.S.P.: Relationship between black carbon and associated optical, physical and radiative properties of aerosols over two contrasting environments. Atmos. Res. 149, 292–299 (2014)
Satheesh, S.K., Ramanathan, V.: Large differences in tropical aerosol forcing at the top of the atmosphere and Earth’s surface. Nature. 405, 60–63 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35011039
Singh, S., Nath, S., Kohli, R., Singh, R.: Aerosols over Delhi during pre-monsoon months: Characteristics and effects on surface radiation forcing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L13808 (2005)
Singh, A., Bloss, W.J., Pope, F.D.: 60 years of UK visibility measurements: impact of meteorology and atmospheric pollutants on visibility. 2085–2101 (2017)
Srivastava, A.K., Ram, K., Singh, S., Kumar, S., Tiwari, S.: Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects over Manora Peak in the Himalayan foothills: seasonal variability and role of transported aerosols. Sci. Total Environ. 502, 287–295 (2015)
Stamnes, K., Tsay, S.C., Wiscombe, W., Jayaweera, K.: Numerically stable algorithm for discrete-ordinate-method radiative transfer in multiple scattering and emitting layered media. Appl. Opt. 27, 2502–2509 (1998)
Venkataraman, C., Reddy, C.K., Jason, S., Reddy, M.S.: Aerosol size and chemical characteristics at Mumbai, India, during the INDOEX-IFP (1999). Atmos. Environ. 36, 1979–1991 (2002)
Verma, S., Prakash, D., Srivastava, A.K., Payra, S.: Radiative forcing estimation of aerosols at an urban site near the thar desert using ground-based remote sensing measurements. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 17, 1294–1304 (2017)
World Health Organization: Ambient air pollution: A global assessment of exposure and burden of disease, Tech. rep., WHO (2016). https://www.who.int/phe/publications/air-pollution-global-assessment/en
Zhao, Y.L., Gao, Y.: Acidic species and chloride depletion in coarse aerosol particles in the US east coast. Sci. Total Environ. 407, 541–547 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Director, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune for his support and encouragement. Authors are grateful to BSNL, Government of India authorities for their corporation and providing space at their microwave tower at sampling station at Sinhagad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 504 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Budhavant, K.B., Gawhane, R.D., Rao, P.S.P. et al. Physico-chemical characterization and sink mechanism of atmospheric aerosols over South-west India. J Atmos Chem 77, 17–33 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-020-09400-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-020-09400-x