Abstract
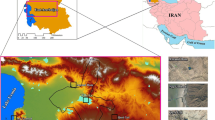
The present paper reports chemistry and fluxes of dust-carbon mixed coarse particles. For the purpose of this study, different carbonaceous fractions i.e. organic carbon ((OC), elemental carbon (EC) and carbonate carbon (CC) of atmospheric dust and their respective local soils were quantified at three sites of National Capital Region (NCR) of Delhi viz. Jawaharlal Nehru University campus (JNU), Connaught Place (CP) and Vishali area of Ghaziabad (GB). It has been observed that the OC and EC levels were approximately five to nine times higher in urban atmospheric dust than their corresponding soils, whereas CC levels were about three times higher than the corresponding soils. Average dustfall fluxes were significantly different at all the sites due to their different land-use patterns. At urban background site (JNU), the dust flux was lowest (172 mg/m2/day) followed by CP, a commercial site, (192 mg/m2/day) and GB, an industrial/residential area, (302 mg/m2/day). Similar to the dustfall pattern, the mean values of OC, EC and CC deposition fluxes were also observed to be lowest at JNU (9.2, 0.8 and 1.0 mg/m2/day, respectively) as compared to CP (12.2, 1.2 and 1.3 mg/m2/day, respectively) and GB sites (11.1, 1.1 and 1.4 mg/m2/day, respectively). Interestingly, unlike fine mode, different correlation pattern of OC and EC in coarse mode dust aerosols at three sites has suggested their independent deposition processes and source contribution. Fluxes of major water soluble inorganic ions (Na+, NH4 +, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, F−, Cl−, NO3 − and SO4 2−) were also determined. Ca2+, Cl− and SO4 2− were found to be the major ionic species of water soluble fraction of the urban dust at all the sites. These interactions are corroborated by the morphology of the mixed aerosols. High levels of measured chemical species and their spatial distribution revealed close correspondence with the local emissions from transport, industries, biomass burning, road dust and construction activities etc.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athique, A., Hill, D.: The multiplexes in India: a cultural economy of urban leisure. Routledge Contemporary South Asia (2010)
Babu, S.S., Moorthy, K.K.: Aerosol black carbon over a tropical coastal station in India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 1–4 (2002)
Bauer, S.E., Mishchenko, M.I., Lacis, A.A., Zhang, S., Perlwitz, J., Metzger, S.M.: Do sulfate and nitrate coatings on mineral dust have important effects on radiative properties and climate modeling? Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres (1984–2012). 112(D6), (2007). doi:10.1029/2005JD006977
Cachier, H., Brémond, M. P., & Buat-Ménard, P. Carbonaceous aerosols from different tropical biomass burning sources (1989)
Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Ho, K.F., Zhang, X.Y., Zou, S.C., Fung, K., et al.: Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in Pearl River Delta Region, China during 2001 winter period. Atmos. Environ. 37(11), 1451–1460 (2003)
Chow, J., Watson, J.: Chemical characteristics of carbonaceous aerosols during dust storms over Xi’an in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 25(5), 847–855 (2008)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Pritchett, L.C., Pierson, W.R., Frazier, C.A., Purcell, R.G.: The DRI thermal/optical reflectance carbon analysis system: description, evaluation and applications in US air quality studies.Atmospheric Environment. Part A. General Topics. 27(8), 1185–1201 (1993)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Chen, L.W.A., Chang, M.O., Robinson, N.F., Trimble, D., Kohl, S.: The IMPROVE_A temperature protocol for thermal/optical carbon analysis: maintaining consistency with a long-term database. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 57(9), 1014–1023 (2007)
Davidson, C.I., Lindberg, S.E., Schmidt, J.A., Cartwright, L.G., Landis, L.R.: Dry deposition of sulfate onto surrogate surfaces. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 90(D1), 2123–2130 (1985)
Deepshikha, S., Satheesh, S.K., Srinivasan, J.: Regional distribution of absorbing efficiency of dust aerosols over India and adjacent continents inferred using satellite remote sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32(3), (2005). doi:10.1029/2004GL022091
DeMott, P.J., Sassen, K., Poellot, M.R., Baumgardner, D., Rogers, D.C., Brooks, S.D., et al.: African dust aerosols as atmospheric ice nuclei. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(14), (2003). doi:10.1029/2003GL017410
Dey, S., Tripathi, S.N., Singh, R.P., Holben, B.N.: Influence of dust storms on the aerosol optical properties over the Indo-Gangetic basin. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres (1984–2012). 109(D20), (2004)
Fang, G.C., Wu, Y.S., Lee, W.J., Chou, T.Y., Lin, I.C.: Ambient air particulates, metallic elements, dry deposition and concentrations at Taichung airport, Taiwan. Atmos. Res. 84(3), 280–289 (2007)
Gadkari, N.M., Pervez, S.: Source investigation of personal particulates in relation to identify major routes of exposure among urban residentials. Atmos. Environ. 41(36), 7951–7963 (2007)
Gelenscer, A.: Carbonaceous aerosols. Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library (2004)
Ginoux, P., Prospero, J.M., Torres, O., Chin, M.: Long-term simulation of global dust distribution with the GOCART model: correlation with North Atlantic oscillation. Environ. Model. Softw. 19(2), 113–128 (2004)
Griffin, D.W., Kellogg, C.A., Shinn, E.A.: Dust in the wind: long range transport of dust in the atmosphere and its implications for global public and ecosystem health. Global Change and Human Health. 2(1), 20–33 (2001)
Gupta, G.P., Singh, S., Kumar, B., Kulshrestha, U.C.: Industrial dust sulphate and its effects on biochemical and morphological characteristics of Morus (Morus alba) plant in NCR Delhi. Environ. Monit. Assess. 187(3), (2015). doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4301-4
Gupta, G.P., Kumar, B., Kulshrestha, U.C.: Impact and pollution indices of urban dust on selected plant species for green belt development: mitigation of the air pollution in NCR Delhi, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 9(2), 1–15 (2016)
Gurugubelli, B., Pervez, S., Tiwari, S.: Characterization and spatiotemporal variation of urban ambient dust fallout in Central India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 13(1), 83–96 (2013)
Han, Y., Cao, J., An, Z., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Jin, Z., et al.: Evaluation of the thermal/optical reflectance method for quantification of elemental carbon in sediments. Chemosphere. 69(4), 526–533 (2007)
Han, Y.M., Cao, J.J., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., An, Z.S., Liu, S.X.: Elemental carbon in urban soils and road dusts in Xi'an, China and its implication for air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 43(15), 2464–2470 (2009a)
Han, Y.M., Cao, J.J., Posmentier, E.S., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Fung, K.K., et al.: The effect of acidification on the determination of elemental carbon, char-, and soot-elemental carbon in soils and sediments. Chemosphere. 75(1), 92–99 (2009b)
He, H., Wang, Y., Ma, Q., Ma, J., Chu, B., Ji, D., et al.: Mineral dust and NOx promote the conversion of SO2 to sulfate in heavy pollution days. Scientific reports. 4, (2014). doi:10.1038/srep04172
Herich, H., Tritscher, T., Wiacek, A., Gysel, M., Weingartner, E., Lohmann, et al.: Water uptake of clay and desert dust aerosol particles at sub-and supersaturated water vapor conditions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(36), 7804–7809 (2009)
Ho, K.F., Lee, S.C., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G.: Characterization of PM 10 and PM 2.5 source profiles for fugitive dust in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 37(8), 1023–1032 (2003)
IUPAC: Glossary of atmospheric chemistry terms. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Applied Chemistry Division, Commission on Atmospheric Chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 62(11), 2167–2219 (1990)
Jankowski, N., Schmidl, C., Marr, I.L., Bauer, H., Puxbaum, H.: Comparison of methods for the quantification of carbonate carbon in atmospheric PM10 aerosol samples. Atmos. Environ. 42(34), 8055–8064 (2008)
Javed, W., Wexler, A.S., Murtaza, G., Ahmad, H.R., Basra, S.M.: Spatial, temporal and size distribution of particulate matter and its chemical constituents in Faisalabad, Pakistan. Atmósfera. 28(2), 99–116 (2015)
Jenkins, B.M., Jones, A.D., Turn, S.Q., Williams, R.B.: Particle concentrations, gas-particle partitioning, and species intercorrelations for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) emitted during biomass burning.Atmospheric. Environment. 30(22), 3825–3835 (1996)
Jha, S.K., Nayak, A.K., Sharma, Y.K., Mishra, V.K., Sharma, D.K.: Fluoride accumulation in soil and vegetation in the vicinity of brick fields. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 80(4), 369–373 (2008)
Kanakidou, M., Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.N., Barnes, I., Dentener, F.J., Facchini, M.C., et al.: Organic aerosol and global climate modelling: a review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 5(4), 1053–1123 (2005)
Khemani, L.T., Momin, G.A., Naik, M.S., Rao, P.P., Kumar, R., Murty, B.V.R.: Impact of alkaline particulates on pH of rain water in India. Water Air Soil Pollut. 25(4), 365–376 (1985)
Kulshrestha, U. C. (2013). Acid Rain, In Encyclopedia of Environmental Management; S.E.Jorgensen, ed. Taylor & Francis: New York, Vol. I, 8–22.
Kulshrestha, U.C., Sharma, D.: Importance of atmospheric dust in India: future scope of research. J. Ind. Geophys. Union. 19(2), 205–209 (2015)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Saxena, A., Kumar, N., Kumari, K.M., Srivastava, S.S.: Chemical composition and association of size-differentiated aerosols at a suburban site in a semi-arid tract of India. J. Atmos. Chem. 29(2), 109–118 (1998)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Jain, M., Sekar, R., Vairamani, M., Sarkar, A.K., Parashar, D.C.: Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of aerosols over Indian Ocean during INDOEX-1999. Curr. Sci. 80(10), 180–185 (2001)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Kulshrestha, M.J., Sekar, R., Sastry, G.S.R., Vairamani, M.: Chemical characteristics of rainwater at an urban site of south-Central India. Atmos. Environ. 37(21), 3019–3026 (2003)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Granat, L., Engardt, M., Rodhe, H.: Review of precipitation monitoring studies in India—a search for regional patterns.Atmospheric. Environment. 39(38), 7403–7419 (2005)
Kumar, B., Verma, K., Kulshrestha, U.: Deposition and mineralogical characteristics of atmospheric dust in relation to land use and land cover change in Delhi (India). Geography Journal. 2014, (2014)
Li, J., Wang, G., Aggarwal, S.G., Huang, Y., Ren, Y., Zhou, B., et al.: Comparison of abundances, compositions and sources of elements, inorganic ions and organic compounds in atmospheric aerosols from Xi'an and New Delhi, two megacities in China and India. Sci. Total Environ. 476, 485–495 (2014)
Maring, H., Savoie, D.L., Izaguirre, M.A., Custals, L., Reid, J.S.: Mineral dust aerosol size distribution change during atmospheric transport. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres (1984–2012). 108(D19), (2003)
Mishra, M., Kulshrestha, U.: Estimation of carbonaceous emission impact on urban soil-dust in Delhi. Journal of Climate Change. 2(2), 119–127 (2016)
Murayama, T., Sugimoto, N., Uno, I., Kinoshita, K., Aoki, K., Hagiwara, N., et al.: Ground-based network observation of Asian dust events of April 1998 in east Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 106(Dsm16), 18345–18360 (2001)
Pachauri, T., Singla, V., Satsangi, A., Lakhani, A., Kumari, K.M.: SEM-EDX characterization of individual coarse particles in Agra, India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 13(2), 523–536 (2013)
Perrino, C., Tiwari, S., Catrambone, M., Torre, S.D., Rantica, E., Canepari, S.: Chemical characterization of atmospheric PM in Delhi, India, during different periods of the year including Diwali festival. Atmospheric Pollution Research. 2(4), 418–427 (2011)
Pipal, A.S., Satsangi, P.G.: Study of carbonaceous species, morphology and sources of fine (PM 2.5) and coarse (PM 10) particles along with their climatic nature in India. Atmos. Res. 154, 103–115 (2015)
Pipal, A.S., Kulshrestha, A., Taneja, A.: Characterization and morphological analysis of airborne PM 2.5 and PM 10 in Agra located in north Central India. Atmos. Environ. 45(21), 3621–3630 (2011)
Pósfai, M., Anderson, J.R., Buseck, P.R., Sievering, H.: Soot and sulfate aerosol particles in the remote marine troposphere. J. Geophys. Res. 104(D17), 21685–21693 (1999)
Prospero, J.M.: Long-range transport of mineral dust in the global atmosphere: impact of African dust on the environment of the southeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96(7), 3396–3403 (1999)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M., Hegde, P.: Atmospheric abundances of primary and secondary carbonaceous species at two high-altitude sites in India: sources and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 42(28), 6785–6796 (2008)
Ramachandran, S., Rengarajan, R., Sarin, M.M.: Atmospheric carbonaceous aerosols: issues, radiative forcing and climate impacts. Curr. Sci. 97(1), 18–20 (2009)
Ramanathan, V., Carmichael, G.: Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 1(4), 221–227 (2008)
Rastogi, N., Sarin, M.M.: Quantitative chemical composition and characteristics of aerosols over western India: one-year record of temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 43(22), 3481–3488 (2009)
Reis, S., Pinder, R.W., Zhang, M., Lijie, G., Sutton, M.A.: Reactive nitrogen in atmospheric emission inventories. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 9(19), 7657–7677 (2009)
Rengarajan, R., Sarin, M.M., Sudheer, A.K.: Carbonaceous and inorganic species in atmospheric aerosols during wintertime over urban and high-altitude sites in North India. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 112(D21), (2007)
Sachdeva, K., Narayanan, P., Arora, P.: Assessment of carbon fractions of aerosols collected under gravity settling at two different heights in the Delhi region. Urban Climate. 5, 104–111 (2013)
Safai, P.D., Raju, M.P., Rao, P.S.P., Pandithurai, G.: Characterization of carbonaceous aerosols over the urban tropical location and a new approach to evaluate their climatic importance. Atmos. Environ. 92, 493–500 (2014)
Satheesh, S.K., Ramanathan, V.: Large differences in tropical aerosol forcing at the top of the atmosphere and Earth's surface. Nature. 405, 60–63 (2000)
Satsangi, A., Pachauri, T., Singla, V., Lakhani, A., Kumari, K.M.: Organic and elemental carbon aerosols at a suburban site. Atmos. Res. 113, 13–21 (2012)
Saxena, A., Kulshreshta, U.C., Kumar, N., Kumari, K.M., Srivastava, S.S.: Dry deposition of nitrate and sulphate on surrogate surfaces. Environ. Int. 18(5), 509–513 (1992)
Seinfeld, J.H., Carmichael, G.R., Arimoto, R., Conant, W.C., Brechtel, F.J., Bates, T.S., et al.: ACE-ASIA: Regional climatic and atmospheric chemical effects of Asian dust and pollution. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 85(3), 367–380 (2004). doi:10.1175/BAMS-85-3-367
Sillanpää, M., Frey, A., Hillamo, R., Pennanen, A.S., Salonen, R.O.: Comparison of the levels of organic, elemental and inorganic carbon in particulate matter in six urban environments in Europe. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions. 5(3), 2719–2747 (2005)
Singh, R., Kulshrestha, M.J., Kumar, B., Chandra, S.: Impact of anthropogenic emissions and open biomass burning on carbonaceous aerosols in urban and rural environments of Indo-Gangetic plain, pp. 1–14. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health (2015)
Singh, S., Kumar, B., Gupta, G.P., Kulshrestha, U.C. et al.: Signatures of increasing energy demand of past two decades as captured in rain water composition and airmass trajectory analysis at Delhi (India). Journal of Energy, Environment & Carbon Credits 4, 43–61 (2014)
Tegen, I.: Modeling the mineral dust aerosol cycle in the climate system. Quat. Sci. Rev. 22(18), 1821–1834 (2003)
Tegen, I., Fung, I.: Contribution to the atmospheric mineral aerosol load from land surface modification. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres (1984–2012). 100(D9), 18707–18726 (1995)
Tegen, I., Schepanski, K.: The global distribution of mineral dust. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 7, 012001 (2009). doi:10.1088/1755-1307/7/1/012001
Ten Brink, H., Maenhaut, W., Hitzenberger, R., Gnauk, T., Spindler, G., Even, A., et al.: INTERCOMP2000: the comparability of methods in use in Europe for measuring the carbon content of aerosol. Atmos. Environ. 38(38), 6507–6519 (2004)
Thurston, G.D., Spengler, J.D.: A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmospheric Environment (1967). 19(1), 9–25 (1985)
Tiwari, S., Srivastava, A.K., Bisht, D.S., Safai, P.D., Parmita, P.: Assessment of carbonaceous aerosol over Delhi in the indo-Gangetic Basin: characterization, sources and temporal variability. Nat. Hazards. 65(3), 1745–1764 (2013)
Turpin, B.J., Huntzicker, J.J.: Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos. Environ. 29(23), 3527–3544 (1995)
Updyke, K.M., Nguyen, T.B., Nizkorodov, S.A.: Formation of brown carbon via reactions of ammonia with secondary organic aerosols from biogenic and anthropogenic precursors. Atmos. Environ. 63, 22–31 (2012)
Wang, Y.Q., Zhang, X.Y., Arimoto, R., Cao, J.J., Shen, Z.X.: Characteristics of carbonate content and carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of northern China soil and dust aerosol and its application to tracing dust sources. Atmos. Environ. 39(14), 2631–2642 (2005)
Watson, J.G., Chow, J.C., Chen, L.W.A.: Summary of organic and elemental carbon/black carbon analysis methods and intercomparisons. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 5(1), 65–102 (2005)
Weingartner, E., Saathoff, H., Schnaiter, M., Streit, N., Bitnar, B., Baltensperger, U.: Absorption of light by soot particles: determination of the absorption coefficient by means of aethalometers. J. Aerosol Sci. 34(10), 1445–1463 (2003)
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the financial support received from Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, to conduct this research work. Analytical assistance provided by DST-PURSE, CIF, SES and Advance Instrumentation Research Facility (AIRF), JNU is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, M., Kulshrestha, U. Chemical characteristics and deposition fluxes of dust-carbon mixed coarse aerosols at three sites of Delhi, NCR. J Atmos Chem 74, 399–421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-016-9349-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-016-9349-1