Abstract
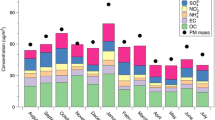
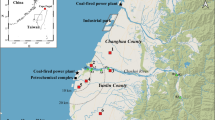
The Tagged Species Source Apportionment (TSSA) algorithm is applied to study contributions to pollutants PM sulfate, SO2 and elemental carbon (EC) in Hong Kong by emitting sectors as well as non-emitting sources within and beyond the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region. We look at three areas of Hong Kong: western new towns, central downtown, and eastern countryside. Pollutant transport from beyond the PRD influenced all three areas during January and October 2004 but the source sectors impacting the three areas were different. Specifically, power plant SO2 from Hong Kong and Shenzhen, and vehicle EC from Shenzhen contribute to 11 ~ 66 % of SO2 concentration, and 33 ~ 75 % of EC concentration in the western new towns, respectively. Ships in and around Hong Kong contribute 8 ~ 56 % to the sulfate concentration in the downtown area, while local moving vehicles take up 28 ~ 81 % of the EC concentration there. The study also shows that diurnal variation of planetary boundary layer (PBL) causes day-night difference in SO2 by as much as 50 %. In addition, 13 ~ 38 % of all SO2 emissions have been converted to PM sulfate.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunachalam, S.: Peer Review of Source Apportionment Tools in CAMx and CMAQ. Institute for the Environment, UNC, Prepared for U.S.EPA Contract No. EP-D-07-102. (2009)
Barth, M.C., Church, A.T.: Regional and global distributions and lifetimes of sulfate aerosols from Mexico City and southeast China. J. Geophys. Res. 104(D23), 30231–30239 (1999)
Benkovitz, C.M., Easter, R.C., Nemesure, S., Wagener, R., Schwartz, S.E.: Sulfate over the North Atlantic and adjacent continental regions: Evaluation for October and November 1986 using a three-dimensional model driven by observation-derived meteorology. J. Geophys. Res. 99(D10), 20725–20756 (1994)
Bhave, P.V., Pouliot, G.A., Zheng, M.: Source apportionment of primary carbonaceous aerosol using the Community Multiscale Air Quality model. Preprints, 27th NATO/CCMS International Technical Meeting on Air Pollution Modeling and its Applications, October 24–29, 2004, Banff, Alberta, Canada. NATO/CCMS, 25–32. (2004)
Binkowski, F.S.: Aerosols in Models-3 CMAQ, Chapter 10 of Science Algorithms of the EPA Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System, EPA/R-99/030. http://www.epa.gov/asmdnerl/CMAQ/ch10.pdf (1999), Accessed 16 October 2011.
Binkowski, F.S., Roselle, S.J.: Models-3 community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) model aerosol component 1: model description. J. Geophys. Res. 108(D6), 4183 (2003). doi:10.1029/2001JD001409
Binkowski, F.S., Shankar, U.: The regional particulate matter model 1. Model description and preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res. 100(D12), 26191–26209 (1995)
Bischof, C., Carle, A., Corliss, G., Griewank, A., Hovland, P.: ADIFOR-Generating derivative codes from FORTRAN programs. Sci. Program. 1, 11–29 (1992)
Carmichael, G.R., Sandu, A., Potra, F.A.: Sensitivity analysis for atmospheric chemistry models via automatic differentiation. Atmos. Env. 31(3), 475–489 (1997)
Cheung, H.C., Wang, T., Baumann, K., Guo, H.: Influence of regional pollution outflow on the concentrations of fine particulate matter and visibility in the coastal area of southern China. Atmo. Environ. 39, 6463–6474 (2005)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Louie, P.K.K., Chen, L.W.A., Sin, D.: Comparison of PM2.5 carbon measurement methods in Hong Kong, China. Environ. Pollut. 137, 334–344 (2005)
CMAS: CMAQ 4.5.1 CARBON_APPORTIONMENT.TXT. http://www.cmascenter.org/help/model_docs/cmaq/4.5.1/ CARBON_APPORTIONMENT.txt (2006b) Accessed 16 October 2011CMAS: CMAQ 4.5.1 SCIENCE_UPDATES.PDF.
CMAS: CMAQ 4.5.1 SULFATE_TRACKING.TXT. http://www.cmascenter.org/help/model_docs/cmaq/4.5.1/SULFATE_TRACKING.txt (2006a) Accessed 16 October 2011
Dunker, A.M.: Efficient calculation of sensitivity coefficients for complex atmospheric models. Atmos. Environ. 15, 1155–1161 (1981)
Dunker, A.M., Yarwood, G., Ortmann, J.P., Wilson, G.M.: The decoupled direct method for sensitivity analysis in a three-dimensional air quality model – implementation, accuracy and efficiency. Environ. Sci. Tech. 36, 2965–2976 (2002)
Elbern, H., Schmitdt, H.: Ozone episode analysis by four-dimensional variational chemistry data assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. 106(D4), 3569–3590 (2001)
ENVIRON: CAMx homepage at http://www.camx.com. (2009) Accessed 16 October 2011
Fang, M., Zheng, M., Wang, F., Chim, K.S., Kot, S.C.: The long-range transport of aerosols from northern China to Hong Kong – a multi-technique study. Atmos. Environ. 33, 1803–1817 (1999)
Fu, J.S., Jang, C.J., Streets, D.G., Li, Z., Kwok, R., Park, R., Han, Z.: MICS-Asia II: modeling gaseous pollutants and evaluating an advanced modeling system over East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 42(15), 3571–3583 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.07.058
Fu, J.S., Streets, D.G., Jang, C.J., Hao, J., He, K., Wang, L., Zhang, Q.: Modeling regional/urban ozone and particulate matter in Beijing, China. J. Air Waste Manag. 57, 37–44 (2009)
Grell, G.A., Dudia, J., Stauffer, D.R.: A description of the Fifth Generation Penn State/NCAR Mesoscale Model (MM5), NCAR Technical Note NCAR/TN-398+STR. (1994)
Hao, J., Wang, L.: Improving urban air quality in China: Beijing case study. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 55, 1298–1305 (2005)
He, Q.S., Li, C.C., Mao, J.T., Lau, A.K.H., Li, P.R.: A study on the aerosol extinction-to-backscatter ratio with combination of micro-pulse LIDAR and MODIS over Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6, 3243–3256 (2006)
Heo, E., Feng, Y.: Recent development of energy use in China at the industrial sector level. http://www.cenetorg.cn/cn/CEAC/2005in/zyhj011.doc (2005). Accessed March 2010.
HKPD: Hong Kong 2030: Planning vision and strategy consultancy study to analyse broad land use pattern of the Pearl River Delta Region. http://www.pland.gov.hk/pland_en/p_study/comp_s/hk2030/eng/consultants/pdf/Tpaper5.pdf (2003) Accessed 16 October 2011
Ho, K.F., Lee, S.C., Yu, J.C., Zou, S.C., Fung, K.: Carbonaceous characteristics of atmospheric particulate matter in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 300, 59–67 (2002)
Ho, K.F., Lee, S.C., Chan, C.K., Yu, J.C., Chow, J.C., Yao, X.H.: Characterization of chemical species in PM2.5 and PM10 aerosols in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 37, 31–39 (2003)
Ho, K.F., Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Chan, C.K.: Source apportionment of PM2.5 in urban area of Hong Kong. J. Hazard. Mater. B138, 73–85 (2006)
Hong, S.Y., Pan, H.L.: Nonlocal boundary layer vertical diffusion in a medium-range forecast model. Mon. Wea. Rev. 124, 2322–2339 (1996)
http://www.cmascenter.org/help/model_docs/cmaq/4.5.1/Science_Updates.pdf (2006c) Accessed 16 October 2011
Huang, J.P.: Numerical simulation study of ozone episodes in complex terrain and coastal region. Thesis MATH 2005 Huang, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology. http://ustlib.ust.hk (2005) Accessed 16 October 2011
Huang, J.P., Fung, J.C.H., Lau, A.K.H.: Integrated processes analysis and systematic meteorological classification of ozone episodes in Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. 111(D20309) (2006a). doi:10.1029/2005JD007012
Huang, X.F., Yu, J.Z., He, L., Yuan, Z.: Water-soluble organic carbon and oxalate in aerosols at a coastal urban site in China: size distribution characteristics, sources, and formation mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. 111(D22212) (2006b). doi:10.1029/2006JD007408
Hwang, D., Byun, D.W., Odman, M.T.: An automatic differentiation technique for sensitivity analysis of numerical advection schemes in air quality models. Atmos. Environ. 31(6), 879–888 (1997)
ICF International: Implementation of Sulfur and Nitrogen Tagging in the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Model: Technical Description and Users’ Guide. (2007a)
ICF International: Implementation of Ozone and Particle Precursor Tagging Methodology in the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Model: Technical Description and Users’ Guide. (2007b)
Jiang, W. Roth, H.: A detailed review and analysis of science, algorithms, and code in the aerosol components of Models-3/CMAQ. 1. Kinetic and thermodynamic processes in the AERO2 module. Report Number PET-1534-03S. (2003)
Kwok, R.H.F., Fung, J.C.H., Lau, A.K.H., Fu, J.S.: Numerical study on seasonal variations of gaseous pollutants and particulate matters in Hong Kong and Pearl River Delta Region. J. Geophys. Res. 115, D16308 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009JD012809
Lau, A.K.H., Wu, W.M., Fung, J.C.H., Henry, R.C., Barron, B.: Significant Marine Source for SO2 levels in Hong Kong. Civic Exchange Hong Kong. http://www.civic-exchange.org/eng/upload/files/200506_MarineSourceSO2.pdf (2005) Accessed 16 October 2011
Lo, J.C.F., Lau, A.K.H., Chen, F., Fung, J.C.H., Leung, K.K.M.: Urban modification in a mesoscale model and the effects on the local circulation in the Pearl River Delta region. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim 46, 457–476 (2007)
Louie, P.K.K., Chow, J.C., Chen, L.W.A., Watson, J.G., Leung, G., Sin D.W.M.: PM2.5 chemical composition in Hong Kong: urban and regional variations. Sci. Total. Env. 338, 267–281. (2005)
Malwer, E.J., Taubman, S.J., Brown, P.D., Iacono, M.J., Clough, S.A.: Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmosphere: PRTM, validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Gephys. Res. 102(D14), 16663–16682 (1997)
Martin, L.R.: Kinetic studies of sulfite oxidation in aqueous solution. In: Calvert, J.G. (ed.) SO2, NO and NO2 oxidation mechanisms: atmospheric considerations. Butterworth Publishers. (1984)
Menut, L., Vautard, R., Beekmann, M., Honoré, C.: Sensitivity of photochemical pollution using the adjoint of a simplified chemistry-transport model. J. Geophys. Res-Atmospheres 105(D12), 15379–15402 (2000)
Myers, T., Douglas, S., Haney, J.: Implementation of the Particle and Precursor Tagging Methodology (PPTM) for CMAQ. ICF International, San Rafael (2006)
Napelenok, S.L., Cohan, D.S., Odman, M.T., Tonse, S.: Extension and evaluation of sensitivity analysis capabilities in a photochemical model. Environ. Mod. Soft. 23(8), 994–999 (2008)
Pleim, J.E., Chang, J.S.: A non-local closure model for vertical mixing in the convective boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. 26A, 965–981 (1992)
Reid, R., Prausnitz, J.M., Poling, B.E.: The properties of gases and liquids, 4th edition, McGraw-Hill, pp 587–588. (1987)
Sillman, S., Logan, J.A., Wofsy, S.C.: The sensitivity of ozone to nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons in regional ozone episodes. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 1837–1851 (1990)
SMOKE: http://www.smoke-model.org/version2.1/html/ (2009) Accessed 16 October 2011
So, K.L., Guo, H., Li, Y.S.: Long-term variation of PM2.5 levels and composition at rural, urban, and roadside sites in Hong Kong: Increasing impact of regional air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 41, 9427–9434 (2007)
Streets, D.G., Bond, T.C., Carmichael, G.R., Fernandes, S.D., Fu, Q., He, D., Klimont, Z., Nelson, S.M., Tsai, N.Y., Wang, M.Q., Woo, J.H., Yarber, K.F.: An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 108(D21), 8809 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002JD003093
Tonnesen, G., Wang, B.: CMAQ Tagged Species Source Apportionment. http://www.wrapair.org/forums/aoh/meetings/040722/UCR_tssa_tracer_v2.ppt (2004) Accessed 16 October 2011
Vautard, R., Beekmann, M., Menut, L.: Applications of adjoint modelling in atmospheric chemistry: sensitivity and inverse modelling. Environ. Model. Soft. 15, 703–709 (2000)
Wai, K.M., Tanner, P.: Relationship between ionic composition in PM10 and the synoptic-scale and mesoscale weather conditions in a south China coastal city: a 4-year study. J. Geophys. Res. 110(D18210). (2005) doi:10.1029/2004JD005385.
Walcek, C.J., Taylor, G.R.: A theoretical method for computing vertical distributions of acidity and sulfate within cumulus clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 43(4), 339–355 (1986)
Wang, Z.S., Chien, C.J., Tonnesen, G.S.: Development of a tagged species source apportionment algorithm (TSSA) to characterize 3-dimensional transport and transformation of precursors and secondary pollutants. J. Geophys. Res. 114, D21206 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008JD010846
Yu, J.Z., Tung, J.W.T., Wu, A.W.M., Lau, A.K.H., Louie, P.K.K., Fung, J.C.H.: Abundance and seasonal characteristics of elemental and organic carbon in Hong Kong PM10. Atmos. Environ. 38, 1151–1521 (2004)
Yuan, Z., Lau, A.K.H., Zhang, H., Yu, J., Louie, P.K.K., Fung, J.C.H.: Identification and spatiotemporal variations of dominant PM10 sources over Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 40(10)), 1803–1815 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.11.030
Zhang, Q., Streets, D.G., Carmichael, G.R., He, K.B., Huo, H., Kannari, A., Klimont, Z., Park, I.S., Reddy, S., Fu, J.S., Chen, D., Duan, L., Lei, Y., Wang, L.T., and Yao, Z.L.: Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission, Atmos. Chem. Phys. 9, 5131–5153 (2009). doi:10.5194/acp-9-5131-2009
Zhang, Q., Streets, D.G., He, K., Wang, Y., Richter, A., Burrows, J.P., Uno, I., Jang, C. J., Chen, D., Yao, Z., and Lei, Y.: NOx emission trends for China, 1995-2004: The view from the ground and the view from space, J. Geophys. Res. 112(D22306), (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JD008684
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants N_HKUST630/04, N_HKUST631/05SB106/07.SC06, RGC612807, RGC615406 and RTG08/09.SC001. The authors sincerely thank the Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department for provision of emission and air quality data, and the Hong Kong Observatory for provision of meteorological data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwok, R., Fung, J.C.H., Lau, A.K.H. et al. Tracking emission sources of sulfur and elemental carbon in Hong Kong/Pearl River Delta region. J Atmos Chem 69, 1–22 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-012-9226-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-012-9226-5