Abstract
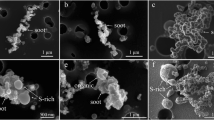
Size, morphology, microstructure, chemical composition and hygroscopic properties of aircraft engine combustor (AEC) soot particles are studied by using a combination of several methods, namely atomic force microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, gravimetry, ionic chromatography analysis and wetting observations. From the microstructure and the composition of soot agglomerates, we find that we can separate AEC soot in two fractions having quite different physico-chemical properties: a main fraction of particles containing essentially amorphous carbon with small amounts of oxygen, sulfur and iron and a fraction of impurities characterized by various structures and a large amount of impurities. These properties of aircraft engine combustor soot are compared to those of soot obtained by burning TC1 aviation kerosene in a laboratory burner. It is shown that TC1 soot can be a good surrogate of the AEC main fraction. Such a finding allows us to perform water uptake measurements and to conclude that the AEC main fraction is rather hydrophobic whereas the AEC fraction of impurities is highly hydrophilic The ability of the two fractions of aircraft engine combustor soot to act as cloud condensation nuclei is discussed with respect to their implication in contrail and cirrus formation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcala-Jornod, C., Van den Bergh, H., Rossi, M.J.: Can soot particles emitted by airplane exhaust contribute to the formation of aviation contrails and cirrus clouds?, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, N.17, 1820, http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2001GL014115 (2002)
Bockhorn, H.: Soot Formation in Combustion: Mechanisms and Models. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1994)
Brunauer, S.: Adsorption of Gases and Vapors, vol. 1. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey (1945)
Carrott, P.J.M.: Adsorption of water-vapor by nonporous carbons. Carbon. 30, 201–205 (1992)
Chen, Y.L., Kreidenweis, S.M., McInnes, L.M., Rogers, D.C., DeMott, P.J.: Single particle analyses of ice nucleating aerosols in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 1391–1394 (1998)
Chughtai, A.R., Miller, N.J., Smith, D.M., Pitts, J.R.: Carbonaceous particle hydration III. J. Atmos. Chem. 34, 259–279 (1999)
Chylek, P., Ramaswamy, V., Cheng, R.J. : Effect of graphitic carbon on the albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 3076–3084 (1984)
Decesari, S., Facchini, M.C., Matta, E., Mircea, M., Fuzzi, S., Chughtai, A.R., Smith, D.M.: Water soluble organic compounds formed by oxidation of soot. Atmos. Environ. 36, 1827–1832 (2002)
Di Stasio, S.: Electron microscopy evidence of aggregation under three different size scales for soot nanoparticles in flame. Carbon 39, 109–118 (2001)
Ferry, D., Suzanne, J., Nitsche, S., Popovicheva, O.B., Shonija, N.K.: Water adsorption and dynamics on kerosene soot under atmospheric conditions. Art. no. 4734. J. Geophys. Res. 107, (2002)
Hendricks, J., Karcher, B., Lohmann, U., and Ponater, M.: Do aircraft black carbon emissions affect cirrus clouds on global scale? Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L12814 http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2005GL022740 (2005)
Gleitsmann, G., Zellner R.: A modeling study of the formation of cloud condensation nuclei in the jet regime of aircraft plumes. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 19543–19555 (1998)
Gregg, S.J., Sing, K.S.W.: Adsorption, surface area and porosity, 2nd edn. Academic, New York (1982)
Grieco, W.J., Howard, J.B., Rainey, L.C., Vander Sande, J.B.: Fullerenic carbon in combustion-generated soot. Carbon 38, 597–614 (2000)
Gysel, M., Nyeki, S., Weingartner, E., Baltensperger, U., Giebl, H., Hitzenberger, R., Petzold, A., Wilson, C.W.: Properties of jet engine combustion particles during the PartEmis experiment: Hygroscopicity at subsaturated conditions. Art. no. 1566. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, (2003)
Jensen, E.J., Toon, O.B., Kinne, S., Sachse, G.W., Anderson, B.E., Chan, K.R., Twohy, C.H., Gandrud, B., Heymsfield, A., Miake-Lye, R.C.: Environmental conditions required for contrail formation and persistence. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 3929–3936 (1998)
Kärcher, B., Peter, T., Biermann, U.M., Schumann, U.: The initial composition of jet condensation trails. J. Atmos. Sci. 53, 3066–3083 (1996)
Kärcher, B., Busen, R., Petzold, A., Schröder, F., Schumann, U., Jensen, E.J.: Physicochemistry of aircraft-generated liquid aerosols, soot, and ice particles – 2. Comparison with observations and sensitivity studies. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 17129–17147 (1998)
Kuhn, M., Petzold, A., Baumgardner, D., Schröder, F.: Particle composition of a young condensation trail and of upper tropospheric aerosol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2679–2682 (1998)
Kuznetsov, B.V., Rakhmanova, T.A., Popovicheva, O.B., Shonija, N.K.: Water adsorption and energetic properties of spark discharge soot: Specific features of hydrophilicity. J. Aerosol Sci. 34, 1465–1479 (2003)
Lahaye, J., Boehm, S., Ehrburge, P. In: Bockhorn, H. (ed.) Soot formation in combustion: mechanisms and models, pp. 307–315. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1994)
Lohmann, U., Karcher, B., Hendricks, J.: Sensitivity studies of cirrus clouds formed by heterogeneous freezing in the ECHAM GCM. J. Geophys. Res. 109, D16204, http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2003JD004443 (2004)
McMurry, P.H., Litchy, M., Huang, P.F., Cai, X., Turpin, B.J., Dick, W.D., Hanson, A.: Elemental composition and morphology of individual particles separated by size and hygroscopicity with the TDMA. Atmos. Environ. 30, 101–108 (1996)
Moehler, O., Linke, C., Saathoff, H., Schnaiter, M., Wagner, R., Schurath, U.: Ice nucleation on flame soot aerosol of different organic carbon content. Meteorol. Z. 14(4), 477–484 (2005)
Petzold, A., Schröder, F.: Jet engine exhaust aerosol characterization. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 28, 62–77 (1998)
Petzold, A., Strom, J., Ohlsson, S., Schröder, F.: Elemental composition and morphology of ice-crystal residual particles in cirrus clouds and contrails. Atmos. Res. 49, 21–34 (1998)
Petzold, A., Dopelheuer, A., Brock, C.A., Schröder, F.: In situ observations and model calculations of black carbon emission by aircraft at cruise altitude. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 22171–22181 (1999)
Petzold, A., Gysel, M., Vancassel, X, Hitzenberger, R., Puxbaum, H., Vrochticky, S., Weingarnter, E., Baltensperger, U., Mirabel, P.: On the effect of organic matter and sulfur-containg compounds on the CCN activation of combustion particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 5, 3187–3203 (2005)
Popovicheva, O.B., Persiantseva, N.M., Trukhin, M.E., Rulev, G.B., Shonija, N.K., Buriko, Y.Y., Starik, A.M., Demirdjian, B., Ferry, D., Suzanne, J.: Experimental characterization of aircraft combustor soot: Microstructure, surface area, porosity and water adsorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2, 4421–4426 (2000)
Popovicheva, O.B., Trukhin, M.E., Persiantseva, N.M., Shonija, N.K., 2001: Water adsorption on aircraft-combustor soot under young plume conditions. Atmos. Environ. 35, 1673–1676 (2001)
Popovicheva, O.B., Persiantseva, N.M., Kuznetsov, B.V., Rakhmanova, T.A., Shonija, N.K., Suzanne, J., Ferry, D.: Microstructure and water adsorbability of aircraft combustor soots and kerosene flame soots: Toward an aircraft-generated soot laboratory surrogate. J. Phys. Chem. 107, 10046–10054 (2003a)
Popovicheva, O.B., Persiantseva, N.M., Shonija, N.K., Zubareva, N.A., Starik, A.M., Lukhovitskaya, E.E., Secundov, A.N., Usenko, D.A., Zakharov, V.M., Suzanne, J., Ferry, D., Demirdjian, B.: Aircraft engine soot: characteristic properties as CCN in upper troposphere. Combustion and Atmospheric Pollution, Ed. by Roy, G.D., Frolov, S.M., Starik A.M., Moscow, Torus, 444–449 (2003b)
Popovicheva, O.B., Persiantseva, N.M., Lukhovitskaya, E.E., Shonija, N.K., Zubareva, N.A., Demirdjian, B., Ferry, D., Suzanne, J.: Aircraft engine soot as contrail nuclei. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, Art. no. L11104 (2004)
Pruppacher, H.R., Klett, J.D.: Microphysics and clouds precipitation. D. Reidel, Hingham Mass (1978)
Schröder, F., Kärcher, B., Petzold, A., Baumann, R., Busen, R., Hoell, C., Schumann, U.: Ultrafine aerosol particles in aircraft plumes: In situ observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2789–2792 (1998)
Schröder, F., Karcher, B., Duroure, C., Strom, J., Petzold, A., Gayet, J.F., Strauss, B., Wendling, P., Borrmann, S.: On the transition of contrails into cirrus clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 57, 464–480 (2000)
Schumann, U., Strom, J., Busen, R., Baumann, R., Gierens, K., Krautstrunk, M., Schröder, F., Stingl, J.: In situ observations of particles in jet aircraft exhausts and contrails for different sulfur-containing fuels. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 6853–6869 (1996)
Schumann, U., Arnold, F., Busen, R., Curtius, J., Karcher, B., Kiendler, A., Petzold, A., Schlager, H., Schröder, F., Wohlfrom, K.H.: Influence of fuel sulfur on the composition of aircraft exhaust plumes: The experiments SULFUR 1–7, J. Geophys. Res. 107, D15, http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2001JD00813 (2002)
Schumann, U.: Formation, properties and climatic effects of contrails. Comptes Rendus de Physique 6(4–5), 549–565 (2005)
Seinfeld, J.H.: Clouds, Contrails and Climate. Nature 391, 837–838 (1998)
Sorokin, A., Arnold, F.: Electrically charged small soot particles in the exhaust of aircraft gas-turbine engine combustor: Comparison of experiment and model. Atmos. Environ. 38, 2611–2618 (2004)
Vartapetyan, R.S., Voloshchuk, A.M.: The mechanism of the adsorption of water molecules on carbon adsorbents. Russ. Chem. Rev. 64, 985–1001 (1995)
Acknowledgments
Russian authors thanks to the CRDF project RC1-2327-MO-02 and the grant of President of Russian Federation, SS-7101.2006.02. The authors kindly acknowledge S. Nitsche for his help in the TEM measurements, D. Pailharey for his help in the AFM measurements, and Dr. A. Starik for consultations. P.O.B. is grateful to ESIL/Université de la Méditerranée, for providing an invited Professorship position during part of this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associated to Université de la Méditerranée (Aix-Marseille II) and to Université Paul Cézanne (Aix-Marseille III)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirdjian, B., Ferry, D., Suzanne, J. et al. Heterogeneities in the Microstructure and Composition of Aircraft Engine Combustor Soot: Impact on the Water Uptake. J Atmos Chem 56, 83–103 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-006-9043-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-006-9043-9