Abstract
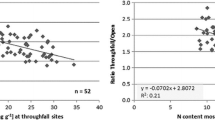
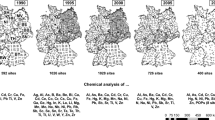
This paper deals with the spatial heterogeneity structure and the influence of the precision of moss data on results interpretation as real spatial variations of atmospheric heavy metal deposition. Different sizes of map mesh net (unit I of 30 × 30 km, unit II of 10 × 10 km, unit III of 3 × 3 km) have divided an area of 90 × 90 km. The protocol used is a nested design with three levels and random draws. The statistical method of components of variance analysis estimates the associated variability for each mesh size. Our results show the poor precision of this biological tool for map purposes on a little scale (unit III). Furthermore, the high residual variance of As, Ba, Cd, Co, Cu, La, Ti, and U hides the spatial variations associated with mesh sizes. In order to obtain useful maps, it should be reasonable to use a 30 × 30 km mesh size, or even larger, to build spatial variation maps of Pb, Sb and with more caution for Cu, Sr, Rb and Zn. For V, As and Cd, the residual variability of moss data was too important to guarantee any spatial origin to the mapped variations. The cost–benefit study shows that the sampling effort has to be concentrated on unit I of 30 × 30 km to optimize future campaigns, and with a particular stress on the sampling repetitions for Cu, Pb, and Sb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayrault, S., Bonhomme, P., Carrot, F., Amblard, G., Sciaretta, M. D., and Galsomiès L., 2000: Multianalysis of trace elements in mosses with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 79, 177–184.
Bargagli, R., 1995: The elemental composition of vegetation and the possible incidence of soil contamination of samples, Sci. Total Environ. 176, 121–128.
Berg, T. and Steinnes, E., 1997: Recent trends in atmospheric deposition of trace elements in Norway as evident from the 1995 moss survey, Sci. Total Environ. 208, 197–206.
Berlekamp, J., Herpin, U., Lieth, H., Markert, B., Weckert, V., Wolterbeek, B., Verburg, T., Zinner, H. J., and Siewers, U., 1998: Geographic classification of heavy metal concentrations in mosses and stream sediments in the Federal Republic of Germany, Water Air Soil Pollut. 101 (1), 177–195.
Cochran, W. G., 1957: Sampling Techniques, Wiley, 428 p.
Fernández, J. A., Aboal, J. R., Couto, J. A. and Carballeira A., 2002: Sampling optimization at the sampling-site scale for monitoring atmospheric deposition using moss chemistry, Atmos. Environ. 36 (7), 1163–1172.
Frontier, S., 1982: Stratégies d’échantillonnage en Ecologie, Edition Masson et les Presses de l’université Laval-Québec, 494 p.
Halleraker, J. H., Reimann, C., De Caritat, P., Finne, T. E., Kashulina, G., Niskaavaara, H. and Bogatyrev, I., 1998: Reliability of moss (Hylocomium splendens and Pleurozium schreberi) as a bioindicator of atmospheric chemistry in the Barents region: Interspecies and field duplicate variability, Sci. Total Environ. 218, 123–139.
Markert, B., 1994: Environmental Sampling for Trace Analysis, VCH Weinheim, 522 p.
Maul, A., 1982: Définition d’une stratégie de prélèvement pour l’analyse microbiologique des eaux de surface, PhD Thesis, University of Metz, France, 124 p.
Qinghong, L. and Brakenhielm, S., 1995: A statistical approach to decompose ecological variation, Water Air Soil Pollut. 85, 1587–1592.
Rahn, K. A., 1997: A graphical technique for distinguishing plant material and soil form atmospheric deposition in biomonitors, BioMAP, First International Workshop on Biomonitoring of Atmospheric Pollution, Lisboa, Portugal.
Reimann, C. and De Caritat, P., 1998: Chemical Elements in the Environment, Factsheets for the Geochemist and Environmental Scientist, Springer-Verlag, 398 p.
Reimann, C., De Caritat, P. and Halleraker, J. H., 1997: Regional atmospheric deposition patterns of Ag, As, Bi, Cd, Hg, Mo, Sb and Tl in a 188,000 km2 area in the european arctic as displayed by terrestrial moss samples – Long-range transport vs local impact, Atmos. Environ. 31 (23), 3887–3901.
Rühling, A. and Steinnes, E., 1998: Atmospheric Heavy Metal Deposition in Europe 1995–1996, Nordic Council of Ministers Nord 15, Copenhagen.
Rühling, A., 1994: Nordisk Ministerrad Report, Nord 9, Copenhagen.
Snedecor, G. W. and Cochran, W. G., 1957: Statistical methods (6th edition), Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa.
Steinnes, E., 1995: A critical evaluation of the use of naturally growing moss to monitor the deposition of atmospheric metals, Sci. Total Environ. 160/161, 243–249.
Steinnes, E., Rühling, A., Lippo, H., and Mäkinen, A., 1997: Reference materials for large scale metal depositon surveys, Accred. Qual. Assur. 2, 243–249.
Wolterbeek, H. T., Kuik, P., Verburg, T. G., Herpin, U., Markert, B., and Thöni, L., 1995: Moss interspecies comparisons in trace element concentrations, Environ. Monit. Assess. 35, 263–286.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amblard-Gross, G., Maul, A., Férard, JF. et al. Spatial Variability of Sampling: Grid Size Impact on Atmospheric Metals and Trace Elements Deposition Mapping with Mosses. J Atmos Chem 49, 39–52 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-004-1213-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-004-1213-z