Abstract
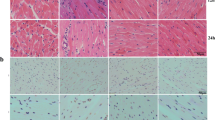
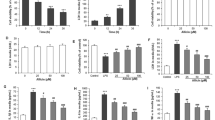
Septic cardiomyopathy is a severe cardiovascular disease with a poor prognosis. Previous studies have reported the involvement of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of septic cardiomyopathy. SGLT2 inhibitors such as dapagliflozin have been demonstrated to improve ischemia–reperfusion injury by alleviating ferroptosis in cardiomyocyte. However, the role of dapagliflozin in sepsis remains unclear. Therefore, our study aims to investigate the therapeutic effects of dapagliflozin on LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy. Our results indicate that dapagliflozin improved cardiac function in septic cardiomyopathy experimental mice. Mechanistically, dapagliflozin works by inhibiting the translation of key proteins involved in ferroptosis, such as GPX4, FTH1, and SLC7A11. It also reduces the transcription of lipid peroxidation-related mRNAs, including PTGS2 and ACSL4, as well as iron metabolism genes TFRC and HMOX1.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Adingupu DD, Gopel SO, Gronros J, Behrendt M, Sotak M, Miliotis T et al (2019) SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin improves coronary microvascular function and cardiac contractility in prediabetic ob/ob(-/-) mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol 18(1):16
Andrew Rhodes LEE, Alhazzani Waleed, Levy Mitchell M, Antonelli Massimo, Ferrer Ricard, Kumar Anand, Sevransky Jonathan E, Sprung Charles L, Nunnally Mark E, Rochwerg Bram, Rubenfeld Gordon D, Angus DC, Annane Djillali, Beale Richard J, Bellinghan Geoffrey J, Bernard Gordon R, Chiche Jean-Daniel, Coopersmith Craig, De Backer Daniel P, French Craig J, Fujishima Seitaro, Gerlach Herwig, Hidalgo Jorge Luis, Hollenberg Steven M, Jones Alan E, Karnad Dilip R, Kleinpell RM, Koh Younsuk, Lisboa Thiago Costa, Machado Flavia R, Marini John J, Marshal JC, Mazuski John E, McIntyre Lauralyn A, McLean Anthony S, Mehta Sangeeta, Moreno Rui P, Myburgh John, Navalesi Paolo, Nishida Osamu, Osborn Tiffany M, Perner Anders, Plunkett Colleen M, Ranieri Marco, Schorr Christa A, Seckel Maureen A, Seymour Christopher W, Shieh Lisa, Shukri Khalid A, Simpson Steven Q, Singer Mervyn, Taylor Thompson B, Townsend SR, Van der Poll Thomas, Jean-Louis Vincent W, Wiersinga Joost, Zimmerman Janice L, Phillip Dellinger R (2016) Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med 43:304–377
Bajic VP, Van Neste C, Obradovic M, Zafirovic S, Radak D, Bajic VB et al (2019) Glutathione “Redox Homeostasis” and Its Relation to Cardiovascular Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:5028181
Belch JJ, Bridges AB, Scott N, Chopra M (1991) Oxygen free radicals and congestive heart failure. Br Heart J 65(5):245–248
Chen YR, Zweier JL (2014) Cardiac mitochondria and reactive oxygen species generation. Circ Res 114(3):524–537
Chen W, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Tan M, Lin J, Qian X et al (2023) Dapagliflozin alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing ferroptosis via MAPK signaling inhibition. Front Pharmacol 14:1078205
Del Re DP, Amgalan D, Linkermann A, Liu Q, Kitsis RN (2019) Fundamental Mechanisms of Regulated Cell Death and Implications for Heart Disease. Physiol Rev 99(4):1765–1817
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei J et al (2019) Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(7):2672–2680
Fang X, Ardehali H, Min J, Wang F (2023) The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 20(1):7–23
Furtado RHM, Bonaca MP, Raz I, Zelniker TA, Mosenzon O, Cahn A et al (2019) Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Previous Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 139(22):2516–2527
Han X, Liu X, Zhao X, Wang X, Sun Y, Qu C et al (2023) Dapagliflozin ameliorates sepsis-induced heart injury by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis and electrical remodeling through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 955:175930
Hill MF, Singal PK (1996) Antioxidant and oxidative stress changes during heart failure subsequent to myocardial infarction in rats. Am J Pathol 148(1):291–300
Hill MF, Singal PK (1997) Right and left myocardial antioxidant responses during heart failure subsequent to myocardial infarction. Circulation 96(7):2414–2420
Hu J, Xu J, Tan X, Li D, Yao D, Xu B et al (2023) Dapagliflozin protects against dilated cardiomyopathy progression by targeting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 396(7):1461–1470
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao N et al (2020a) Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis 11(2):88
Li N, Wang W, Zhou H, Wu Q, Duan M, Liu C et al (2020b) Ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis is involved in sepsis-induced cardiac injury. Free Radic Biol Med 160:303–318
Li Y, Jiang Y, Zhou W, Wu Y, Zhang S, Ding G et al (2022) Maintaining homeostasis of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum with NSC228155 alleviates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Free Radic Biol Med 181:270–287
Liesa M, Palacin M, Zorzano A (2009) Mitochondrial dynamics in mammalian health and disease. Physiol Rev 89(3):799–845
Lin Y, Xu Y, Zhang Z (2020) Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction (SIMD): the Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Mitochondria. Inflammation 43(4):1184–1200
Lin K, Yang N, Luo W, Qian JF, Zhu WW, Ye SJ et al (2022) Direct cardio-protection of Dapagliflozin against obesity-related cardiomyopathy via NHE1/MAPK signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43(10):2624–2635
Liu YC, Yu MM, Shou ST, Chai YF (2017) Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and Treatments. Front Immunol 8:1021
Lv X, Wang H (2016) Pathophysiology of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Mil Med Res 3:30
Mallat Z, Philip I, Lebret M, Chatel D, Maclouf J, Tedgui A (1998) Elevated levels of 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha in pericardial fluid of patients with heart failure: a potential role for in vivo oxidant stress in ventricular dilatation and progression to heart failure. Circulation 97(16):1536–1539
Mancias JD, Wang X, Gygi SP, Harper JW, Kimmelman AC (2014) Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature 509(7498):105–109
Mi Y, Wei C, Sun L, Liu H, Zhang J, Luo J et al (2023) Melatonin inhibits ferroptosis and delays age-related cataract by regulating SIRT6/p-Nrf2/GPX4 and SIRT6/NCOA4/FTH1 pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 157:114048
Nikolaou PE, Efentakis P, Abu Qourah F, Femmino S, Makridakis M, Kanaki Z et al (2021) Chronic Empagliflozin Treatment Reduces Myocardial Infarct Size in Nondiabetic Mice Through STAT-3-Mediated Protection on Microvascular Endothelial Cells and Reduction of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 34(7):551–571
Nikolaou PE, Mylonas N, Makridakis M, Makrecka-Kuka M, Iliou A, Zerikiotis S et al (2022) Cardioprotection by selective SGLT-2 inhibitors in a non-diabetic mouse model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: a class or a drug effect? Basic Res Cardiol 117(1):27
Niu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Lu J, Chen Y, Hao W et al (2022) Canagliflozin Ameliorates NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation Through Inhibiting NF-kappaB Signaling and Upregulating Bif-1. Front Pharmacol 13:820541
Olgar Y, Turan B (2019) A sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin comparison with insulin shows important effects on Zn(2+)-transporters in cardiomyocytes from insulin-resistant metabolic syndrome rats through inhibition of oxidative stress (1). Can J Physiol Pharmacol 97(6):528–535
Peng S, Xu J, Ruan W, Li S, Xiao F (2017) PPAR-gamma Activation Prevents Septic Cardiac Dysfunction via Inhibition of Apoptosis and Necroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:8326749
Qi Z, Liu R, Ju H, Huang M, Li Z, Li W et al (2023) microRNA-130b-3p Attenuates Septic Cardiomyopathy by Regulating the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathways and Directly Targeting ACSL4 against Ferroptosis. Int J Biol Sci 19(13):4223–4241
Ravikumar N, Sayed MA, Poonsuph CJ, Sehgal R, Shirke MM, Harky A (2021) Septic Cardiomyopathy: From Basics to Management Choices. Curr Probl Cardiol 46(4):100767
Reifsnider, O. S., Kansal, A. R., Gandhi, P. K., Cragin, L., Brand, S. B., Pfarr, E., et al. (2021). Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin versus canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, or standard of care in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care, 9(1).
Rudiger A, Dyson A, Felsmann K, Carre JE, Taylor V, Hughes S et al (2013) Early functional and transcriptomic changes in the myocardium predict outcome in a long-term rat model of sepsis. Clin Sci (lond) 124(6):391–401
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M et al (2016) The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 315(8):801–810
Solov’eva T, Davydova V, Krasikova I, Yermak I (2013) Marine compounds with therapeutic potential in gram-negative sepsis. Mar Drugs 11(6):2216–2229
Stockwell BR, FriedmannAngeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ et al (2017) Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 171(2):273–285
Sun H, Chen D, Xin W, Ren L, Li Q, Han X (2023) Targeting ferroptosis as a promising therapeutic strategy to treat cardiomyopathy. Front Pharmacol 14:1146651
van der Aart-van der Beek AB, de Boer RA, Heerspink HJL (2022) Kidney and heart failure outcomes associated with SGLT2 inhibitor use. Nat Rev Nephrol 18(5):294–306
Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A et al (2019) Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 380(4):347–357
Yagoda N, von Rechenberg M, Zaganjor E, Bauer AJ, Yang WS, Fridman DJ et al (2007) RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 447(7146):864–868
Yang WS, Stockwell BR (2008) Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem Biol 15(3):234–245
Yang H, Zhang Z (2021) Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: the role of mitochondrial dysfunction. Inflamm Res 70(4):379–387
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M, Shchepinov MS, Stockwell BR (2016) Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(34):E4966-4975
Yapa NMB, Lisnyak V, Reljic B, Ryan MT (2021) Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease. FEBS Lett 595(8):1184–1204
Yu YW, Que JQ, Liu S, Huang KY, Qian L, Weng YB et al (2021) Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitor of Dapagliflozin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Limiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Modulating Autophagy. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:768214
Zanotti-Cavazzoni SL, Hollenberg SM (2009) Cardiac dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin Crit Care 15(5):392–397
Zechendorf, E., O'Riordan, C. E., Stiehler, L., Wischmeyer, N., Chiazza, F., Collotta, D., et al. (2020). Ribonuclease 1 attenuates septic cardiomyopathy and cardiac apoptosis in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. JCI Insight, 5(8).
Zhong J, Tan Y, Lu J, Liu J, Xiao X, Zhu P et al (2019) Therapeutic contribution of melatonin to the treatment of septic cardiomyopathy: A novel mechanism linking Ripk3-modified mitochondrial performance and endoplasmic reticulum function. Redox Biol 26:101287
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (92068116 and 82370305) and the Jiangsu Distinguished Young Scholars Fund (Approval No: BK20211501); the Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists in Nanjing (JQX22001); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023M731631); Nanjing Postdoctoral Science Foundation for Jinxuan Zhao and Jiangsu “Mass Innovation and Entrepreneurship” Talent Program to Jinxuan Zhao; Anhui Medical University Research Enhancement Program Funding Project(2023xkjT029); Anhui Provincial Natural Science Research Project for Higher Education Institutions(KJ2021ZD0027) and Collaborative Project between the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University and Hefei Zhongke Ion Medical Technology Equipment Co., Ltd.(CIM-HT-2018–327).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JX, HC and JZ conceived and designed the study. KH, PJ, YH and JH performed the experiments. KH and PJ drafted the manuscript. BS contributed to data collection and analysis. All authors have read and approved the manuscript, and all data were generated internally.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures with animals were approved by the Institution Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (Anhui, China) (No. LLSC20230846) and performed in accordance with the guidelines from Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, K., Jiang, P., Hu, J. et al. Dapagliflozin attenuates LPS-induced myocardial injury by reducing ferroptosis. J Bioenerg Biomembr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-024-10020-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-024-10020-3