Abstract
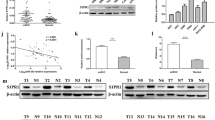
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is one of the most common renal malignancies in the urinary system. Numerous studies have demonstrated that miRNAs can regulate tumorigenesis and progression. This study aims to investigate the role and regulatory mechanism of miR-6838-5p in RCC. Our study confirmed that miR-6838-5p was upregulated in human RCC tissues (30/42, 77.43%, P < 0.01) and RCC cell lines (P < 0.05) compared to adjacent non-neoplastic tissues and normal renal epithelial cells. In vitro, overexpression of miR-6838-5p enhanced cell proliferation and invasion in human RCC cell lines (ACHN and 786-O), which were detected by CCK-8, Transwell and Colony formation assays (P < 0.05), and knockdown of miR-6838-5p suppressed cell proliferation and invasion (P < 0.05). Results of Bioinformatics analysis combined with Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay demonstrated that miR-6838-5p could bind to Cyclin D binding myb-like transcription factor 1 (DMTF1). In addition, RT-qPCR and Western blotting confirmed that DMTF1 was downregulated in RCC tissues and cell lines. Meanwhile, it was demonstrated that overexpression of miR-6838-5p inhibited DMTF1 level in ACHN cells. Next, we confirmed that DMTF1 overexpression reversed the inhibitory effects of overexpression of miR-6838-5p on phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), tumor protein 53(p53), murine double minute 2 (MDM2) and alternative reading frame (ARF) protein levels in the ARF-p53 signaling pathway. In conclusion, our research showed that miR-6838-5p enhanced the proliferation and invasion of RCC cells by inhibiting the DMTF1/ARF-p53 axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Carrasco-Garcia E, Moreno M, Moreno-Cugnon L, Matheu A (2017) Increased Arf/p53 activity in stem cells, aging and cancer. Aging Cell 16:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12574
Chmielik E, Rusinek D, Oczko-Wojciechowska M, Jarzab M, Krajewska J, Czarniecka A, Jarzab B (2018) Heterogeneity of thyroid cancer. Pathobiology 85:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1159/000486422
Di Franco G et al (2020) Renal cell carcinoma: the role of radical surgery on different patterns of local or distant recurrence. Surg Oncol 35:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suronc.2020.08.002
Ferragut Cardoso AP, Udoh KT, States JC (2020) Arsenic-induced changes in miRNA expression in cancer and other diseases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 409:115306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.115306
Fogli S, Porta C, del Re M, Crucitta S, Gianfilippo G, Danesi R, Rini BI, Schmidinger M (2020) Optimizing treatment of renal cell carcinoma with VEGFR-TKIs: a comparison of clinical pharmacology and drug-drug interactions of anti-angiogenic drugs. Cancer Treatment Rev 84:101966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.101966
Humphrey PA, Moch H, Cubilla AL, Ulbright TM, Reuter VE (2016) The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part B: prostate and bladder tumours. Eur Urol 70:120–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.028
Inoue K, Fry EA (2016) Aberrant splicing of the DMP1-ARF-MDM2-p53 pathway in cancer. Int J Cancer 139:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30003
Inoue K, Fry EA (2018) Tumor suppression by the EGR1, DMP1, ARF, p53, and PTEN network. Cancer Investig 36:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2018.1533965
Inoue K, Wen R, Rehg JE, Adachi M, Sherr CJ (2000) Disruption of the ARF transcriptional activator DMP1 facilitates cell immortalization, Ras transformation, and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 14:1797–1809
Kandettu A, Radhakrishnan R, Chakrabarty S, Sriharikrishnaa S, Kabekkodu SP (2020) The emerging role of miRNA clusters in breast cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1874:188413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188413
Ko A, Han SY, Song J (2016) Dynamics of ARF regulation that control senescence and cancer. BMB Rep 49:598–606. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.11.120
Ko A, Han SY, Song J (2018) Regulatory network of ARF in cancer development. Mol Cells 41:381–389. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2018.0100
Li J, Jiang D, Zhang Q, Peng S, Liao G, Yang X, Tang J, Xiong H, Pang J (2020) MiR-301a promotes cell proliferation by repressing PTEN in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 12:4309–4320. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S253533
Li S, Feng Z, Zhang X, Lan D, Wu Y (2019) Up-regulation of microRNA-200c-3p inhibits invasion and migration of renal cell carcinoma cells via the SOX2-dependent Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int 19:231. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0944-5
Liu HT, Fan WX (2020) MiRNA-1246 suppresses the proliferation and migration of renal cell carcinoma through targeting CXCR4. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:5979–5987. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202006_21491
Liu S, Wang Y, Li W, Yu S, Wen Z, Chen Z, Lin F (2019) MiR-221-5p acts as an oncogene and predicts worse survival in patients of renal cell cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 119:109406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109406
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL, Siegel RL (2019) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69:363–385. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21565
Munteanu VC, Munteanu RA, Onaciu A, Berindan-Neagoe I, Petrut B, Coman I (2020) MiRNA-based inspired approach in diagnosis of prostate cancer. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56020094
Niklaus NJ, Humbert M, Tschan MP (2018) Cisplatin sensitivity in breast cancer cells is associated with particular DMTF1 splice variant expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2800–2806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.042
Peng Y, Dong W, Lin TX, Zhong GZ, Huang J (2015) MicroRNA-155 promotes bladder cancer growth by repressing the tumor suppressor DMTF1. Oncotarget 6:16043–16058. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3755
Quan J, Pan X, Li Y, Hu Y, Tao L, Li Z, Zhao L, Wang J, Li H, Lai Y, Zhou L, Lin C, Gui Y, Ye J, Zhang F, Lai Y (2019) MiR-23a-3p acts as an oncogene and potential prognostic biomarker by targeting PNRC2 in RCC. Biomed Pharmacother 110:656–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.065
Reiter JG, Baretti M, Gerold JM, Makohon-Moore AP, Daud A, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Azad NS, Kinzler KW, Nowak MA, Vogelstein B (2019) An analysis of genetic heterogeneity in untreated cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 19:639–650. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0185-x
Roerink SF, Sasaki N, Lee-Six H, Young MD, Alexandrov LB, Behjati S, Mitchell TJ, Grossmann S, Lightfoot H, Egan DA, Pronk A, Smakman N, van Gorp J, Anderson E, Gamble SJ, Alder C, van de Wetering M, Campbell PJ, Stratton MR, Clevers H (2018) Intra-tumour diversification in colorectal cancer at the single-cell level. Nature 556:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0024-3
Roulot A, Héquet D, Guinebretière JM, Vincent-Salomon A, Lerebours F, Dubot C, Rouzier R (2016) Tumoral heterogeneity of breast cancer. Ann Biol Clin 74:653–660. https://doi.org/10.1684/abc.2016.1192
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Spadaccino F, Netti GS, Rocchetti MT, Castellano G, Stallone G, Ranieri E (2020) Diagnostic and prognostic markers of renal cell carcinoma. G Ital Nefrol 37:2020–vol2
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Szabó Z, Szegedi K, Gombos K, Mahua C, Flaskó T, Harda K, Halmos G (2016) Expression of miRNA-21 and miRNA-221 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and their possible role in the development of ccRCC. Urol Oncol 34:533.e21–533.e27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.06.011
Tschan MP, Federzoni EA, Haimovici A, Britschgi C, Moser BA, Jin J, Reddy VA, Sheeter DA, Fischer KM, Sun P, Torbett BE (2015) Human DMTF1β antagonizes DMTF1α regulation of the p14(ARF) tumor suppressor and promotes cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1849:1198–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.07.009
Usher-Smith J, Simmons RK, Rossi SH, Stewart GD (2020) Current evidence on screening for renal cancer. Nat Rev Urol 17:637–642. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-020-0363-3
Yang X, Lou Y, Wang M, Liu C, Liu Y, Huang W (2019) MiR-675 promotes colorectal cancer cell growth dependent on tumor suppressor DMTF1. Mol Med Rep 19:1481–1490. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9780
Zeng R, Huang J, Sun Y, Luo J (2020) Cell proliferation is induced in renal cell carcinoma through miR-92a-3p upregulation by targeting FBXW7. Oncol Lett 19:3258–3268. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11443
Zhang C et al (2020) MiR-30b-5p up-regulation related to the dismal prognosis for patients with renal cell cancer. J Clin lab anal :e23599. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23599
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants who participated in this study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ designed the study. XQZ and YW drafted and wrote the manuscript. DZ and HCL collected and analyzed the data. TC and JZ contributed samples collection and intellectual input. JZ revised the manuscript critically for intellectual content. All authors gave intellectual input to the study and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Xi’an Jiaotong University (Xi’an, China).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, X., Wu, Y., Zhang, D. et al. MiR-6838-5p facilitates the proliferation and invasion of renal cell carcinoma cells through inhibiting the DMTF1/ARF-p53 axis. J Bioenerg Biomembr 53, 191–202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09888-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09888-2