Abstract
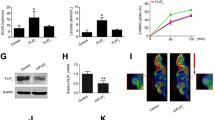
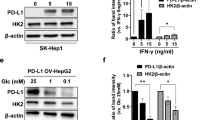
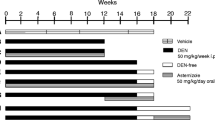
Hypoxic conditions, which large or infiltrative hypovascular tumors may encounter, also produce acidic environments. Carbonic anhydrase-IX (CA-IX), an enzyme involved in lowering pH, is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In the present study, whether inhibition of CA-IX enhances the efficacy of a hexokinase II inhibitor in an in vivo murine model was examined and its prognostic implication in HCC patients was investigated. CA-IX expression was evaluated using quantitative real-time PCR and western blot analysis using human HCC cell lines. 3-bromopyruvate (3-BP), a hexokinase II inhibitor, and acetazolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, were used to target hexokinase II and CA-IX in vitro and in vivo, respectively. A human HCC cell line (Huh-7) was tested as a subcutaneous tumor model in BALB/c nu/nu mice. The prognostic role of CA-IX was evaluated in the TCGA database. Quantitative real-time PCR and western blot analysis revealed that CA-IX expression was activated in the presence of 3-BP. Further analysis showed that introducing an additional stress by treating the orally active CA-IX inhibitor (acetazolamide) can synergistically increase the efficacy of 3-BP in vivo, which was confirmed using a mouse model. We also found that HCC patients with high CA-IX expression show poor overall survival in TCGA database. These results indicate CA-IX is a promising therapeutic target for enhancing the efficacy of 3-BP and can be a prognostic factor for HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki H, Kang PM, Hampe J, Yoshimura K, Noma T, Matsuzaki M, Izumo S (2002) Direct activation of mitochondrial apoptosis machinery by c-Jun N-terminal kinase in adult cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 277(12):10244–10250. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112355200
Benej M, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J (2014) Carbonic anhydrase IX: regulation and role in cancer. Subcell Biochem 75:199–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7359-2_11
Budak-Alpdogan T, Chen B, Warrier A, Medina DJ, Moore D, Bertino JR (2009) Retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene expression determines the response to sequential flavopiridol and doxorubicin treatment in small-cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15(4):1232–1240. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0810
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S, Geschwind JF, Kunjithapatham R, Buijs M, Syed LH, Rao PP, Ota S, Kwak BK, Loffroy R, Vali M (2010) 3-Bromopyruvate induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, overcomes autophagy and causes apoptosis in human HCC cell lines. Anticancer Res 30(3):923–935
Gwak GY, Yoon JH, Kim KM, Lee HS, Chung JW, Gores GJ (2005) Hypoxia stimulates proliferation of human hepatoma cells through the induction of hexokinase II expression. J Hepatol 42(3):358–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2004.11.020
Kim W, Yoon JH, Jeong JM, Cheon GJ, Lee TS, Yang JI, Park SC, Lee HS (2007) Apoptosis-inducing antitumor efficacy of hexokinase II inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 6(9):2554–2562. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0115
Kivela AJ, Parkkila S, Saarnio J, Karttunen TJ, Kivela J, Parkkila AK et al (2000) Expression of transmembrane carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes IX and XII in normal human pancreas and pancreatic tumours. Histochem Cell Biol 114(3):197–204
Korkeila E, Talvinen K, Jaakkola PM, Minn H, Syrjanen K, Sundstrom J et al (2009) Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX suggests poor outcome in rectal cancer. Br J Cancer 100(6):874–880. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604949
Lee EW, Khan S (2017) Recent advances in transarterial embolotherapies in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol 23(4):265–272. https://doi.org/10.3350/cmh.2017.0111
Martinez-Zaguilan R, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Chu YW, Gillies RJ, Hendrix MJ (1996) Acidic pH enhances the invasive behavior of human melanoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 14(2):176–186
Parkkila S, Rajaniemi H, Parkkila AK, Kivela J, Waheed A, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J, Sly WS (2000) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor suppresses invasion of renal cancer cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(5):2220–2224. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.040554897
Pastorekova S, Ratcliffe PJ, Pastorek J (2008) Molecular mechanisms of carbonic anhydrase IX-mediated pH regulation under hypoxia. BJU Int 101(Suppl 4):8–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07642.x
Shen Z, Wang X, Yu X, Zhang Y, Qin L (2017) MMP16 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 8(42):72197–72204. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20060
Supuran CT (2008) Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(2):168–181. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2467
Supuran CT, Alterio V, Di Fiore A, K DA, Carta F, Monti SM et al (2018) Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX targets primary tumors, metastases, and cancer stem cells: three for the price of one. Med Res Rev 38(6):1799–1836. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21497
Svastova E, Zilka N, Zat'ovicova M, Gibadulinova A, Ciampor F, Pastorek J et al (2003) Carbonic anhydrase IX reduces E-cadherin-mediated adhesion of MDCK cells via interaction with beta-catenin. Exp Cell Res 290(2):332–345
Swinson DE, Jones JL, Richardson D, Wykoff C, Turley H, Pastorek J et al (2003) Carbonic anhydrase IX expression, a novel surrogate marker of tumor hypoxia, is associated with a poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 21(3):473–482. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2003.11.132
Tezuka M, Hayashi K, Kubota K, Sekine S, Okada Y, Ina H, Irie T (2007) Growth rate of locally recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: comparing the growth rate of locally recurrent tumor with that of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 52(3):783–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9537-y
van den Beucken T, Magagnin MG, Savelkouls K, Lambin P, Koritzinsky M, Wouters BG (2007) Regulation of Cited2 expression provides a functional link between translational and transcriptional responses during hypoxia. Radiother Oncol 83(3):346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2007.04.026
Weinstein-Oppenheimer CR, Henriquez-Roldan CF, Davis JM, Navolanic PM, Saleh OA, Steelman LS et al (2001) Role of the Raf signal transduction cascade in the in vitro resistance to the anticancer drug doxorubicin. Clin Cancer Res 7(9):2898–2907
Yu SJ, Yoon JH, Lee JH, Myung SJ, Jang ES, Kwak MS, Cho EJ, Jang JJ, Kim YJ, Lee HS (2011) Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase-IX enhances hexokinase II inhibitor-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32(7):912–920. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2011.24
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by grants from the SNUH Research Fund (No. 04-2011-0660) and the Liver Research Foundation of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, E.J., Yu, S.J., Kim, K. et al. Carbonic anhydrase-IX inhibition enhances the efficacy of hexokinase II inhibitor for hepatocellular carcinoma in a murine model. J Bioenerg Biomembr 51, 121–129 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09788-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09788-6