Abstract
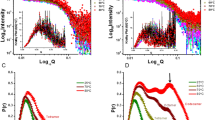
The first low resolution solution structure of the soluble domain of subunit b (b 22–156) of the Escherichia coli F1FO ATPsynthase was determined from small-angle X-ray scattering data. The dimeric protein has a boomerang-like shape with a total length of 16.2±0.3 nm. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) shows that the protein binds effectively to the subunit δ, confirming their described neighborhood. Using the recombinant C-terminal domain (δ91–177) of subunit δ and the C-terminal peptides of subunit b, b 120–140 and b 140–156, FCS titration experiments were performed to assign the segments involved in δ−b assembly. These data identify the very C-terminal tail b 140–156 to interact with δ91–177. The novel 3D structure of this peptide has been determined by NMR spectroscopy. The molecule adopts a stable helix formation in solution with a flexible tail between amino acid 140 to 145.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altendorf K, Stalz W, Greie J, Deckers-Hebestreit G (2000) J Exp Biol 203:19–28
Andrade MA, Chacon P, Merelo JJ, Moran F (1993) Protein Eng 6:383–390
Bhatt D, Cole SP, Grabar TB, Claggett SB, Cain BD (2005) J Bioenerg Biomembr 37:67–74
Biuković G, Rössle M, Gayen S, Mu Y, Grüber G (2007) Biochemistry 46:2070–2078
Böhm G (1992) Protein Eng 5:191–195
Boulin CJ, Kempf R, Koch MHJ, McLaughlin SM (1986) Nucl Instrum Methods A 249:399–407
Boulin CJ, Kempf R, Gabriel A, Koch MHJ (1988) Nucl Instrum Methods A 269:312–320
Brusilow WSA, Scarpetta MA, Hawthorne CA, Clark WP (1989) J Biol Chem 264:1528–1533
Capaldi RA, Aggeler R, Wilkens S, Grüber G (1996) J Bioenerg Biomembr 28:397–402
Del Rizzo PA, Bi Y, Dunn SD, Shilton BH (2002) Biochemistry 41:6875–6884
Del Rizzo PA, Bi Y, Dunn SD (2006) J Mol Biol 364:735–746
DeLano WL (2001) The pyMol molecular graphics system. DeLano Scientific, San Carlos, CA
Deléage G, Geourjon C (1993) Comp Appl Biosci 9:197–199
Dickson VK, Silvester JA, Fearnley IM, Leslie AGW, Walker JE (2006) EMBO J 25:2911–2918
Dmitriev O, Jones PC, Jiang W, Fillingame RH (1999) J Biol Chem 274:15598–15604
Dunn SD, Chandler J (1998) J Biol Chem 273:8646–8651
Dunn SD, Revington M, Cipriano DJ, Shilton BH (2000) J Bioenerg Biomembr 32:347–355
Grüber G (2000) J Bioenerg Biomembr 32:341–346
Grüber G, Hausrath A, Sagermann M, Capaldi RA (1997) FEBS Lett 410:165–168
Grüber G, Godovac-Zimmermann J, Link TA, Coskun Ü, Rizzo VF, Betz C, Bailer S (2002) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298:383–391
Guinier A, Fournet G (1955) Small angle scattering of X-rays. Wiley, New York
Hausrath AC, Grüber G, Matthews BW, Capaldi RA (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13697–13702
Herrmann T, Güntert P, Wüthrich K (2002) J Mol Biol 319:209–227
Hornung T, Volkov OA, Zaida TMA, Delannoy S, Wise JG, Vogel PD (2008) Biophys J 94:5053–5064
Hunke C, Chen WJ, Schäfer HJ, Grüber G (2007) Protein Expr Purif 53:378–383
Jemilawon J, Awuah Asiamah I, Bernstein HJ, Darakev G, Darakev N, Kamburov P (2007) Use of CBFlib for map support. In: Poster presentation at poster session B, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Biology and Synchrotron Radiation (BSR 2007), 13–17 August 2007, Manchester, UK
Keis S, Kaim G, Dimroth P, Cook GM (2004) Biochm Biophys Acta 1676:112–117
Kneller DG, Goddard TD (1997) SPARKY 3.105 edit. University of California, San Francisco, CA
Konarev PV, Volkov VV, Sokolova AV, Koch MHJ, Svergun DI (2003) J Appl Crystallogr 36:1277–1282
Laemmli UK (1970) Nature 227:680–685
Manavalan P, Johnson WC Jr (1987) Anal Biochem 167:76–85
McLachlin DT, Dunn SD (2000) Biochemistry 39:3486–3490
McLachlin DT, Coveny AM, Clark SM, Dunn SD (2000) J Biol Chem 275:17571–17577
Ogilvie I, Aggeler R, Capaldi RA (1997) J Biol Chem 272:16652–16656
Pedersen PL, Ko YH, Hong S (2000) J Bioenerg Biomembr 32:325–332
Petoukhov MV, Konarev PV, KiKhney AG, Svergun DI (2007) J Appl Cryst 40:223–228
Provencher SW (1982) Comput Phys Commun 27:213–227
Revington M, Dunn SD, Shaw GS (2002) Protein Sci 11:1227–1238
Rodgers AJW, Capaldi RA (1998) J Biol Chem 273:29406–29410
Rodgers AJ, Wilkens S, Aggeler R, Morris MB, Howitt SM, Capaldi RA (1997) J Biol Chem 272:31058–31064
Sreerama N, Woody RW (1993) Anal Biochem 209:32–44
Stalz W, Greie J, Deckers-Hebestreit G, Altendorf K (2003) J Biol Chem 278:27068–27071
Svergun DI (1992) J Appl Crystallogr 25:495–503
Svergun DI (1993) J Appl Crystallogr 26:258–267
Svergun DI (1997) J Appl Crystallogr 30:792–797
Svergun DI, Petoukhov MV, Koch MHJ (2001) Biophys J 80:2946–2953
Takeyama M, Noumi T, Maeda M, Futai M (1988) J Biol Chem 263:16106–16112
Vogel PD (2000) J Bioenerg Biomembr 32:413–421
Weber J (2006) Biochim Biophys Acta 1757:1162–1170
Wilkens S (2000) J Bioenerg Biomembr 32:333–340
Wilkens S, Dunn SD, Chandler J, Dahlquist FW, Capaldi RA (1997) Nat Struct Biol 4:198–201
Wise JG, Vogel PD (2008) Biophys J 94:5040–5052
Wood KS, Dunn SD (2007) J Biol Chem 282:31920–31927
Wüthrich K (1986) NMR of proteins and nucleic acids. Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Priya, R., Tadwal, V.S., Roessle, M.W. et al. Low resolution structure of subunit b (b 22–156) of Escherichia coli F1FO ATP synthase in solution and the b−δ assembly. J Bioenerg Biomembr 40, 245–255 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-008-9154-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-008-9154-x