Abstract
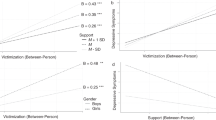
The current study examined the moderating role of friendship quality on the relation between maternal anxiety and internalizing symptoms in a 3-year prospective study of adolescent development. Participants included 177 adolescents (Mage = 16.05, SDage = 0.91) and their mothers. Mothers reported their own levels of anxiety; youth completed self-reports of internalizing symptoms and friendship quality. Positive friendship quality moderated the relation between maternal anxiety and initial levels of internalizing symptoms. Maternal anxiety was associated with steeper increases in internalizing symptoms over time, but only for those with greater negative peer interactions. Findings underscore the important role of both parental and peer relationships in the development of internalizing symptoms and highlight specific avenues for clinical interventions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angold, A., Costello, E. J., & Worthman, C. M. (1998). Puberty and depression: The roles of age, pubertal status, and pubertal timing. Psychological Medicine, 28, 51–61.
Asselmann, E., Wittchen, H., Lieb, R., Höfler, M., & Beesdo-Baum, K. (2016). Does low coping efficacy mediate the association between negative life events and incident psychopathology? A prospective-longitudinal community study among adolescents and young adults. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 25(2), 171–180. https://doi.org/10.1017/S204579601500013X.
Bados, A., Gómez-Benito, J., & Balaguer, G. (2010). The state-trait anxiety inventory, trait version: Does it really measure anxiety? Journal of Personality Assessment, 92(6), 560–567. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223891.2010.513295.
Beal, A. C., Ausiello, J., & Perrin, J. M. (2001). Social influences on health-risk behaviors among minority middle school students. Journal of Adolescent Health, 28(6), 474–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1054-139X(01)00194-X.
Beesdo, K., Pine, D. S., Lieb, R., & Wittchen, H. (2010). Incidence and risk patterns of anxiety and depressive disorders and categorization of generalized anxiety disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 67(1), 47–57. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.177.
Beidel, D. C., & Turner, S. M. (1997). At risk for anxiety: I. psychopathology in the offspring of anxious parents. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(7), 918–924. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199707000-00013.
Beidel, D. C., Turner, S. M., & Morris, T. L. (2000). Behavioral treatment of childhood social phobia. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68(6), 1072–1080. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.68.6.1072.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107(2), 238–246. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.107.2.238.
Berndt, T. J. (1996). Exploring the effects of friendship quality on social development. In W. M. Bukowski, A. F. Newcomb, & &. W. W. Hartup (Eds.), The company they keep: Friendship in childhood and adolescence (pp. 346–365). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Biederman, J., Faraone, S. V., Hirshfeld-Becker, D. R., Friedman, D., Robin, J. A., & Rosenbaum, J. F. (2001). Patterns of psychopathology and dysfunction in high-risk children of parents with panic disorder and major depression. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 158(1), 49–57. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.158.1.49.
Biederman, J., Petty, C., Faraone, S. V., Henin, A., Hirshfeld-Becker, D., Pollack, M. H., et al. (2006). Effects of parental anxiety disorders in children at high risk for panic disorder: A controlled study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 94(1–3), 191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2006.04.012.
Bieling, P. J., Antony, M. M., & Swinson, R. P. (1998). The state–trait anxiety inventory, trait version: Structure and content re-examined. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 36(7–8), 777–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(98)00023-0.
Bouma, E. M. C., Ormel, J., Verhulst, F. C., & Oldehinkel, A. J. (2008). Stressful life events and depressive problems in early adolescent boys and girls: The influence of parental depression, temperament and family environment. Journal of Affective Disorders, 105(1–3), 185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2007.05.007.
Brittian, A. S., Toomey, R. B., Gonzales, N. A., & Dumka, L. E. (2013). Perceived discrimination, coping strategies, and Mexican origin adolescents’ internalizing and externalizing behaviors: Examining the moderating role of gender and cultural orientation. Applied Developmental Science, 17(1), 4–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2013.748417.
Brown, B. B. (2004). Adolescents’ relationships with peers. In R. M. Lerner & L. Steinberg (Eds.), Handbook of adolescent psychology (2nd ed., pp. 363–394). New York: Wiley.
Buhrmester, D. (1998). Need fulfillment, interpersonal competence, and the developmental contexts of early adolescent friendship. In W. M. Bukowski, A. F. Newcomb, & W. W. Hartup (Eds.), The company they keep: Friendship in childhood and adolescence (pp. 158–185). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Burstein, M., Ginsburg, G. S., Petras, H., & Ialongo, N. (2010a). Parent psychopathology and youth internalizing symptoms in an urban community: A latent growth model analysis. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 41(1), 61–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-009-0152-y.
Burstein, M., Ginsburg, G. S., & Tein, J. (2010b). Parental anxiety and child symptomatology: An examinzation of additive and interactive effects of parent psychopathology. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 38(7), 897–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-010-9415-0.
Calmes, C. A., & Roberts, J. E. (2008). Rumination in interpersonal relationships: Does co-rumination explain gender differences in emotional distress and relationship satisfaction among college students? Cognitive Therapy and Research, 32(4), 577–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-008-9200-3.
Carter, J. S., Dellucci, T., Turek, C., & Mir, S. (2015). Predicting depressive symptoms and weight from adolescence to adulthood: Stressors and the role of protective factors. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 44(11), 2122–2140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-015-0301-5.
Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality (2016). Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2015 National Survey on drug use and health (HHS Publication No. SMA 16-4984, NSDUH Series H-51). Retrieved from http://www.samhsa.gov/data/
Challacombe, F., & Salkovskis, P. (2009). A preliminary investigation of the impact of maternal obsessive-compulsive disorder and panic disorder on parenting and children. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23(7), 848–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.04.002.
Chorpita, B. F., Yim, L., Moffitt, C., Umemoto, L. A., & Francis, S. E. (2000). Assessment of symptoms of DSM-IV anxiety and depression in children: A revised child anxiety and depression scale. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38(8), 835–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(99)00130-8.
Chorpita, B. F., Moffitt, C. E., & Gray, J. (2005). Psychometric properties of the revised child anxiety and depression scale in a clinical sample. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 43(3), 309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2004.02.004.
Cohen, J. R., Spiro, C. N., Young, J. F., Gibb, B. E., Hankin, B. L., & Abela, J. R. Z. (2015). Interpersonal risk profiles for youth depression: A person-centered, multi-wave, longitudinal study. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 43(8), 1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0023-x.
Collins, W. A., & Laursen, B. (2004). Changing relationships, changing youth: Interpersonal contexts of adolescent development. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 24(1), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272431603260882.
Coplan, R. J., Arbeau, K. A., & Armer, M. (2008). Don't fret, be supportive! Maternal characteristics linking child shyness to psychosocial and school adjustment in kindergarten. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36(3), 359–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-007-9183-7.
Costello, E. J., Egger, H. L., & Angold, A. (2005). The developmental epidemiology of anxiety disorders: Phenomenology, prevalence, and comorbidity. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 14(4), 631–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2005.06.003.
De Los Reyes, A., & Kazdin, A. E. (2005). Informant discrepancies in the assessment of childhood psychopathology: A critical review, theoretical framework, and recommendations for further study. Psychological Bulletin, 131(4), 483–509. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.131.4.483.
Dowling, N. A., Shandley, K., Oldenhof, E., Youssef, G. J., Thomas, S. A., Frydenberg, E., & Jackson, A. C. (2016). The intergenerational transmission of problem gambling: The mediating role of parental psychopathology. Addictive Behaviors, 5912–5917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.03.002.
Edwards, E. S., Holzman, J. B., Burt, N. M., Rutherford, H. J. V., Mayes, L. C., & Bridgett, D. J. (2017). Maternal emotion regulation strategies, internalizing problems and infant negative affect. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 48, 59–68.https://doi-org.proxy-um.researchport.umd.edu/10.1016/j.appdev.2016.12.001.
Epkins, C. C., & Heckler, D. R. (2011). Integrating etiological models of social anxiety and depression in youth: Evidence for a cumulative interpersonal risk model. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 14(4), 329–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-011-0101-8.
Essau, C. A., Ishikawa, S., Sasagawa, S., Otsui, K., Sato, H., Okajima, I., Georgiou, G. A., O’Callaghan, J., & Bray, D. (2013). Psychopathological symptoms in two generations of the same family: A cross-cultural comparison. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 48(12), 2017–2026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-013-0673-3.
Evans, S. E., Steel, A. L., & DiLillo, D. (2013). Child maltreatment severity and adult trauma symptoms: Does perceived social support play a buffering role? Child Abuse & Neglect, 37(11), 934–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2013.03.005.
Felton, J. W., Cole, D. A., Havewala, M., Kurdziel, G., & Brown, V. (2018). Talking together, thinking alone: Relations among co-rumination, peer relationships, and rumination. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-018-0937-z.
Festa, C. C., & Ginsburg, G. S. (2011). Parental and peer predictors of social anxiety in youth. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 42(3), 291–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-011-0215-8.
Folger, S. F., & Wright, M. O. (2013). Altering risk following child maltreatment: Family and friend support as protective factors. Journal of Family Violence, 28, 325–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-013-9510-4.
Francis, S. E., & Chorpita, B. F. (2011). Parental beliefs about child anxiety as a mediator of parent and child anxiety. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 35(1), 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-009-9255-9.
Furman, W., & Buhrmester, D. (1985). Children's perceptions of the personal relationships in their social networks. Developmental Psychology, 21, 1016–1022.
Georgiades, K., Lewinsohn, P. M., Monroe, S. M., & Seeley, J. R. (2006). Major depressive disorder in adolescence: The role of subthreshold symptoms. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 45(8), 936–944. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.chi.0000223313.25536.47.
Ginsburg, G. S., Grover, R. L., & Ialongo, N. (2004). Parenting behaviors among anxious and non-anxious mothers: Relation with concurrent and long-term child outcomes. Child & Family Behavior Therapy, 26(4), 23–41. https://doi.org/10.1300/J019v26n04_02.
Gluschkoff, K., Keltikangas-Järvinen, L., Pulkki-Råback, L., Jokela, M., Viikari, J., Raitakari, O., & Hintsanen, M. (2017). Hostile parenting, parental psychopathology, and depressive symptoms in the offspring: A 32-year follow-up in the Young Finns study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 208, 208436–208442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.11.002.
Grant, K. E., O’Koon, J. H., Davis, T. H., Roache, N. A., Poindexter, L. M., Armstrong, M. L., et al. (2000). Protective factors affecting low-income urban African American youth exposed to stress. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 20(4), 388–417. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272431600020004002.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 26, 41–54.
Gregory, A. M., & Eley, T. C. (2007). Genetic influences on anxiety in children: What we've learned and where we're heading. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 10(3), 199–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-007-0022-8.
Herzer, M., Umfress, K., Aljadeff, G., Ghai, K., & Zakowski, S. G. (2009). Interactions with parents and friends among chronically ill children: Examining social networks. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 30(6), 499–508. https://doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0b013e3181c21c82.
Hirshfeld-Becker, D. R., Micco, J. A., Henin, A., Petty, C., Faraone, S. V., Mazursky, H., et al. (2012). Psychopathology in adolescent offspring of parents with panic disorder, major depression, or both: A 10-year follow-up. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 169(11), 1175–1184. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11101514.
Hishinuma, E. S., Miyamoto, R. H., Nishimura, S. T., Goebert, D. A., Yuen, N. Y. C., Makini, G. K., Jr., et al. (2001). Prediction of anxiety disorders using the state-trait anxiety inventory for multiethnic adolescents. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 15(6), 511–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0887-6185(01)00079-2.
Holt, M. K., & Espelage, D. L. (2005). Social support as a moderator between dating violence victimization and depression/anxiety among African American and Caucasian adolescents. School Psychology Review, 34(3), 309–328.
Humphreys, K. L., Katz, S. J., Lee, S. S., Hammen, C., Brennan, P. A., & Najman, J. M. (2013). The association of ADHD and depression: Mediation by peer problems and parent–child difficulties in two complementary samples. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 122(3), 854–867. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033895.
Kerns, C. E., Pincus, D. B., McLaughlin, K. A., & Comer, J. S. (2017). Maternal emotion regulation during child distress, child anxiety accommodation, and links between maternal and child anxiety. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 50, 52–59 https://doi-org.proxy-um.researchport.umd.edu/10.1016/j.janxdis.2017.05.002.
Kessler, R. C., Demler, O., Frank, R. G., Olfson, M., Pincus, H. A., Walters, E. E., et al. (2005). Prevalence and treatment of mental disorders, 1990 to 2003. The New England Journal of Medicine, 352(24), 2515–2523. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa043266.
Kliewer, W., Murrelle, L., Mejia, R., Torres de G., Y., & Angold, A. (2001). Exposure to violence against a family member and internalizing symptoms in Colombian adolescents: The protective effects of family support. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 69(6), 971–982. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.69.6.971.
Knappe, S., Beesdo, K., Fehm, L., Höfler, M., Lieb, R., & Wittchen, H. (2009). Do parental psychopathology and unfavorable family environment predict the persistence of social phobia? Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23(7), 986–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.06.010.
Kugbey, N., Osei-Boadi, S., & Atefoe, E. A. (2015). The influence of social support on the levels of depression, anxiety and stress among students in Ghana. Journal of Education and Practice, 6(25), 135–140.
La Greca, A. M., & Harrison, H. M. (2005). Adolescent peer relations, friendships, and romantic relationships: Do they predict social anxiety and depression? Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 34(1), 49–61. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15374424jccp3401_5.
Landman-Peeters, K. M. C., Hartman, C. A., van der Pompe, G., den Boer, J. A., Minderaa, R. B., & Ormel, J. (2005). Gender differences in the relation between social support, problems in parent-offspring communication, and depression and anxiety. Social Science & Medicine, 60(11), 2549–2559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.10.024.
Lee, C. S., & Goldstein, S. E. (2016). Loneliness, stress, and social support in young adulthood: Does the source of support matter? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45(3), 568–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-015-0395-9.
Liber, J. M., van Widenfelt, B. M., Goedhart, A. W., Utens, E. J., van der Leeden, A. M., Markus, M. T., & Treffers, P. A. (2008). Parenting and parental anxiety and depression as predictors of treatment outcome for childhood anxiety disorders: Has the role of fathers been underestimated? Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 37(4), 747–758. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374410802359692.
Liberman, L. C., & Öst, L. (2016). The relation between fears and anxiety in children with specific phobia and parental fears and anxiety. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(2), 598–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-015-0222-7.
Martin, N. C., Felton, J. W., & Cole, D. A. (2016). Predictors of youths’ posttraumatic stress symptoms following a natural disaster: The 2010 Nashville, Tennessee, flood. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 45(3), 335–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2014.982279.
Merikangas, K. R., Dierker, L. C., & Szamari, P. (1998). Psychopathology among offspring of parents with substance abuse and/or anxiety disorders: A high risk study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 39(5), 711–720. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021963098002522.
Merikangas, K. R., Avenevoli, S., Dierker, L., & Grillon, C. (1999). Vulnerability factors among children at risk for anxiety disorders. Biological Psychiatry, 46(11), 1523–1535. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00172-9.
Merikangas, K. R., Lieb, R., Wittchen, H. -., & Avenevoli, S. (2003). Family and high-risk studies of social anxiety disorder. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 108(Suppl417), 28–37. doi:https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0447.108.s417.5.x.
Merikangas, K. R., He, J., Burstein, M., Swanson, S. A., Avenevoli, S., Cui, L., et al. (2010). Lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in U.S. adolescents: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication-Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(10), 980–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2010.05.017.
Micco, J. A., Henin, A., Mick, E., Kim, S., Hopkins, C. A., Biederman, J., & Hirshfeld-Becker, D. R. (2009). Anxiety and depressive disorders in offspring at high risk for anxiety: A meta-analysis. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23(8), 1158–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.07.021.
Möller, E. L., Majdandžić, M., & Bögels, S. M. (2015). Parental anxiety, parenting behavior, and infant anxiety: Differential associations for fathers and mothers. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24(9), 2626–2637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0065-7.
Murthi, M., & Espelage, D. L. (2005). Childhood sexual abuse, social support, and psychological outcomes: A loss framework. Child Abuse & Neglect, 29(11), 1215–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2005.03.008.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2010). Mplus User’s guide. Sixth edition. Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Nangle, D. W., Erdley, C. A., Newman, J. E., Mason, C. A., & Carpenter, E. M. (2003). Popularity, friendship quantity, and friendship quality: Interactive influences on Children's loneliness and depression. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 32(4), 546–555. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3204_7.
Negriff, S., & Susman, E. J. (2011). Pubertal timing, depression, and externalizing problems: A framework, review, and examination of gender differences. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(3), 717–746. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-7795.2010.00708.x.
Newman, B. M., Newman, P. R., Griffen, S., O'Connor, K., & Spas, J. (2007). The relationship of social support to depressive symptoms during the transition to high school. Adolescence, 42(167), 441–459.
Nivard, M. G., Lubke, G. H., Dolan, C. V., Evans, D. M., St. Pourcain, B., Munafò, M. R., & Middeldorp, C. M. (2017). Joint developmental trajectories of internalizing and externalizing disorders between childhood and adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 29, 919–928. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579416000572.
Parker, J. G., Rubin, K. H., Erath, S. A., Wojslawowicz, J. C., & Buskirk, A. A. (2006). Peer relationships, child development, and adjustment: A developmental psychopathology perspective. In D. Cicchetti & D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Developmental psychopathology: Vol. 1. Theory and method (2nd ed., pp. 419–493). New York: Wiley.
Paul, L. A., Felton, J. W., Adams, Z. W., Welsh, K., Miller, S., & Ruggiero, K. J. (2015). Mental health among adolescents exposed to a tornado: The influence of social support and its interactions with sociodemographic characteristics and disaster exposure. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 28(3), 232–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.22012.
Piacentini, J., Peris, T. S., Bergman, R. L., Chang, S., & Jaffer, M. (2007). Functional impairment in childhood OCD : Development and psychometrics properties of the child obsessive-compulsive impact scale--revised (COIS--R). Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(4), 645–653. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374410701662790.
Rapee, R. M. (1997). Potential role of childrearing practices in the development of anxiety and depression. Clinical Psychology Review, 17(1), 47–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7358(96)00040-2.
Rasing, S. A., Creemers, D. M., Janssens, J. M., & Scholte, R. J. (2015). The association between perceived maternal and paternal psychopathology and depression and anxiety symptoms in adolescent girls. Frontiers in Psychology, 6.
Roemer, L., Lee, J. K., Salters-Pedneault, K., Erisman, S. M., Orsillo, S. M., & Mennin, D. S. (2009). Mindfulness and emotion regulation difficulties in generalized anxiety disorder: Preliminary evidence for independent and overlapping contributions. Behavior Therapy, 40(2), 142–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2008.04.001.
Rose, A. J. (2002). Co-rumination in the friendships of girls and boys. Child Development, 73(6), 1830–1843. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00509.
Roza, S. J., Hofstra, M. B., van der Ende, J., & Verhulst, F. C. (2003). Stable prediction of mood and anxiety disorders based on behavioral and emotional problems in childhood: A 14-year follow-up during childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 160(12), 2116–2121. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.160.12.2116.
Rubin, K. H., Dwyer, K. M., Booth-LaForce, C., Kim, A. H., Burgess, K. B., & Rose-Krasnor, L. (2004). Attachment, friendship, and psychosocial functioning in early adolescence. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 24(4), 326–356. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272431604268530.
Rudolph, J., & Zimmer-Gembeck, M. J. (2014). Parent relationships and adolescents' depression and social anxiety: Indirect associations via emotional sensitivity to rejection threat. Australian Journal of Psychology, 66(2), 110–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajpy.12042.
Rueger, S. Y., Malecki, C. K., Pyun, Y., Aycock, C., & Coyle, S. (2016). A meta-analytic review of the association between perceived social support and depression in childhood and adolescence. Psychological Bulletin, 142(10), 1017–1067. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000058.
Salzinger, S., Feldman, R. S., Rosario, M., & Ng-Mak, D. S. (2011). Role of parent and peer relationships and individual characteristics in middle school children's behavioral outcomes in the face of community violence. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(2), 395–407. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-7795.2010.00677.x.
Schwartz-Mette, R. A., & Rose, A. J. (2012). Co-rumination mediates contagion of internalizing symptoms within youths' friendships. Developmental Psychology, 48(5), 1355–1365. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027484.
Schweizer, K. (2010). Improving the interpretability of the variances of latent variables by uniform and factor-specific standardizations of loadings. Methodology: European Journal of Research Methods for the Behavioral and Social Sciences, 6(4), 152–159. https://doi.org/10.1027/1614-2241/a000017.
Siegel, S. J., & Alloy, L. B. (1990). Interpersonal perceptions and consequences of depressive-significant other relationships: A naturalistic study of college roommates. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 99, 361–373.
Spence, S. H., Donovan, C., & Brechman-Toussaint, M. (2000). The treatment of childhood social phobia: The effectiveness of a social skills training-based, cognitive-behavioural intervention, with and without parental involvement. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41(6), 713–726. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00659.
Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., Lushene, R., Vagg, P. R., & Jacobs, G. A. (1983). Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, CA. Consulting Psychologists Press.
Steiger, J. H. (1990). Structural model evaluation and modification: An interval estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 25, 173–180.
Su, S., Pettit, G. S., & Erath, S. A. (2016). Peer relations, parental social coaching, and young adolescent social anxiety. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 4289–4297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2015.11.007.
Sumter, S. R., Bokhorst, C. L., Steinberg, L., & Westenberg, P. M. (2009). The developmental pattern of resistance to peer influence in adolescence: Will the teenager ever be able to resist? Journal of Adolescence, 32(4), 1009–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2008.08.010.
Sylvester, C. E., Hyde, T. S., & Reichler, R. J. (1987). The diagnostic interview for children and personality inventory for children in studies of children at risk for anxiety disorders or depression. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 26(5), 668–675. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-198709000-00010.
Teetsel, R. N., Ginsburg, G. S., & Drake, K. L. (2014). Anxiety-promoting parenting behaviors: A comparison of anxious mothers and fathers. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 45(2), 133–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-013-0384-8.
Tillery, R., Disabatino, K., Parra, G. R., Buckholdt, K. E., & Jobe-Shields, L. (2014). Examination of consistency of adolescent and parent reports across several psychosocial constructs. Personal Relationships, 21(4), 599–611. https://doi.org/10.1111/pere.12051.
Tucker, L. R., & Lewis, C. (1973). A reliability coefficient for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika, 38(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291170.
Tull, M. T., Stipelman, B. A., Salters-Pedneault, K., & Gratz, K. L. (2009). An examination of recent non-clinical panic attacks, panic disorder, anxiety sensitivity, and emotion regulation difficulties in the prediction of generalized anxiety disorder in an analogue sample. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23(2), 275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2008.08.002.
van der Bruggen, C. O., Stams, G. J., & Bögels, S. M. (2008). Research review: The relation between child and parent anxiety and parental control: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(12), 1257–1269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01898.x.
van der Pol, L. D., Groeneveld, M. G., Endendijk, J. J., van Berkel, S. R., Hallers-Haalboom, E. T., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Mesman, J. (2016). Associations between fathers’ and mothers’ psychopathology symptoms, parental emotion socialization, and preschoolers’ social-emotional development. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(11), 3367–3380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-016-0490-x.
Warner, V., Mufson, L., & Weissman, M. M. (1995). Offspring at high and low risk for depression and anxiety: Mechanisms of psychiatric disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 34(6), 786–797. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199506000-00020.
Weinberg, A., & Klonsky, E. D. (2009). Measurement of emotion dysregulation in adolescents. Psychological Assessment, 21(4), 616–621. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016669.
Wichstrom, L. (1999). The emergence of gender differences in depressed mood during adolescence: The role of intensified gender socialization. Developmental Psychology, 35, 232–245.
Woodhead, E. L., Northrop, L., & Edelstein, B. (2016). Stress, social support, and burnout among long-term care nursing staff. Journal of Applied Gerontology, 35(1), 84–105. https://doi.org/10.1177/0733464814542465.
Wrzus, C., & Neyer, F. J. (2016). Co-development of personality and friendships across the lifespan: An empirical review on selection and socialization. European Psychologist, 21(4), 254–273. https://doi.org/10.1027/1016-9040/a000277.
Zhang, B., Yan, X., Zhao, F., & Yuan, F. (2015). The relationship between perceived stress and adolescent depression: The roles of social support and gender. Social Indicators Research, 123(2), 501–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0739-y.
Funding
This research was funded in part by a grant from the National Institute of Drug Abuse Grant R01DA018647.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Mazneen Havewala, Julia W. Felton, Carl W. Lejuez declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was conducted in compliance with all procedures approved by the University of Maryland Institutional Review Board. All protocols were consistent with national and international ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Experiment Participants
The University of Maryland Institutional Review Board approved this study. All the study procedures, including informed consent forms, followed the protocol previously approved by the ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Havewala, M., Felton, J.W. & Lejuez, C.W. Friendship Quality Moderates the Relation between Maternal Anxiety and Trajectories of Adolescent Internalizing Symptoms. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 41, 495–506 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-019-09742-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-019-09742-1