Abstract
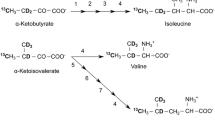
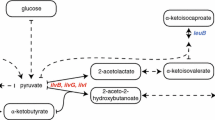
The production of stable isotope-labeled proteins is critical in structural analyses of large molecular weight proteins using NMR. Although prokaryotic expression systems using Escherichia coli have been widely used for this purpose, yeast strains have also been useful for the expression of functional eukaryotic proteins. Recently, we reported a cost-effective stable isotope-labeled protein expression using the hemiascomycete yeast Kluyveromyces lactis (K. lactis), which allow us to express exogenous proteins at costs comparable to prokaryotic expression systems. Here, we report the successful production of highly deuterated (>90 %) protein in the K. lactis system. We also examined the methyl-selective 1H, 13C-labeling of Ile, Leu, and Val residues using commonly used amino acid precursors. The efficiency of 1H- 13C-incorporation varied significantly based on the amino acid. Although a high level of 1H-13C-incorporation was observed for the Ile δ1 position, 1H, 13C-labeling rates of Val and Leu methyl groups were limited due to the mitochondrial localization of enzymes involved in amino acid biosynthesis and the lack of transporters for α-ketoisovalerate in the mitochondrial membrane. In line with this notion, the co-expression with branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferase in the cytosol significantly improved the incorporation rates of amino acid precursors. Although it would be less cost-effective, addition of 13C-labeled valine can circumvent problems associated with precursors and achieve high level 1H, 13C-labeling of Val and Leu. Taken together, the K. lactis system would be a good alternative for expressing large eukaryotic proteins that need deuteration and/or the methyl-selective 1H, 13C-labeling for the sensitive detection of NMR resonances.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colón M, Hernández F, López K, Quezada H, González J, López G, Aranda C, González A (2011) Saccharomyces cerevisiae Bat1 and Bat2 aminotransferases have functionally diverged from the ancestral-like Kluyveromyces lactis orthologous enzyme. PLoS One 6:e16099
Gardner KH, Zhang X, Gehring K, Kay LE (1998) Solution NMR studies of a 42 KDa Escherichia Coli maltose binding protein/β-cyclodextrin complex: chemical shift assignments and analysis. J Am Chem Soc 120:11738–11748
Gossert AD, Hinniger A, Gutmann S, Jahnke W, Strauss A, Fernández C (2011) A simple protocol for amino acid type selective isotope labeling in insect cells with improved yields and high reproducibility. J Biomol NMR 51:449–456
Gross JD, Gelev VM, Wagner G (2003) A sensitive and robust method for obtaining intermolecular NOEs between side chains in large protein complexes. J Biomol NMR 25:235–242
Harju S, Fedosyuk H, Peterson K (2004) Rapid isolation of yeast genomic DNA: bust n’ Grab. BMC Biotechnol 4:8
Kellis M, Birren BW, Lander ES (2004) Proof and evolutionary analysis of ancient genome duplication in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 428:617–624
Matsumoto M, Ueda T, Shimada I (2010) Theoretical analyses of the transferred cross-saturation method. J Magn Reson 205:114–124
Morgan WD, Kragt A, Feeney J (2000) Expression of deuterium-isotope-labelled protein in the yeast Pichia pastoris for NMR studies. J Biomol NMR 17:337–347
Ryan ED, Kohlhaw GB (1974) Subcellular localization of isoleucine-valine biosynthetic enzymes in yeast. J Bacteriol 120:631–637
Ryan ED, Tracy JW, Kohlhaw GB (1973) Subcellular localization of the leucine biosynthetic enzymes in yeast. J Bacteriol 116:222–225
Sastry M, Xu L, Georgiev IS, Bewley CA, Nabel GJ, Kwong PD (2011) Mammalian production of an isotopically enriched outer domain of the HIV-1 gp120 glycoprotein for NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 50:197–207
Shimada I, Ueda T, Matsumoto M, Sakakura M, Osawa M, Takeuchi K, Nishida N, Takahashi H (2009) Cross-saturation and transferred cross-saturation experiments. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 54:123–140
Solà A, Maaheimo H, Ylönen K, Ferrer P, Szyperski T (2004) Amino acid biosynthesis and metabolic flux profiling of Pichia pastoris. Eur J Biochem 271:2462–2470
Solà A, Jouhten P, Maaheimo H, Sánchez-Ferrando F, Szyperski T, Ferrer P (2007) Metabolic flux profiling of Pichia pastoris grown on glycerol/methanol mixtures in chemostat cultures at low and high dilution rates. Microbiology 153:281–290
Sugiki T, Shimada I, Takahashi H (2008) Stable isotope labeling of protein by Kluyveromyces lactis for NMR study. J Biomol NMR 42:159–162
Takahashi H, Nakanishi T, Kami K, Arata Y, Shimada I (2000) A novel NMR method for determining the interfaces of large protein-protein complexes. Nat Struct Biol 7:220–223
Tugarinov V, Hwang PM, Ollerenshaw JE, Kay LE (2003) Cross-correlated relaxation enhanced 1H − 13C NMR spectroscopy of methyl groups in very high molecular weight proteins and protein complexes. J Am Chem Soc 125:10420–10428
Tugarinov V, Sprangers R, Kay LE (2007) Probing side-chain dynamics in the proteasome by relaxation violated coherence transfer NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 129:1743–1750
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Japan New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) and the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI; to I.S.). Funding was also provided by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI; grant numbers 24370048 to H. T. and K. T., 24102524 to H. T. and 25121743 to K. T.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazawa-Onami, M., Takeuchi, K., Takano, T. et al. Perdeuteration and methyl-selective 1H, 13C-labeling by using a Kluyveromyces lactis expression system. J Biomol NMR 57, 297–304 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-013-9789-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-013-9789-8