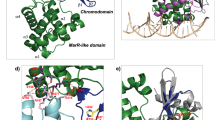
Abstract
The THAP (THanatos-Associated Protein) domain is an evolutionary conserved C2CH zinc-coordinating domain shared with a large family of cellular factors (THAP proteins). Many members of the THAP family act as transcription factors that control cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, angiogenesis, apoptosis and epigenetic gene silencing. They recognize specific DNA sequences in the promoters of target genes and subsequently recruit effector proteins. Recent structural and functional studies have allowed getting better insight into the nuclear and cellular functions of some THAP members and the molecular mechanisms by which they recognize DNA. The present article reviews recent advances in the knowledge of the THAP domains structures and their interaction with DNA, with a particular focus on NMR. It provides the solution structure of the THAP domain of THAP11, a recently characterized human THAP protein with important functions in transcription and cell growth in colon cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auguin D, Barthe P, Auge-Senegas MT, Stern MH, Noguchi M, Roumestand C (2004) Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the pleckstrin homology domain of the human protein kinase B (PKB/Akt). Interaction with inositol phosphates. J Biomol NMR 28(2):137–155
Balakrishnan MP, Cilenti L, Mashak Z, Popat P, Alnemri ES, Zervos AS (2009) THAP5 is a human cardiac-specific inhibitor of cell cycle that is cleaved by the proapoptotic Omi/HtrA2 protease during cell death. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297(2):H643–H653
Bessiere D, Lacroix C, Campagne S, Ecochard V, Guillet V, Mourey L, Lopez F, Czaplicki J, Demange P, Milon A, Girard JP, Gervais V (2008) Structure-function analysis of the THAP zinc finger of THAP1, a large C2CH DNA-binding module linked to Rb/E2F pathways. J Biol Chem 283(7):4352–4363
Bonetti M, Barzaghi C, Brancati F, Ferraris A, Bellacchio E, Giovanetti A, Ialongo T, Zorzi G, Piano C, Petracca M, Albanese A, Nardocci N, Dallapiccola B, Bentivoglio AR, Garavaglia B, Valente EM (2009) Mutation screening of the DYT6/THAP1 gene in Italy. Mov Disord Off J Mov Disord Soc 24(16):2424–2427
Bouvet P (2001) Determination of nucleic acid recognition sequences by SELEX. Methods Mol Biol 148:603–610
Bragg DC, Armata IA, Nery FC, Breakefield XO, Sharma N (2011) Molecular pathways in dystonia. Neurobiol Dis 42(2):136–147
Bressman SB, Raymond D, Fuchs T, Heiman GA, Ozelius LJ, Saunders-Pullman R (2009) Mutations in THAP1 (DYT6) in early-onset dystonia: a genetic screening study. Lancet Neurol 8(5):441–446
Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 54:905–921
Campagne S, Saurel O, Gervais V, Milon A (2010) Structural determinants of specific DNA-recognition by the THAP zinc finger. Nucleic Acids Res 38(10):3466–3476
Campagne S, Muller I, Milon A, Gervais V (2012) Towards the classification of DYT6 dystonia mutants in the DNA-binding domain of THAP1. Nucleic Acids Res 40(19):9927–9940
Cayrol C, Lacroix C, Mathe C, Ecochard V, Ceribelli M, Loreau E, Lazar V, Dessen P, Mantovani R, Aguilar L, Girard JP (2007) The THAP-zinc finger protein THAP1 regulates endothelial cell proliferation through modulation of pRB/E2F cell-cycle target genes. Blood 109(2):584–594
Clouaire T, Roussigne M, Ecochard V, Mathe C, Amalric F, Girard JP (2005) The THAP domain of THAP1 is a large C2CH module with zinc-dependent sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(19):6907–6912
Cornilescu G, Delaglio F, Bax A (1999) Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J Biomol NMR 13(3):289–302
De Souza SantosE, De Bessa SA, Netto MM, Nagai MA (2008) Silencing of LRRC49 and THAP10 genes by bidirectional promoter hypermethylation is a frequent event in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 33(1):25–31
Dejosez M, Krumenacker JS, Zitur LJ, Passeri M, Chu LF, Songyang Z, Thomson JA, Zwaka TP (2008) Ronin is essential for embryogenesis and the pluripotency of mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell 133(7):1162–1174
Dejosez M, Levine SS, Frampton GM, Whyte WA, Stratton SA, Barton MC, Gunaratne PH, Young RA, Zwaka TP (2010) Ronin/Hcf-1 binds to a hyperconserved enhancer element and regulates genes involved in the growth of embryonic stem cells. Genes Dev 24(14):1479–1484
Djarmati A, Schneider SA, Lohmann K, Winkler S, Pawlack H, Hagenah J, Bruggemann N, Zittel S, Fuchs T, Rakovic A, Schmidt A, Jabusch HC, Wilcox R, Kostic VS, Siebner H, Altenmuller E, Munchau A, Ozelius LJ, Klein C (2009) Mutations in THAP1 (DYT6) and generalised dystonia with prominent spasmodic dysphonia: a genetic screening study. Lancet Neurol 8(5):447–452
Dosset P, Hus JC, Blackledge M, Marion D (2000) Efficient analysis of macromolecular rotational diffusion from heteronuclear relaxation data. J Biomol NMR 16(1):23–28
Fuchs T, Gavarini S, Saunders-Pullman R, Raymond D, Ehrlich ME, Bressman SB, Ozelius LJ (2009) Mutations in the THAP1 gene are responsible for DYT6 primary torsion dystonia. Nat Genet 41(3):286–288
Gavarini S, Cayrol C, Fuchs T, Lyons N, Ehrlich ME, Girard JP, Ozelius LJ (2010) Direct interaction between causative genes of DYT1 and DYT6 primary dystonia. Ann Neurol 68(4):549–553
Johnson BA (2004) Using NMR View to visualize and analyze the NMR spectra of macromolecules. Methods Mol Biol 278:313–352
Kaiser FJ, Osmanoric A, Rakovic A, Erogullari A, Uflacker N, Braunholz D, Lohnau T, Orolicki S, Albrecht M, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Klein C, Lohmann K (2010) The dystonia gene DYT1 is repressed by the transcription factor THAP1 (DYT6). Ann Neurol 68(4):554–559
Kalodimos CG, Biris N, Bonvin AM, Levandoski MM, Guennuegues M, Boelens R, Kaptein R (2004) Structure and flexibility adaptation in nonspecific and specific protein-DNA complexes. Science 305(5682):386–389
Keller RLJ (2004) The computer aided resonance assignment tutorial, 1st edn. Cantina Verlag, Switzerland
Laity JH, Lee BM, Wright PE (2001) Zinc finger proteins: new insights into structural and functional diversity. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11(1):39–46
Laskowski RA, Rullmannn JA, MacArthur MW, Kaptein R, Thornton JM (1996) AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J Biomol NMR 8(4):477–486
Layton CJ, Hellinga HW (2011) Quantitation of protein-protein interactions by thermal stability shift analysis. Protein Sci. doi:10.1002/pro.674
Lian WX, Yin RH, Kong XZ, Zhang T, Huang XH, Zheng WW, Yang Y, Zhan YQ, Xu WX, Yu M, Ge CH, Guo JT, Li CY, Yang XM (2012) THAP11, a novel binding protein of PCBP1, negatively regulates CD44 alternative splicing and cell invasion in a human hepatoma cell line. FEBS Lett 586(10):1431–1438
Liew CK, Crossley M, Mackay JP, Nicholas HR (2007) Solution structure of the THAP domain from Caenorhabditis elegans C-terminal binding protein (CtBP). J Mol Biol 366(2):382–390
Lohmann K, Uflacker N, Erogullari A, Lohnau T, Winkler S, Dendorfer A, Schneider SA, Osmanovic A, Svetel M, Ferbert A, Zittel S, Kuhn AA, Schmidt A, Altenmuller E, Munchau A, Kamm C, Wittstock M, Kupsch A, Moro E, Volkmann J, Kostic V, Kaiser FJ, Klein C, Bruggemann N (2012) Identification and functional analysis of novel THAP1 mutations. Eur J Hum Genet EJHG 20(2):171–175
Macfarlan T, Kutney S, Altman B, Montross R, Yu J, Chakravarti D (2005) Human THAP7 is a chromatin-associated, histone tail-binding protein that represses transcription via recruitment of HDAC3 and nuclear hormone receptor corepressor. J Biol Chem 280(8):7346–7358
Mazars R, Gonzalez-de-Peredo A, Cayrol C, Lavigne AC, Vogel JL, Ortega N, Lacroix C, Gautier V, Huet G, Ray A, Monsarrat B, Kristie TM, Girard JP (2010) The THAP-zinc finger protein THAP1 associates with coactivator HCF-1 and O-GlcNAc transferase: a link between DYT6 and DYT3 dystonias. J Biol Chem 285(18):13364–13371
Muller U (2009) The monogenic primary dystonias. Brain 132(Pt 8):2005–2025
Nakamura S, Yokota D, Tan L, Nagata Y, Takemura T, Hirano I, Shigeno K, Shibata K, Fujisawa S, Ohnishi K (2012) Down-regulation of Thanatos-associated protein 11 by BCR-ABL promotes CML cell proliferation through c-Myc expression. Int J Cancer J Int Du Cancer 130(5):1046–1059
Parker JB, Palchaudhuri S, Yin H, Wei J, Chakravarti D (2012) A transcriptional regulatory role of the THAP11-HCF-1 complex in colon cancer cell function. Mol Cell Biol 32(9):1654–1670
Ponstingl H, Otting G (1998) Rapid measurement of scalar three-bond 1HN–1H alpha spin coupling constants in 15 N-labelled proteins. J Biomol NMR 12(2):319–324
Privalov PL, Dragan AI, Crane-Robinson C, Breslauer KJ, Remeta DP, Minetti CA (2007) What drives proteins into the major or minor grooves of DNA? J Mol Biol 365(1):1–9
Privalov PL, Dragan AI, Crane-Robinson C (2011) Interpreting protein/DNA interactions: distinguishing specific from non-specific and electrostatic from non-electrostatic components. Nucleic Acids Res 39(7):2483–2491
Roussigne M, Cayrol C, Clouaire T, Amalric F, Girard JP (2003a) THAP1 is a nuclear proapoptotic factor that links prostate-apoptosis-response-4 (Par-4) to PML nuclear bodies. Oncogene 22(16):2432–2442
Roussigne M, Kossida S, Lavigne AC, Clouaire T, Ecochard V, Glories A, Amalric F, Girard JP (2003b) The THAP domain: a novel protein motif with similarity to the DNA-binding domain of P element transposase. Trends Biochem Sci 28(2):66–69
Sabogal A, Lyubimov AY, Corn JE, Berger JM, Rio DC (2010) THAP proteins target specific DNA sites through bipartite recognition of adjacent major and minor grooves. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17(1):117–123
Sattler M, Schleucher J, Griesinger C (1999) Heteronuclear multidimensional NMR experiments for the structure determination of proteins in solution employing pulsed field gradients. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 34(2):93–158
Sengel C, Gavarini S, Sharma N, Ozelius LJ, Bragg DC (2011) Dimerization of the DYT6 dystonia protein, THAP1, requires residues within the coiled-coil domain. J Neurochem 118(6):1087–1100
Sohn AS, Glockle N, Doetzer AD, Deuschl G, Felbor U, Topka HR, Schols L, Riess O, Bauer P, Muller U, Grundmann K (2010) Prevalence of THAP1 sequence variants in German patients with primary dystonia. Mov Disord Off J Mov Disord Soc 25(12):1982–1986
Song W, Chen Y, Huang R, Chen K, Pan P, Yang Y, Shang HF (2011) Novel THAP1 gene mutations in patients with primary dystonia from Southwest China. J Neurol Sci 309(1–2):63–67
Studier FW (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):207–234
Wagner G, Braun W, Havel TF, Schaumann T, Go N, Wuthrich K (1987) Protein structures in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. The polypeptide fold of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor determined using two different algorithms, DISGEO and DISMAN. J Mol Biol 196(3):611–639
Wuthrich K (1986) NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Wiley, Hoboken
Xiao J (2010) Novel human pathological mutations. Gene symbol: THAP1. Disease: dystonia 6. Hum Genet 127(4):469
Zhu CY, Li CY, Li Y, Zhan YQ, Li YH, Xu CW, Xu WX, Sun HB, Yang XM (2009) Cell growth suppression by thanatos-associated protein 11(THAP11) is mediated by transcriptional downregulation of c-Myc. Cell Death Differ 16(3):395–405
Acknowledgments
EU structural funds and the Région Midi-Pyrénées are acknowledged for funding the NMR equipment. Microcalorimetry and thermal shift assays equipments have been acquired by the IBiSA Integrated Screening Platform of Toulouse (PICT, IPBS, CNRS—Université de Toulouse). Access via TGIR national facility for high field NMR was provided in ICSN, CNRS, Gif/Yvette, where 950 MHz NMR spectra were recorded. J.P. Girard is acknowledged for initiating this work at the IPBS and for continuous support and advices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10858_2012_9699_MOESM1_ESM.eps
Relaxation parameters for the THAP domain of THAP11. The values of the 15N longitudinal and transversal relaxation rates R1, R2 as well as the S2 order parameter for individual residues are shown as a function of residue number in the sequence. (EPS 2560 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gervais, V., Campagne, S., Durand, J. et al. NMR studies of a new family of DNA binding proteins: the THAP proteins. J Biomol NMR 56, 3–15 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-012-9699-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-012-9699-1