Abstract
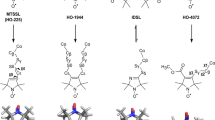
The measurement of 1H transverse paramagnetic relaxation enhancement (PRE) has been used in biomolecular systems to determine long-range distance restraints and to visualize sparsely-populated transient states. The intrinsic flexibility of most nitroxide and metal-chelating paramagnetic spin-labels, however, complicates the quantitative interpretation of PREs due to delocalization of the paramagnetic center. Here, we present a novel, disulfide-linked nitroxide spin label, R1p, as an alternative to these flexible labels for PRE studies. When introduced at solvent-exposed α-helical positions in two model proteins, calmodulin (CaM) and T4 lysozyme (T4L), EPR measurements show that the R1p side chain exhibits dramatically reduced internal motion compared to the commonly used R1 spin label (generated by reacting cysteine with the spin labeling compound often referred to as MTSL). Further, only a single nitroxide position is necessary to account for the PREs arising from CaM S17R1p, while an ensemble comprising multiple conformations is necessary for those observed for CaM S17R1. Together, these observations suggest that the nitroxide adopts a single, fixed position when R1p is placed at solvent-exposed α-helical positions, greatly simplifying the interpretation of PRE data by removing the need to account for the intrinsic flexibility of the spin label.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenbach C, Oh KJ, Trabanino RJ, Hideg K, Hubbell WL (2001) Estimation of inter-residue distances in spin labeled proteins at physiological temperatures: experimental strategies and practical limitations. Biochemistry 40:15471–15482
Berliner LJ, Grünwald J, Hankovszky HO, Hideg K (1982) A novel reversible thiol-specific spin label: papain active site labeling and inhibition. Anal Biochem 119:450–455
Bermejo GA, Strub MP, Ho C, Tjandra N (2009) Determination of the solution-bound conformation of an amino acid binding protein by NMR paramagnetic relaxation enhancement: use of a single flexible paramagnetic probe with improved estimation of its sampling space. J Am Chem Soc 131:9532–9537
Bridges MD, Hideg K, Hubbell WL (2010) Resolving conformational and rotameric exchange in spin-labeled proteins using saturation recovery EPR. Appl Magn Reson 37:363–390
Budil DE, Lee S, Saxena S, Freed JH (1996) Nonlinear-least-squares analysis of slow-motion EPR spectra in one and two dimensions using a modified Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. J Magn Reson Ser A 120:155–189
Chang SL, Szabo A, Tjandra N (2003) Temperature dependence of domain motions of calmodulin probed by NMR relaxation at multiple fields. J Am Chem Soc 125:11379–11384
Chou JJ, Case DA, Bax A (2003) Insights into the mobility of methyl-bearing side chains in proteins from 3JCC and 3JCN couplings. J Am Chem Soc 125:8959–8966
Clore GM (2008) Visualizing lowly-populated regions of the free energy landscape of macromolecular complexes by paramagnetic relaxation enhancement. Mol Biosyst 4:1058–1069
Clore GM (2011) Exploring sparsely populated states of macromolecules by diamagnetic and paramagnetic NMR relaxation. Protein Sci 20:229–246
Clore GM, Gronenborn AM (1994) Multidimensional heteronuclear nuclear magnetic resonance of proteins. Methods Enzymol 239:349–363
Clore GM, Iwahara J (2009) Theory, practice, and applications of paramagnetic relaxation enhancement for the characterization of transient low-population states of biological macromolecules and their complexes. Chem Rev 109:4108–4139
Clore GM, Kuszewski J (2002) χ1 rotamer populations and angles of mobile surface side chains are accurately predicted by a torsion angle database potential of mean force. J Am Chem Soc 124:2866–2867
Columbus L (2001) Investigating backbone and side chain dynamics of α-helices in the nanosecond regime with site-directed spin labeling. PhD Dissertation, UCLA, pp 51–58
Columbus L, Kalai T, Jeko J, Hideg K, Hubbell WL (2001) Molecular motion of spin labeled side chains in α-helices: analysis by variation of side chain structure. Biochemistry 40:3828–3846
Crisma M, Deschamps JR, George C, Flippen-Anderson JL, Kaptein B, Broxterman QB, Moretto A, Oancea S, Jost M, Formaggio F et al (2005) A topographically and conformationally constrained, spin-labeled, α-amino acid: crystallographic characterization in peptides. J Pept Res 65:564–579
Fawzi NL, Doucleff M, Suh JY, Clore GM (2010) Mechanistic details of a protein–protein association pathway revealed by paramagnetic relaxation enhancement titration measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:1379–1384
Fleissner MR (2007) X-ray structures of nitroxide side chains in proteins: a basis for interpreting distance measurements and dynamic studies by electron paramagnetic resonance. PhD Thesis, UCLA
Fleissner MR, Cascio D, Hubbell WL (2009) Structural origin of weakly ordered nitroxide motion in spin-labeled proteins. Protein Sci 18:893–908
Flippen-Anderson JL, George C, Valle G, Valente E, Bianco A, Formaggio F, Crisma M, Toniolo C (1996) Crystallographic characterization of geometry and conformation of TOAC, a nitroxide spin-labelled Cα,α-disubstituted glycine, in simple derivatives and model peptides. Int J Pept Protein Res 47:231–238
Griffith OH, Jost PC (1976) Lipid spin labels in biological membranes. In: Berliner LJ (ed) Spin labeling: theory and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 454–523
Guo ZF, Cascio D, Hideg K, Kalai T, Hubbell WL (2007) Structural determinants of nitroxide motion in spin-labeled proteins: tertiary contact and solvent-inaccessible sites in helix G of T4 lysozyme. Protein Sci 16:1069–1086
Guo ZF, Cascio D, Hideg K, Hubbell WL (2008) Structural determinants of nitroxide motion in spin-labeled proteins: solvent-exposed sites in helix B of T4 lysozyme. Protein Sci 17:228–239
Haussinger D, Huang JR, Grzesiek S (2009) DOTA-M8: an extremely rigid, high-affinity lanthanide chelating tag for PCS NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 131:14761–14767
Hu K, Doucleff M, Clore GM (2009) Using multiple quantum coherence to increase the 15N resolution in a three-dimensional TROSY HNCO experiment for accurate PRE and RDC measurements. J Magn Reson 200:173–177
Hubbell WL, McConnell HM (1971) Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc 93:314–326
Hubbell WL, Cafiso DS, Altenbach C (2000) Identifying conformational changes with site-directed spin labeling. Nat Struct Biol 7:735–739
Ikura M, Clore GM, Gronenborn AM, Zhu G, Klee CB, Bax A (1992) Solution structure of a calmodulin-target peptide complex by multidimensional NMR. Science 256:632–638
Iwahara J, Clore GM (2006) Detecting transient intermediates in macromolecular binding by paramagnetic NMR. Nature 440:1227–1230
Iwahara J, Schwieters CD, Clore GM (2004a) Characterization of nonspecific protein-DNA interactions by 1H paramagnetic relaxation enhancement. J Am Chem Soc 126:12800–12808
Iwahara J, Schwieters CD, Clore GM (2004b) Ensemble approach for NMR structure refinement against 1H paramagnetic relaxation enhancement data arising from a flexible paramagnetic group attached to a macromolecule. J Am Chem Soc 126:5879–5896
Iwahara J, Zweckstetter M, Clore GM (2006) NMR structural and kinetic characterization of a homeodomain diffusing and hopping on nonspecific DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15062–15067
Iwahara J, Tang C, Clore GM (2007) Practical aspects of 1H transverse paramagnetic relaxation enhancement measurements on macromolecules. J Magn Reson 184:185–195
Kalai T, Balog M, Jeko J, Hideg K (1998) 3-substituted 4-bromo-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-1-yloxyl radicals as versatile synthons for synthesis of new paramagnetic heterocycles. Synthesis-Stuttgart, pp 1476–1482
Keizers PHJ, Ubbink M (2011) Paramagnetic tagging for protein structure and dynamics analysis. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 58:88–96
Keizers PHJ, Desreux JF, Overhand M, Ubbink M (2007) Increased paramagnetic effect of a lanthanide protein probe by two-point attachment. J Am Chem Soc 129:9292–9293
Kusnetzow AK, Altenbach C, Hubbell WL (2006) Conformational states and dynamics of rhodopsin in micelles and bilayers. Biochemistry 45:5538–5550
Lindfors HE, Venkata BS, Drijfhout JW, Ubbink M (2011) Linker length dependent binding of a focal adhesion kinase derived peptide to the src SH3-SH2 domains. FEBS Lett 585:601–605
Mchaourab HS, Lietzow MA, Hideg K, Hubbell WL (1996) Motion of spin-labeled side chains in T4 lysozyme, correlation with protein structure and dynamics. Biochemistry 35:7692–7704
Meador WE, Means AR, Quiocho FA (1992) Target enzyme recognition by calmodulin—2.4Å structure of a calmodulin-peptide complex. Science 257:1251–1255
Otting G (2010) Protein NMR using paramagnetic ions. Ann Rev Biophys 39:387–405
Schwieters CD, Kuszewski JJ, Tjandra N, Clore GM (2003) The Xplor-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package. J Magn Reson 160:65–73
Schwieters CD, Kuszewski JJ, Clore GM (2006) Using Xplor-NIH for NMR molecular structure determination. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 48:47–62
Su XC, Man B, Beeren S, Liang H, Simonsen S, Schmitz C, Huber T, Messerle BA, Otting G (2008) A dipicolinic acid tag for rigid lanthanide tagging of proteins and paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 130:10486–10847
Takayama Y, Clore GM (2011) Intra- and intermolecular translocation of the bi-domain transcription factor Oct1 characterized by liquid crystal and paramagnetic NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:E169–E176
Tang C, Iwahara J, Clore GM (2006) Visualization of transient encounter complexes in protein–protein association. Nature 444:383–386
Tang C, Schwieters CD, Clore GM (2007) Open-to-closed transition in apo maltose-binding protein observed by paramagnetic NMR. Nature 449:1078–1082
Tang C, Louis JM, Aniana A, Suh JY, Clore GM (2008) Visualizing transient events in amino-terminal autoprocessing of HIV-1 protease. Nature 455:693–696
Timofeev VP, Tsetlin VI (1983) Analysis of mobility of protein side-chains by spin label technique. Biophys Struct Mech 10:93–108
Todd AP, Cong J, Levinthal F, Levinthal C, Hubbell WL (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis of colicin E1 provides specific attachment sites for spin labels whose spectra are sensitive to local conformation. Proteins 6:294–305
Volkov AN, Worrall JAR, Holtzmann E, Ubbink M (2006) Solution structure and dynamics of the complex between cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase determined by paramagnetic NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18945–18950
Volkov AN, Ubbink M, van Nuland NAJ (2010) Mapping the encounter state of a transient protein complex by PRE NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 48:225–236
Warshaviak DT, Serbulea L, Houk KN, Hubbell WL (2011) Conformational analysis of a nitroxide side chain in an a-helix with density functional theory. J Phys Chem B 115:397–405
Zhang ZW, Fleissner MR, Tipikin DS, Liang ZC, Moscicki JK, Earle KA, Hubbell WL, Freed JH (2010) Multifrequency electron spin resonance study of the dynamics of spin labeled T4 lysozyme. J Phys Chem B 114:5503–5521
Acknowledgments
We thank Vincenzo Venditti and Mengli Cai for helpful suggestions, Dusty Baber and Jinfa Ying for assistance with NMR spectrometers, and Evan Brooks and Mária Balog for expert technical assistance. This work was in part supported by funds from the Intramural Program of the NIH, NIDDK and the Intramural AIDS Targeted Antiviral Program of the Office of the Director of the NIH (to G.M.C.), NIH grants R01EY05216 (to W.L.H.), and the Jules Stein Professorship Endowment (to W.L.H.). The synthesis of new spin label reagents was supported by Hungarian National Research Funds (OTKA K81123).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Nicolas L. Fawzi, Mark R. Fleissner and Nicholas J. Anthis contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fawzi, N.L., Fleissner, M.R., Anthis, N.J. et al. A rigid disulfide-linked nitroxide side chain simplifies the quantitative analysis of PRE data. J Biomol NMR 51, 105 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-011-9545-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-011-9545-x