Abstract
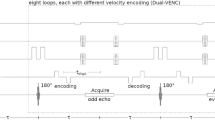
Thermal convection and high intensity solvent resonances can significantly hamper diffusion estimates in pulsed gradient spin-echo nuclear magnetic resonance diffusion experiments on biomolecule samples. To overcome these two problems, a new double functional NMR diffusion sequence, double echo PGSTE-WATERGATE, is presented. The new sequence provides excellent convection compensation and solvent suppression (with a suppression factor in excess of at least 105 in a single scan) in biomolecular NMR diffusion experiments. Due to its stimulated echo nature, the new sequence is much less susceptible to spin–spin relaxation than Hahn spin-echo based sequences. Furthermore, the new sequence is not susceptible to spin diffusion due to the application of bipolar pulsed gradients. The new sequence is also much easier to set up compared to previously developed stimulated echo based convection compensation and solvent suppression sequence. The utility of the new sequence is demonstrated on an aqueous lysozyme sample.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boden N, Corne SA, Halford-Maw P, Fogarty D, Jolley KW (1992) Sample cell for high-precision temperature-dependence NMR experiments. J Magn Reson 98:92–108
Chou JJ, Baber JL, Bax A (2004) Characterization of phospholipid mixed micelles by translational diffusion. J Biomol NMR 29:299–308
Dvinskikh SV, Furó I (2000) Cross-relaxation effects in stimulated-echo-type PGSE NMR experiments by bipolar and monopolar gradient pulses. J Magn Reson 146:283–289
Esturau N, Sánchez-Ferrando F, Gavin JA, Roumestand C, Delsuc M-A, Parella T (2001) The use of sample rotation for minimizing convection effects in self-diffusion NMR measurements. J Magn Reson 153:48–55
Goux WJ, Verkruyse LA, Salter SJ (1990) The impact of Rayleigh-Benard convection on NMR pulsed-field-gradient diffusion measurements. J Magn Reson 88:609–614
Hayamizu K, Price WS (2004) A new type of sample tube for reducing convection effects in PGSE-NMR measurements of self-diffusion coefficients of liquid samples. J Magn Reson 167:328–333
He Q, Wei Z (2001) Convection compensated electrophoretic NMR. J Magn Reson 150:126–131
Hedin N, Furó I (1998) Temperature imaging by 1H NMR and suppression of convection in NMR probes. J Magn Reson 131:126–130
Hedin N, Yu TY, Furó I (2000) Growth of C12E8 micelles with increasing temperature. A convection-compensated PGSE NMR study. Langmuir 16:7548–7550
Holz M, Weingärtner H (1991) Calibration in accurate spin-echo self-diffusion measurements using proton and less-common nuclei. J Magn Reson 92:115–125
Holz M, Mao X-A, Seiferling D, Sacco A (1996) Experimental study of dynamic isotope effects in molecular liquids: detection of translation-rotation coupling. J Chem Phys 104:669–679
Jerschow A (2000) Thermal convection currents in NMR: flow profiles and implications for coherence pathway selection. J Magn Reson 145:125–131
Jerschow A, Müller N (1997) Suppression of convection artifacts in stimulated-echo diffusion experiments. Double-stimulated-echo experiments. J Magn Reson 125:372–375
Jerschow A, Müller N (1998) Convection compensation in gradient enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 132:13–18
Kato H, Saito T, Nabeshima M, Shimada K, Kinugasa S (2006) Assessment of diffusion coefficients of general solvents by PFG-NMR: investigation of the sources error. J Magn Reson 180:266–273
Liu M, Mao X-A, Ye C, Huang H, Nicholson JK, Lindon JC (1998) Improved WATERGATE pulse sequences for solvent suppression in NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 132:125–129
Loening NM, Keeler J (1999) Measurement of convection and temperature profiles in liquid samples. J Magn Reson 139:334–341
Lounila J, Oikarinen K, Ingman P, Jokisaari J (1996) Effects of thermal convection on NMR and their elimination by sample rotation. J Magn Reson 118:50–54
Mao X-A, Kohlmann O (2001) Diffusion-broadened velocity spectra of convection in variable-temperature BP-LED experiments. J Magn Reson 150:35–38
Martínez-Viviente E, Pregosin PS (2003) Low temperature 1H-, 19F-, and 31P-PGSE diffusion measurements. Applications to cationic alcohol complexes. Helv Chim Acta 86:2364–2378
Momot KI, Kuchel PW (2004) Convection-compensating PGSE experiment incorporating excitation-sculpting water suppression (CONVEX). J Magn Reson 169:92–101
Momot KI, Kuchel PW (2005) Convection-compensating diffusion experiments with phase-sensitive double-quantum filtering. J Magn Reson 174:229–236
Nilsson M, Morris GA (2005) Improving pulse sequences for 3D DOSY: convection compensation. J Magn Reson 177:203–211
Ogg RJ, Kingsley PB, Taylor JS (1994) WET, a T1- and B1-insensitive water-suppression method for in vivo localized 1H NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 104B:1–10
Ortner K, Sivanandam VN, Buchberger W, Müller N (2007) Analysis of glycans in glycoproteins by diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 388:173–177
Saarinen TR, Johnson CS Jr (1988) Imaging of transient magnetization gratings in NMR. Analogies with laser-induced gratings and applications to diffusion and flow. J Magn Reson 78:257–270
Simorellis AK, Flynn PF (2004) A PFG NMR experiment for translational diffusion measurements in low-viscosity solvents containing multiple resonances. J Magn Reson 170:322–328
Smallcombe SH, Patt SL, Keifer PA (1995) WET solvent suppression and its applications to LC NMR and high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 117A:295–303
Sørland GH, Seland JG, Krane J, Anthonsen HW (2000) Improved convection compensating pulsed field gradient spin-echo and stimulated-echo methods. J Magn Reson 142:323–325
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:288–292
Stilbs P (1987) Fourier transform pulsed-gradient spin-echo studies of molecular diffusion. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 19:1–45
Zhang X, Li C-G, Ye C-H, Liu M-L (2001) Determination of molecular self-diffusion coefficient using multiple spin-echo NMR spectroscopy with removal of convection and background gradient artifacts. Anal Chem 73:3528–3534
Zheng G, Stait-Gardner T, Anil Kumar PG, Torres AM, Price WS (2008a) PGSTE-WATERGATE: an STE-based PGSE NMR sequence with excellent solvent suppression. J Magn Reson 191:159–163
Zheng G, Torres AM, Price WS (2008b) Solvent suppression using phase-modulated binomial-like sequences and applications to diffusion measurements. J Magn Reson 194:108–114
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by a NSW BioFirst Award from the NSW Ministry for Science & Medical Research (W. S. P.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, G., Price, W.S. Simultaneous convection compensation and solvent suppression in biomolecular NMR diffusion experiments. J Biomol NMR 45, 295–299 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9367-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9367-2