Abstract
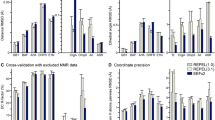
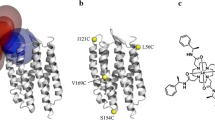
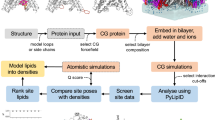
To fully describe the fold space and ultimately the biological function of membrane proteins, it is necessary to determine the specific interactions of the protein with the membrane. This property of membrane proteins that we refer to as structural topology cannot be resolved using X-ray crystallography or solution NMR alone. In this article, we incorporate into XPLOR-NIH a hybrid objective function for membrane protein structure determination that utilizes solution and solid-state NMR restraints, simultaneously defining structure, topology, and depth of insertion. Distance and angular restraints obtained from solution NMR of membrane proteins solubilized in detergent micelles are combined with backbone orientational restraints (chemical shift anisotropy and dipolar couplings) derived from solid-state NMR in aligned lipid bilayers. In addition, a supplementary knowledge-based potential, E z (insertion depth potential), is used to ensure the correct positioning of secondary structural elements with respect to a virtual membrane. The hybrid objective function is minimized using a simulated annealing protocol implemented into XPLOR-NIH software for general use.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bay DC, Rommens KL, Turner RJ (2008) Small multidrug resistance proteins: a multidrug transporter family that continues to grow. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:1814–1838
Bertram R, Quine JR, Chapman MS, Cross TA (2000) Atomic refinement using orientational restraints from solid-state NMR. J Magn Reson 147:9–16
Buffy JJ, Hong T, Yamaguchi S, Waring AJ, Lehrer RI, Hong M (2003) Solid-state NMR investigation of the depth of insertion of protegrin-1 in lipid bilayers using paramagnetic Mn2+. Biophys J 85:2363–2373
Buffy JJ, Traaseth NJ, Mascioni A, Gor’kov PL, Chekmenev EY, Brey WW, Veglia G (2006) Two-dimensional solid-state NMR reveals two topologies of sarcolipin in oriented lipid bilayers. Biochemistry 45:10939–10946
Calhoun JR, Liu W, Spiegel K, Dal Peraro M, Klein ML, Valentine KG, Wand AJ, DeGrado WF (2008) Solution NMR structure of a designed metalloprotein and complementary molecular dynamics refinement. Structure 16:210–215
Chou JJ, Kaufman JD, Stahl SJ, Wingfield PT, Bax A (2002) Micelle-induced curvature in a water-insoluble HIV-1 env peptide revealed by NMR dipolar coupling measurement in stretched polyacrylamide gel. J Am Chem Soc 124:2450–2451
Cornilescu G, Delaglio F, Bax A (1999) Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J Biomol NMR 13:289–302
Cowieson NP, Kobe B, Martin JL (2008) United we stand: combining structural methods. Curr Opin Struct Biol 18:617–622
De Angelis AA, Howell SC, Nevzorov AA, Opella SJ (2006) Structure determination of a membrane protein with two trans-membrane helices in aligned phospholipid bicelles by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 128:12256–12267
Dominguez C, Boelens R, Bonvin AM (2003) HADDOCK: a protein–protein docking approach based on biochemical or biophysical information. J Am Chem Soc 125:1731–1737
Durr UH, Yamamoto K, Im SC, Waskell L, Ramamoorthy A (2007) Solid-state NMR reveals structural and dynamical properties of a membrane-anchored electron-carrier protein, cytochrome b5. J Am Chem Soc 129:6670–6671
Franzin CM, Teriete P, Marassi FM (2007) Structural similarity of a membrane protein in micelles and membranes. J Am Chem Soc 129:8078–8079
Gabel F, Simon B, Sattler M (2006) A target function for quaternary structural refinement from small angle scattering and NMR orientational restraints. Eur Biophys J 35:313–327
Gabel F, Simon B, Nilges M, Petoukhov M, Svergun D, Sattler M (2008) A structure refinement protocol combining NMR residual dipolar couplings and small angle scattering restraints. J Biomol NMR 41:199–208
Gong XM, Franzin CM, Thai K, Yu J, Marassi FM (2007) Nuclear magnetic resonance structural studies of membrane proteins in micelles and bilayers. Methods Mol Biol 400:515–529
Hallock KJ, Henzler Wildman K, Lee DK, Ramamoorthy A (2002) An innovative procedure using a sublimable solid to align lipid bilayers for solid-state NMR studies. Biophys J 82:2499–2503
Hong M (2006) Oligomeric structure, dynamics, and orientation of membrane proteins from solid-state NMR. Structure 14:1731–1740
Hu J, Asbury T, Achuthan S, Li C, Bertram R, Quine JR, Fu R, Cross TA (2007) Backbone structure of the amantadine-blocked trans-membrane domain M2 proton channel from influenza A virus. Biophys J 92:4335–4343
Im W, Brooks CL 3rd (2004) De novo folding of membrane proteins: an exploration of the structure and NMR properties of the fd coat protein. J Mol Biol 337:513–519
Ketchem RR, Lee KC, Huo S, Cross TA (1996) Macromolecular structural elucidation with solid-state NMR-derived orientational constraints. J Biomol NMR 8:1–14
Ketchem R, Roux B, Cross T (1997) High-resolution polypeptide structure in a lamellar phase lipid environment from solid state NMR derived orientational constraints. Structure 5:1655–1669
Kim S, Quine JR, Cross TA (2001) Complete cross-validation and R-factor calculation of a solid-state NMR derived structure. J Am Chem Soc 123:7292–7298
Kordel J, Pearlman DA, Chazin WJ (1997) Protein solution structure calculations in solution: solvated molecular dynamics refinement of calbindin D9 k. J Biomol NMR 10:231–243
Kuszewski J, Gronenborn AM, Clore GM (1996) Improving the quality of NMR and crystallographic protein structures by means of a conformational database potential derived from structure databases. Protein Sci 5:1067–1080
Kuszewski J, Gronenborn AM, Clore GM (1997) Improvements and extensions in the conformational database potential for the refinement of NMR and X-ray structures of proteins and nucleic acids. J Magn Reson 125:171–177
Lee J, Chen J, Brooks CL III, Im W (2008) Application of solid-state NMR restraint potentials in membrane protein modeling. J Magn Reson 193:68–76
Linge JP, Williams MA, Spronk CA, Bonvin AM, Nilges M (2003) Refinement of protein structures in explicit solvent. Proteins 50:496–506
Mackenzie KR (2006) Folding and stability of alpha-helical integral membrane proteins. Chem Rev 106:1931–1977
Mahalakshmi R, Marassi FM (2008) Orientation of the Escherichia coli outer membrane protein OmpX in phospholipid bilayer membranes determined by solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 47(25):6531–6538
Mani R, Tang M, Wu X, Buffy JJ, Waring AJ, Sherman MA, Hong M (2006) Membrane-bound dimer structure of a beta-hairpin antimicrobial peptide from rotational-echo double-resonance solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 45:8341–8349
Marassi FM, Opella SJ (2002) Using pisa pies to resolve ambiguities in angular constraints from PISEMA spectra of aligned proteins. J Biomol NMR 23:239–242
Mascioni A, Karim C, Zamoon J, Thomas DD, Veglia G (2002) Solid-state NMR and rigid body molecular dynamics to determine domain orientations of monomeric phospholamban. J Am Chem Soc 124:9392–9393
Metcalfe EE, Zamoon J, Thomas DD, Veglia G (2004) (1)H/(15)N heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy shows four dynamic domains for phospholamban reconstituted in dodecylphosphocholine micelles. Biophys J 87:1205–1214
Metcalfe EE, Traaseth NJ, Veglia G (2005) Serine 16 phosphorylation induces an order-to-disorder transition in monomeric phospholamban. Biochemistry 44:4386–4396
Moore DT, Berger BW, DeGrado WF (2008) Protein–protein interactions in the membrane: sequence, structural, and biological motifs. Structure 16:991–1001
Nevzorov AA, Opella SJ (2003) Structural fitting of PISEMA spectra of aligned proteins. J Magn Reson 160:33–39
Nilges M, Gronenborn AM, Brunger AT, Clore GM (1988) Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins by simulated annealing with interproton distance restraints. Application to crambin, potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor and barley serine proteinase inhibitor 2. Protein Eng 2:27–38
Opella SJ, Marassi FM (2004) Structure determination of membrane proteins by NMR spectroscopy. Chem Rev 104:3587–3606
Page RC, Li C, Hu J, Gao FP, Cross TA (2007) Lipid bilayers: an essential environment for the understanding of membrane proteins. Magn Reson Chem 45:S2–S11
Page RC, Kim S, Cross TA (2008) Transmembrane helix uniformity examined by spectral mapping of torsion angles. Structure 16:787–797
Park SH, Prytulla S, De Angelis AA, Brown JM, Kiefer H, Opella SJ (2006) High-resolution NMR spectroscopy of a GPCR in aligned bicelles. J Am Chem Soc 128:7402–7403
Poget SF, Girvin ME (2007) Solution NMR of membrane proteins in bilayer mimics: small is beautiful, but sometimes bigger is better. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:3098–3106
Poget SF, Cahill SM, Girvin ME (2007) Isotropic bicelles stabilize the functional form of a small multidrug-resistance pump for NMR structural studies. J Am Chem Soc 129:2432–2433
Quine JR, Achuthan S, Asbury T, Bertram R, Chapman MS, Hu J, Cross TA (2006) Intensity and mosaic spread analysis from PISEMA tensors in solid-state NMR. J Magn Reson 179:190–198
Ramamoorthy A, Wu CH, Opella SJ (1999) Experimental aspects of multidimensional solid-state NMR correlation spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 140:131–140
Ramamoorthy A, Wei Y, Dong-Kuk L (2004) PISEMA solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Ann Rep NMR Spectrosc 52:1–52
Sanders CR, Hare BJ, Howard KP, Prestegard JH (1994) Magnetically-oriented phospholipid micelles as a tool for the study of membrane-associated molecules. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 26:421–444
Schwieters CD, Kuszewski JJ, Tjandra N, Clore GM (2003) The xplor-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package. J Magn Reson 160:65–73
Senes A, Chadi DC, Law PB, Walters RF, Nanda V, Degrado WF (2007) E(z), a depth-dependent potential for assessing the energies of insertion of amino acid side-chains into membranes: derivation and applications to determining the orientation of transmembrane and interfacial helices. J Mol Biol 366:436–448
Shaanan B, Gronenborn AM, Cohen GH, Gilliland GL, Veerapandian B, Davies DR, Clore GM (1992) Combining experimental information from crystal and solution studies: joint X-ray and NMR refinement. Science 257:961–964
Stouffer AL, Acharya R, Salom D, Levine AS, Di Costanzo L, Soto CS, Tereshko V, Nanda V, Stayrook S, DeGrado WF (2008) Structural basis for the function and inhibition of an influenza virus proton channel. Nature 451:596–599
Straus SK, Scott WR, Watts A (2003) Assessing the effects of time and spatial averaging in 15N chemical shift/15N–1H dipolar correlation solid state NMR experiments. J Biomol NMR 26:283–295
Tamm LK, Lai AL, Li Y (2007) Combined NMR and EPR spectroscopy to determine structures of viral fusion domains in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:3052–3060
Toke O, O’Connor RD, Weldeghiorghis TK, Maloy WL, Glaser RW, Ulrich AS, Schaefer J (2004) Structure of (KIAGKIA)3 aggregates in phospholipid bilayers by solid-state NMR. Biophys J 87:675–687
Traaseth NJ, Buffy JJ, Zamoon J, Veglia G (2006) Structural dynamics and topology of phospholamban in oriented lipid bilayers using multidimensional solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 45:13827–13834
Traaseth NJ, Ha KN, Verardi R, Shi L, Buffy JJ, Masterson LR, Veglia G (2008a) Structural and dynamic basis of phospholamban and sarcolipin inhibition of ca(2+)-ATPase. Biochemistry 47:3–13
Traaseth NJ, Verardi R, Veglia G (2008b) Asymmetric methyl group labeling as a probe of membrane protein homo-oligomers by NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 130:2400–2401
Traaseth NJ, Shi L, Verardi R, Mullen DG, Barany G, Veglia G (2009) Structure and topology of monomeric phospholamban in lipid membranes determined by a hybrid solution and solid-state NMR approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:10165–10170
Vasquez V, Sotomayor M, Cordero-Morales J, Schulten K, Perozo E (2008) A structural mechanism for MscS gating in lipid bilayers. Science 321:1210–1214
von Heijne G (2006) Membrane-protein topology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:909–918
Wang W, Black SS, Edwards MD, Miller S, Morrison EL, Bartlett W, Dong C, Naismith JH, Booth IR (2008) The structure of an open form of an E. coli mechanosensitive channel at 3.45 A resolution. Science 321:1179–1183
Weyand S, Shimamura T, Yajima S, Suzuki S, Mirza O, Krusong K, Carpenter EP, Rutherford NG, Hadden JM, O’Reilly J, Ma P, Saidijam M, Patching SG, Hope RJ, Norbertczak HT, Roach PC, Iwata S, Henderson PJ, Cameron AD (2008) Structure and molecular mechanism of a nucleobase-cation-symport-1 family transporter. Science 322:709–713
Wu CH, Ramamoorthy A, Opella SJ (1994) High-resolution heteronuclear dipolar solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson Ser A 109:270–272
Wu CH, Ramamoorthy A, Gierasch LM, Opella SJ (1995) Simultaneous characterization of the amide 1H chemical shift, 1H–15N dipolar, and 15N chemical shift interaction tensors in a peptide bond by three-dimensional solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 117:6148–6149
Xia B, Tsui V, Case DA, Dyson HJ, Wright PE (2002) Comparison of protein solution structures refined by molecular dynamics simulation in vacuum, with a generalized born model, and with explicit water. J Biomol NMR 22:317–331
Zamoon J, Mascioni A, Thomas DD, Veglia G (2003) NMR solution structure and topological orientation of monomeric phospholamban in dodecylphosphocholine micelles. Biophys J 85:2589–2598
Zamoon J, Nitu F, Karim C, Thomas DD, Veglia G (2005) Mapping the interaction surface of a membrane protein: unveiling the conformational switch of phospholamban in calcium pump regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:4747–4752
Zhou Y, Cierpicki T, Jimenez RH, Lukasik SM, Ellena JF, Cafiso DS, Kadokura H, Beckwith J, Bushweller JH (2008) NMR solution structure of the integral membrane enzyme DsbB: functional insights into DsbB-catalyzed disulfide bond formation. Mol Cell 31:896–908
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank J. Hoch and B. Roux for helpful discussions, R. Bertram for sharing the DC and CSA python modules, C. Schwieters for help with the XPLOR-NIH code, and P. Gor’kov and others at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory. This work was supported by grants to G.V. from the NIH (GM64742, HL80081, GM072701). This work was carried out in part using hardware and software provided by the University of Minnesota Supercomputing Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10858_2009_9328_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
The NIH-XPLOR scripts for the hybrid method are available for downloading at the authors’ website (www.chem.umn.edu/groups/veglia). (PDF 2,813 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Traaseth, N.J., Verardi, R. et al. A refinement protocol to determine structure, topology, and depth of insertion of membrane proteins using hybrid solution and solid-state NMR restraints. J Biomol NMR 44, 195–205 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9328-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9328-9