Abstract
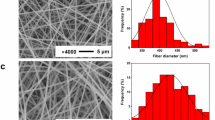
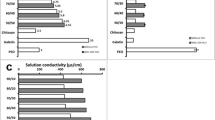
Fabricating novel materials for biomedical applications mostly require the use of biodegradable materials. In this work biodegradable materials like polylactic acid (PLA) and chitosan (CHS) were used for designing electrospun mats. This work reports the physical and chemical characterization of the PLA–CHS composite, prepared by the electrospinning technique using a mixed solvent system. The addition of chitosan into PLA, offered decrease in fiber diameter in the composites with uniformity in the distribution of fibers with an optimum at 0.4wt% CHS. The fiber formation and the reduction in fiber diameter were confirmed by the SEM micrograph. The inverse gas chromatography and contact angle measurements supported the increase of hydrophobicity of the composite membrane with increase of filler concentration. The weak interaction between PLA and chitosan was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis. The stability of the composite was established by zeta potential measurements. Cytotoxicity studies of the membranes were also carried out and found that up to 0.6% CHS the composite material was noncytotoxic. The current findings are very important for the design and development of new materials based on polylactic acid-chitosan composites for environmental and biomedical applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vroman I, Tighzert L. Biodegradable polymers. Materials. 2009;2:307–44.
Adeosun SO, Lawal GI, Balogun SA, Akpan EI. Review of green polymer nanocomposites. J Miner Mater Charact Eng. 2012;11:385.
Stevens ES. Green plastics: an introduction to the new science of biodegradable plastics. Binghamton: Princeton University Press; 2002.
Kulkarni Vishakha S, Butte Kishor D, Rathod Sudha S. Natural polymers–A comprehensive review. Int J Res Pharm Biomed Sci. 2012;3:1579–613.
Grujic R, Vukic M, Gojkovic V. Application of biopolymers in the food industry. In: Pellicer E, Nikolic D, Sort J, Baró M, Zivic F, Grujovic N, et al, editors. Advances in applications of industrial biomaterials. Cham: Springer; 2017. p. 103–19.
Azeredo HM, Rosa MF, Mattoso LH. Nanocellulose in bio-based food packaging applications. Ind Crops Prod. 2017;97:664–71.
Torino MI, Font de Valdez G, Mozzi F. Biopolymers from lactic acid bacteria. Novel applications in foods and beverages. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:834.
Kas HS. Chitosan: properties, preparations and application to microparticulate systems. J Microencapsul. 1997;14:689–711.
Sangeetha Y, Meenakshi S, SairamSundaram C. Corrosion mitigation of N-(2-hydroxy-3-trimethyl ammonium) propyl chitosan chloride as inhibitor on mild steel. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72:1244–9.
Riedel U, Nickel J. Natural fibre‐reinforced biopolymers as construction materials–new discoveries. Die Angew Makromol Chem. 1999;272:34–40.
Thoen J, Busch R. Industrial chemicals from biomass–Industrial concepts. In: Birgit Kamm, Patrick R Gruber, Michael Kamm, editors. Biorefineries-industrial processes and products: status quo and future directions. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim; 2006, p. 347–65.
Aeschelmann F, Carus M. Biobased building blocks and polymers in the world: capacities, production, and applications–status quo and trends towards 2020. Ind Biotechnol. 2015;11:154–9.
Jiang T, Abdel-Fattah WI, Laurencin CT. In vitro evaluation of chitosan/poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid) sintered microsphere scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27:4894–903.
Henton DE, Gruber P, Lunt J, Randall J. Polylactic acid technology. Nat Fibers Biopolym biocomposites. 2005;16:527–77.
Fortunati E, Luzi F, Puglia D, Petrucci R, Kenny JM, Torre L. Processing of PLA nanocomposites with cellulose nanocrystals extracted from Posidonia oceanica waste: Innovative reuse of coastal plant. Ind Crops Prod. 2015;67:439–47.
McCarthy CW, Ahrens DC, Joda D, Curtis TE, Bowen PK, Guillory RJ, et al. Fabrication and short-term in vivo performance of a natural elastic lamina–polymeric hybrid vascular graft. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:16202–12.
Lasprilla AJ, Martinez GA, Lunelli BH, Jardini AL, Maciel Filho R. Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices—a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2012;30:321–8.
Sakai R, John B, Okamoto M, Seppälä JV, Vaithilingam J, Hussein H, et al. Fabrication of polylactide‐based biodegradable thermoset scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Macromol Mater Eng. 2013;298:45–52.
Li G, Wang ZX, Fu WJ, Hong BF, Wang XX, Cao L, et al. Introduction to biodegradable polylactic acid ureteral stent application for treatment of ureteral war injury. BJU Int. 2011;108:901–6.
Yong SK, Shrivastava M, Srivastava P, Kunhikrishnan A, Bolan N. Environmental applications of chitosan and its derivatives. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2015;233:1–43.
Kumar PS, Srinivasan S, Lakshmanan VK, Tamura H, Nair SV, Jayakumar R. β-Chitin hydrogel/nano hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;85:584–91.
Kavitha K, Keerthi TS, Mani TT. Chitosan polymer used as carrier in various pharmaceutical formulations: brief review. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Techol. 2011;2:249–58.
Wan AC, Tai BC. CHITIN—a promising biomaterial for tissue engineering and stem cell technologies. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31:1776–85.
Yang TL. Chitin-based materials in tissue engineering: applications in soft tissue and epithelial organ. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:1936–63.
Bartley J. Should chitosan and tranexamic acid be combined for improved hemostasis after sinus surgery? Med Hypotheses. 2013;81:1036–8.
Bojar W, Kucharska M, Ciach T, Koperski Ł, Jastrzębski Z, Szałwiński M. Bone regeneration potential of the new chitosan-based alloplastic biomaterial. J Biomater Appl. 2014;28:1060–8.
Bhardwaj N, Kundu SC. Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol Adv. 2010;28:325–47.
Tomaszewski W, Szadkowski M. Investigation of electrospinning with the use of a multi-jet electrospinning head. Fibres Text East Eur. 2005;13:22.
Ohkawa K, Cha D, Kim H, Nishida A, Yamamoto H. Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2004;25:1600–5.
Kriegel C, Kit KM, McClements DJ, Weiss J. Influence of surfactant type and concentration on electrospinning of chitosan–poly (ethylene oxide) blend nanofibers. Food Biophys. 2009;4:213–28.
Au HT, Pham LN, Vu TH, Park JS. Fabrication of an antibacterial non-woven mat of a poly (lactic acid)/chitosan blend by electrospinning. Macromol Res. 2012;20:51–58.
Van der Schueren L, De Meyer T, Steyaert I. et al. Polycaprolactone and polycaprolactone/chitosan nanofibres functionalised with the pH-sensitive dye Nitrazine Yellow. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;91:284–93.
Sundaramurthi D, Vasanthan KS, Kuppan P, Krishnan UM, Sethuraman S. Electrospun nanostructured chitosan–poly (vinyl alcohol) scaffolds: a biomimetic extracellular matrix as dermal substitute. Biomed Mater. 2012;7:045005.
Sonseca A, Peponi L, Sahuquillo O, Kenny JM, Giménez E. Electrospinning of biodegradable polylactide/hydroxyapatite nanofibers: study on the morphology, crystallinity structure and thermal stability. Polym Degrad Stab. 2012;97:2052–9.
Xu C, Yang F, Wang S, Ramakrishna S. In vitro study of human vascular endothelial cell function on materials with various surface roughness. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;71:154–61.
Megelski S, Stephens JS, Chase DB, Rabolt JF. Micro-and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules. 2002;35:8456–66.
Kim GM, Michler GH, Pötschke P. Deformation processes of ultrahigh porous multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polycarbonate composite fibers prepared by electrospinning. Polym (Guildf). 2005;46:7346–51.
Zheng J, Zhang H, Zhao Z, Han CC. Construction of hierarchical structures by electrospinning or electrospraying. Polym (Guildf). 2012;53:546–54.
Augustine R, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S. An in vitro method for the determination of microbial barrier property (MBP) of porous polymeric membranes for skin substitute and wound dressing applications. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;12:12–19.
Yang T, Wu D, Lu L, Zhou W, Zhang M. Electrospinning of polylactide and its composites with carbon nanotubes. Polym Compos. 2011;32:1280–8.
Zhao R, Li X, Sun B, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Tang Z, et al. Electrospun chitosan/sericin composite nanofibers with antibacterial property as potential wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;68:92–97.
Furukawa T, Sato H, Murakami R, Zhang J, Duan YX, Noda I, et al. Structure, dispersibility, and crystallinity of poly (hydroxybutyrate)/poly (L-lactic acid) blends studied by FT-IR microspectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Macromolecules. 2005;38:6445–54.
Chu Z, Zhao T, Li L, Fan J, Qin Y. Characterization of antimicrobial poly (lactic acid)/nano-composite films with silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Materials. 2017;10:659.
Morán JI, Alvarez VA, Cyras VP, Vázquez A. Extraction of cellulose and preparation of nanocellulose from sisal fibers. Cellulose. 2008;15:149–59.
Mofokeng JP, Luyt AS, Tábi T, Kovács J. Comparison of injection moulded, natural fibre-reinforced composites with PP and PLA as matrices. J Thermoplast Compos Mater. 2012;25:927–48.
Haafiz MM, Hassan A, Zakaria Z, Inuwa IM, Islam MS, Jawaid M. Properties of polylactic acid composites reinforced with oil palm biomass microcrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;98:139–45.
Xu J, Zhang J, Gao W, Liang H, Wang H, Li J. Preparation of chitosan/PLA blend micro/nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater Lett. 2009;63:658–60.
Cordeiro N, Gouveia C, Moraes AG, Amico SC. Natural fibers characterization by inverse gas chromatography. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;84:110–7.
Deepa B, Abraham E, Cordeiro N, Mozetic M, Mathew AP, Oksman K, et al. Utilization of various lignocellulosic biomass for the production of nanocellulose: a comparative study. Cellulose. 2015;22:1075–90.
Deepa B, Abraham E, Pothan LA, Cordeiro N, Faria M, Thomas S. Biodegradable nanocomposite films based on sodium alginate and cellulose nanofibrils. Materials. 2016;9:50.
Hanaor D, Michelazzi M, Leonelli C, Sorrell CC. The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2012;32:235–44.
Han D, Steckl AJ. Superhydrophobic and oleophobic fibers by coaxial electrospinning. Langmuir. 2009;25:9454–62.
Acknowledgements
The first author is grateful to the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) Government of India and University Grants Commission for the financial funding for this research by giving Junior Research Fellowship. We thank Dr. Jayakumar Rangasamy for his valuable advices regarding zeta potential measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, M.S., Pillai, P.K.S., Faria, M. et al. Electrospun polylactic acid-chitosan composite: a bio-based alternative for inorganic composites for advanced application. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 29, 137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-018-6146-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-018-6146-1