Abstract
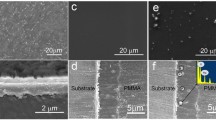
Poly(l-lactic acid)/vaterite composite materials were coated onto metallic magnesium substrates to control rapid degradation and to improve biocompatibility. Two types of composites were prepared by adding 30 and 60 wt% of vaterite to poly(l-lactic acid) (PLLA). The composite coating layer that contained 30 wt% vaterite in the PLLA matrix had almost no pores on the surface and suppressed the initial rapid degradation of the Mg substrate. After immersion in a culture medium for 7 days, pores of 0.5–1.0 μm in diameter formed on the surface. The composite coating layer that contained 60 wt% vaterite with pores of 1.0–2.0 μm in diameter on the surface did not suppress the degradation of the Mg substrate. During immersion, the pH of the media near the composite coating surfaces was maintained at 7.4–7.5 because of the degradation of PLLA and because the vaterite particles dissolved in the solution. Proliferation of murine osteoblast-like cells (MC3T3-E1) on the substrates was improved using composite coatings. Cells on the coating that contained 60 wt% vaterite had significantly higher proliferation than those on a bare Mg substrate. Our coating provides the optimum combination to suppress the initial Mg degradation and to promote cell growth on the coating surface by adjusting the vaterite content in the composite.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Staiger MP, Pietak AM, Huadmai J, Dias G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1728–34.
Witte F, Kaese V, Haferkamp H, Switzer E, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Wirth CJ, Windhagen H. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3557–63.
Witte F, Hort N, Vogt C, Cohen S, Kainer KU, Willumeit R, Feyerabend F. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2008;12:63–72.
Witte F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: a review. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:1680–92.
Zeng R, Dietzel W, Witte F, Hort N, Blawert C. Progress and challenge for magnesium alloys as biomaterials. Adv Eng Biomater. 2008;10:B3–14.
Mueller WD, Nascimento ML. Lorenzo de Mele MF. Critical discussion of the results from different corrosion studies of Mg and Mg alloys for biomaterial applications. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:1749–55.
Xu L, Yamamoto A. Characteristics and cytocompatibility of biodegradable polymer film on magnesium by spin coating. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;93:67–74.
Wong HM, Yeung KWK, Lam KO, Tam V, Chu PK, Luk KDK, Cheung KMC. A biodegradable polymer-based coating to control the performance of magnesium alloy orthopaedic implants. Biomaterials. 2010;31:2084–96.
Hubbell JA. Bioactive biomaterials. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1999;10:123–9.
Kokubo T, Kim HM, Kawashita M. Novel bioactive materials with different mechanical properties. Biomaterials. 2003;24:2161–75.
Hiromoto S, Yamamoto A. High corrosion resistance of magnesium coated with hydroxyapatite directly synthesized in an aqueous solution. Electrochemica Acta. 2009;54:7085–93.
Song YW, Shan DY, Han EH. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy for biomaterial application. Mater Lett. 2008;62:3276–9.
Maeda H, Kasuga T, Nogami M, Hibino Y, Hata K, Ueda M, Ota Y. Biomimetic apatite formation on poly(lactic acid) composites containing calcium carbonates. J Mater Res. 2002;17:727–30.
Kasuga T, Maeda H, Kato K, Nogami M, Hata K-I, Ueda M. Preparation of poly(lactic acid) composites containing calcium carbonate (vaterite). Biomaterials. 2003;24:3247–53.
Maeda H, Kasuga T, Hench LL. Preparation of poly(l-lactic acid)-polysiloxane calcium carbonate hybrid membranes for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1216–22.
Chen HL, Hwang JC. Some comments on the degree of crystallinity defined by the enthalpy of melting. Polymer. 1995;36:4355–7.
Yamamoto A, Hiromoto S. Effect of inorganic salts, amino acids and proteins on the degradation of pure magnesium in vitro. Mater Sci Eng, C. 2009;29:1559–68.
Schubert DW, Dunkel T. Spin coating from a molecular point of view: its concentration regimes, influence of molar mass and distribution. Mater Res Innovat. 2003;7:314–21.
Ishiyama M, Miyazono Y, Sasamoto K, Ohkuwa Y, Ueno K. A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazoloum salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta. 1997;44:1299–305.
Tominaga H, Ishiyama M, Ohseto F, Sasamoto K, Hamamoto T, Suzuki K, Watanabe M. A water-soluble tetrazolium salt useful for colorimetric cell viability assay. Anal Commun. 1999;36:47–50.
Lampin M, Warocquier-Clerout R, Legris C, Degrange M, Sigot-Luizard MF. Correlation between substratum roughness and wettability, cell adhesion, and cell migration. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;36:99–108.
Webster TJ, Ergun C, Doremus RH, Siegel RW, Bizios R. Enhanced functions of osteoblasts on nanophase ceramics. Biomaterials. 2000;21:1803–10.
Maeno S, Niki Y, Matsumoto H, Morioka H, Yatabe T, Funayama A, Toyama Y, Taguchi T, Tanaka J. The effect of calcium ion concentration on osteoblast viability, proliferation and differentiation in monolayer and 3D culture. Biomaterials. 2005;26:4847–58.
Zreiqat H, Howlett CR, Zannettino A, Evans P, Tanzil GS, Knabe C, Shakibaei M. Mechanisms of magnesium-stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62:175–84.
Yamasaki Y, Yoshida Y, Okazaki M, Shimazu A, Kubo T, Akagawa A, Hamada Y, Takahashi J, Matsuura N. Synthesis of functionally graded MgCO3 apatite accelerating osteoblast adhesion. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62:99–105.
Puleo DA, Nanci A. Understanding and controlling the bone-implant interface. Biomaterials. 1999;20:2311–21.
Kohn DH, Sarmadi M, Helman JI, Krebsbach PH. Effects of pH on human bone marrow stromal cells in vitro: implications for tissue engineering of bone. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;60:292–9.
Arnett TR. Extracellular pH regulates bone cell function. J Nutr. 2008;138:4155–85.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Hirotaka Maeda for helpful discussions. This work was supported in part by the Institute of Ceramics Research and Education (ICRE), Nagoya Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, S., Yamamoto, A. & Kasuga, T. Poly(l-lactic acid)/vaterite composite coatings on metallic magnesium. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 2639–2647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5302-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5302-5