Abstract
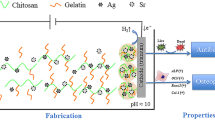
To develop Ti implants with potent antibacterial activity, a novel “sandwich-type” structure of sulfhydrylated chitosan (Chi-SH)/gelatin (Gel) polyelectrolyte multilayer films embedding silver (Ag) nanoparticles was coated onto titanium substrate using a spin-assisted layer-by-layer assembly technique. Ag ions would be enriched in the polyelectrolyte multilayer films via the specific interactions between Ag ions and –HS groups in Chi-HS, thus leading to the formation of Ag nanoparticles in situ by photo-catalytic reaction (ultraviolet irradiation). Contact angle measurement and field emission scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy were employed to monitor the construction of Ag-containing multilayer on titanium surface, respectively. The functional multilayered films on titanium substrate [Ti/PEI/(Gel/Chi-SH/Ag) n /Gel] could efficiently inhibit the growth and activity of Bacillus subtitles and Escherichia coli onto titanium surface. Moreover, studies in vitro confirmed that Ti substrates coating with functional multilayer films remained the biological functions of osteoblasts, which was reflected by cell morphology, cell viability and ALP activity measurements. This study provides a simple, versatile and generalized methodology to design functional titanium implants with good cyto-compatibility and antibacterial activity for potential clinical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darouiche RO. Treatment of infections associated with surgical implants. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1422–9.
Hickok NJ, Shapiro IM. Immobilized antibiotics to prevent orthopaedic implant infections. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:1165–76.
Roy M, Fielding GA, Beyenal H, Bandyopadhyay A, Bose S. Mechanical, in vitro antimicrobial, and biological properties of plasma-sprayed silver-doped hydroxyapatite coating. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:1341–9.
Fei J, Liu GD, Pan CJ, Chen JY, Zhou YG, Xiao SH, Wang Y, Yu HJ. Preparation, release profiles and antibacterial properties of vancomycin-loaded Ca–P coating titanium alloy plate. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22:989–95.
Zhao L, Chu PK, Zhang Y, Wu Z. Antibacterial coatings on titanium implants. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;91:470–80.
Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA, Jimenez de Aberasturi D, de Larramendi IR, Rojo T, Serpooshan V, Parak WJ, Mahmoudi M. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30:499–511.
Zheng YF, Zhang BB, Wang BL, Wang YB, Li L, Yang QB, Cui LS. Introduction of antibacterial function into biomedical TiNi shape memory alloy by the addition of element Ag. Acta Biomater. 2011;7:2758–67.
Gargiulo N, Cusano AM, Causa F, Caputo D, Netti PA. Silver-containing mesoporous bioactive glass with improved antibacterial properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24:2129–35.
Zheng Y, Li J, Liu X, Sun J. Antimicrobial and osteogenic effect of Ag-implanted titanium with a nanostructured surface. Int J Nanomed. 2012;7:875–84.
Li B, Liu X, Cao C, Dong Y, Ding C. Biological and antibacterial properties of plasma sprayed wollastonite/silver coatings. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;91:596–603.
Agarwal A, Weis TL, Schurr MJ, Faith NG, Czuprynski CJ, McAnulty JF, et al. Surfaces modified with nanometer-thick silver-impregnated polymeric films that kill bacteria but support growth of mammalian cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31:680–90.
Rycenga M, Cobley CM, Zeng J, Li W, Moran CH, Zhang Q, Qin D, Xia Y. Controlling the synthesis and assembly of silver nanostructures for plasmonic applications. Chem Rev. 2011;111:3669–712.
Bedel L, Cayron C, Jouve M, Maury F. Embedded layer of Ag nanoparticles prepared by a combined PECVD/PVD process producing SiOxCy–Ag nanocomposite thin films. Nanotechnology. 2012;23:015603.
Visai L, De Nardo L, Punta C, Melone L, Cigada A, Imbriani M, Arciola CR. Titanium oxide antibacterial surfaces in biomedical devices. Int J Artif Organs. 2011;34:929–46.
Monteiro DR, Gorup LF, Takamiya AS, Ruvollo-Filho AC, de Camargo ER, Barbosa DB. The growing importance of materials that prevent microbial adhesion: antimicrobial effect of medical devices containing silver. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;34:103–10.
Ewald A, Glückermann SK, Thull R, Gbureck U. Antimicrobial titanium/silver PVD coatings on titanium. Biomed Eng Online. 2006;5:22.
AshaRani PV, Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano. 2009;3:279–90.
Yuan WY, Lu ZS, Li CM. Charged drug delivery by ultrafast exponentially grown weak polyelectrolyte multilayers: amphoteric properties, ultrahigh loading capacity and pH-responsiveness. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:L9351–7.
de Villiers MM, Otto DP, Strydom SJ, Lvov YM. Introduction to nanocoatings produced by layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63:701–15.
Wong SY, Moskowitz JS, Veselinovic J, Rosario RA, Timachova K, Blaisse MR, et al. Dual functional polyelectrolyte multilayer coatings for implants: permanent microbicidal base with controlled release of therapeutic agents. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:17840–8.
Gao G, Lange D, Hilpert K, Kindrachuk J, Zou Y, Cheng JT, Kazemzadeh-Narbat M, Yu K, Wang R, Straus SK, Brooks DE, Chew BH, Hancock RE, Kizhakkedathu JN. The biocompatibility and biofilm resistance of implant coatings based on hydrophilic polymer brushes conjugated with antimicrobial peptides. Biomaterials. 2011;32:3899–909.
Shukla A, Fleming KE, Chuang HF, Chau TM, Loose CR, Stephanopoulos GN, Hammond PT. Controlling the release of peptide antimicrobial agents from surfaces. Biomaterials. 2010;31:2348–57.
Fu J, Ji J, Yuan W, Shen J. Construction of anti-adhesive and antibacterial multilayer films via layer-by-layer assembly of heparin and chitosan. Biomaterials. 2005;26:6684–92.
Shen L, Wang B, Wang J, Fu J, Picart C, Ji J. Asymmetric free-standing film with multifunctional anti-bacterial and self-cleaning properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:4476–83.
Eby DM, Luckarift HR, Johnson GR. Hybrid antimicrobial enzyme and silver nanoparticle coatings for medical instruments. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2009;1:1553–60.
He T, Chan V. Covalent layer-by-layer assembly of polyethyleneimine multilayer for antibacterial applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95:454–64.
Wu J, Hou S, Ren D, Mather PT. Antimicrobial properties of nanostructured hydrogel webs containing silver. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10:2686–93.
Jung WK, Koo HC, Kim KW, Shin S, Kim SH, Park YH. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008;74:2171–8.
Percival SL, Bowler PG, Russell D. Bacterial resistance to silver in wound care. J Hosp Infect. 2005;60:1–7.
Park E, Kim H, Song J, Oh H, Song H, Jang J. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles decorated polypyrrole nanotubes for antimicrobial application. Macromol Res. 2012;20:1096–101.
Zhang H, Qadeer A, Chen W. In situ gelable interpenetrating double network hydrogel formulated from binary components: thiolated chitosan and oxidized dextran. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12:1428–37.
Liu S, Ng AK, Xu R, Wei J, Tan CM, Yang Y, Chen Y. Antibacterial action of dispersed single-walled carbon nanotubes on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis investigated by atomic force microscopy. Nanoscale. 2010;2:2744–50.
Liu N, Chen XG, Park HG, Liu CG, Liu CS, Meng XH, Yu LJ. Effect of MW and concentration of chitosan on antibacterial activity of Escherichia coli. Carbohydr Polym. 2006;64:60–5.
Hu Y, Cai K, Luo Z, Zhang Y, Li L, Lai M, Hou Y, Huang Y, Li J, Ding X, Zhang B, Sung KL. Regulation of the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and osteogenesis in vivo by microenvironmental modification of titanium alloy surfaces. Biomaterials. 2012;33:3515–28.
Wu ZM, Zhang XG, Zheng C, Li CX, Zhang SM, Dong RN, Yu DM. Disulfide-crosslinked chitosan hydrogel for cell viability and controlled protein release. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2009;37:198–206.
Cai K, Hu Y, Luo Z, Kong T, Lai M, Sui X, Wang Y, Yang L, Deng L. Cell-specific gene transfection from a gene-functionalized poly(d,l-lactic acid) substrate fabricated by the layer-by-layer assembly technique. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:7479–81.
Shu S, Zhang X, Wu Z, Wang Z, Li C. Gradient cross-linked biodegradable polyelectrolyte nanocapsules for intracellular protein drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2010;31:6039–49.
Mi FL, Wu YY, Lin YH, Sonaje K, Ho YC, Chen CT, Juang JH, Sung HW. Oral delivery of peptide drugs using nanoparticles self-assembled by poly(gamma-glutamic acid) and a chitosan derivative functionalized by trimethylation. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19:1248–55.
Cai K, Rechtenbach A, Hao J, Bossert J, Jandt KD. Polysaccharide–protein surface modification of titanium via a layer-by-layer technique: characterization and cell behaviour aspects. Biomaterials. 2005;26:5960–71.
Chang S, Combs ZA, Gupta MK, Davis R, Tsukruk VV. In situ growth of silver nanoparticles in porous membranes for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010;2:3333–9.
Skrabalak SE, Au L, Li X, Xia Y. Facile synthesis of Ag nanocubes and Au nanocages. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:2182–90.
Gan W, Xu B, Dai HL. Activation of thiols at a silver nanoparticle surface. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011;50:6622–5.
Gan W, Gonella G, Zhang M, Dai HL. Reactions and adsorption at the surface of silver nanoparticles probed by second harmonic generation. J Chem Phys. 2011;134:0411040–1.
Lichter JA, Van Vliet KJ, Rubner MF. Design of antibacterial surfaces and interfaces: polyelectrolyte multilayers as a multifunctional platform. Macromolecules. 2009;42:8573–86.
Beer C, Foldbjerg R, Hayashi Y, Sutherland DS, Autrup H. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles—nanoparticle or silver ion? Toxicol Lett. 2012;208:286–92.
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27:76–83.
Peetsch A, Greulich C, Braun D, Stroetges C, Rehage H, Siebers B, Köller M, Epple M. Silver-doped calcium phosphate nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and toxic effects toward mammalian and prokaryotic cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;102:724–9.
Shi Z, Neoh KG, Zhong SP, Yung LY, Kang ET, Wang W. In vitro antibacterial and cytotoxicity assay of multilayered polyelectrolyte-functionalized stainless steel. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;76:826–34.
Wang QF, Zhong L, Sun JQ, Shen JC. Incorporation of silver ions into ultrathin titanium phosphate. Chem Mater. 2006;18:1988–94.
Cao H, Liu X, Meng F, Chu PK. Biological actions of silver nanoparticles embedded in titanium controlled by micro-galvanic effects. Biomaterials. 2011;32:693–705.
Lok CN, Ho CM, Chen R, He QY, Yu WY, Sun H, Tam PK, Chiu JF, Che CM. Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles. J Proteome Res. 2006;5:916–24.
Cao H, Qiao Y, Liu X, Lu T, Cui T, Meng F, Chu PK. Electron storage mediated dark antibacterial action of bound silver nanoparticles: smaller is not always better. Acta Biomater. 2013;9:5100–10.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Municipal Government (CSTC, 2011JJJQ10004 and JJA10056), China Ministry of Science and Technology (973 Project No. 2009CB930000), Natural Science Foundation of China (51173216 and 31200712), National Key Technology R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology (2012BAI18B04) and the “111” project (B06023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Xu, D., Hu, Y. et al. Surface modification of titanium substrates with silver nanoparticles embedded sulfhydrylated chitosan/gelatin polyelectrolyte multilayer films for antibacterial application. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 1435–1448 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5190-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5190-8