Abstract
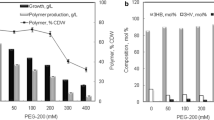
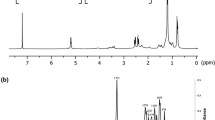
The synthesis of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate is investigated in this work for it potential application as drug carrier for cancer therapy. The bacterial isolate Bacillus cereus FB11 has synthesized poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) copolymer under nutrient stress conditions using glucose as a sole carbon source. The FTIR spectrum of the purified copolymer showed the characteristic absorption bands at 1,719, 1,260 and 2,931 cm−1 attributing to C=O, C–O stretching and C–H vibrations, respectively. The result of 1H-NMR confirmed that it was composed of 88 mol % of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 12 mol % of 3-hydroxyvalerate monomeric subunits. The nanoparticles were fabricated from copolymer and used as a carrier for anticancer drug ellipticine. The in vitro drug release studies showed that % inhibition of A549 cancer cell line receiving ellipticine loaded poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) nanoparticles was two-fold higher in comparison to ellipticine alone. This drug delivery system offers exciting possibilities for cancer therapy by increasing the bioavailability of anti-neoplastic drug to the tumor site.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Q, Tainsky MA. Epigenetic silencing of IRF7 and/or IRF5 in lung cancer cells leads to increased sensitivity to oncolytic viruses. PLoS One. 2011;6e:28683.
Zhang W, Chen Y, Wei H, Zheng C, Sun R, Zhang J, Tian Z. Antiapoptotic activity of autocrine interleukin-22 and therapeutic effects of interleukin-22-small interfering RNA on human lung cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6432–9.
Daraselia N, Wang Y, Budoff A, Lituev A, Potapova O, Vansant G, Monforte J, Mazo I, Ossovskaya VS. Molecular signature and pathway analysis of human primary squamous and adenocarcinoma lung cancers. Am J Cancer Res. 2012;2:93–103.
Stiborová M, Bieler CA, Wiessler M, Frei E. The anticancer agent ellipticine on activation by cytochrome P450 forms covalent DNA adducts. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001;62:675–84.
Wu M, Ye Z, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhao X. Release of hydrophobic anticancer drug from a newly designed self-assembling peptide. Mol BioSyst. 2011;7:2040–7.
Wu Y, Sadatmousavi P, Wang R, Lu S, Yuan Y-F, Chen P. Self-assembling peptide-based nanoparticles enhance anticancer effect of ellipticine in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3221–33.
Jain KK. Advances in the field of nanooncology. BMC Med. 2010;8:83.
Chen GQ. A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio and materials industry. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:2434–46.
Suriyamongkol P, Weselake R, Narine S, Moloney M, Shah S. Biotechnological approaches for the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in microorganisms and plants—a review. Biotech Adv. 2007;25:148–75.
Tajima K, Igari T, Nishimura D, Nakamura M, Satoh Y, Munekata M. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus sp. INT005 accumulating polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) from gas field soil. J Biosci Bioeng. 2003;95:77–81.
Mizuno K, Ohta A, Hyakutake M, Ichinomiya Y, Tsuge T. Isolation of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacteria from a polluted soil and characterization of the isolated strain Bacillus cereus YB-4. Polym Degrad Stab. 2010;95(8):1335–9.
Sun J, Dai ZW, Chen GQ. Oligomers of polyhydroxyalkanoates stimulated calcium ion channels in mammalian cells. Biomaterials. 2007;28:3896–903.
Bayram C, Denkbas EB, Kılıçay E, Hazer B, Çakmak HB, Noda I. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) (PHBHHX) microspheres preparation and characterization of triamcinolone acetonide-loaded. J Bioactive Compatible Polym. 2008;23:334.
Francis L, Meng D, Knowles J, Keshavarz T, Boccaccini AR, Roy I. Controlled delivery of gentamicin using poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) microspheres. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:4294–314.
Wu Q, Wang Y, Chen GQ. Medical application of microbial biopolyesters polyhydroxyalkanoates. Artif Cell Blood Sub Biot. 2009;37:1–12.
Weisberg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogentic study. J Bacteriol. 1991;173(2):697–703.
Eck RV, Dayhoff MO. Atlas of protein sequence and structure. Silver Springs: National Biomedical Research Foundation; 1966.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evo. 2007;24:1596–9.
Kung SS, Chuang YC, Chen CH, Chien CC. Isolation of polyhydroxyalkanoates-producing bacteria using a combination of phenotypic and genotypic approach. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2007;44:364–71.
Lee SY, Choi JIL. In: Manual of industrial microbiology and biotechnology. 2nd ed., A.L. Demain, J. E. Davies (eds), ASM Press, Washington, DC, 1999, p 616–627.
Bandrup J, Immergut EH. Polymer handbook. 3rd ed. New York: Interscience Press; 1989.
Xiong YC, Yao YC, Zhan XY, Chen GQ. Application of polyhydroxyalkanoates nanoparticles as intracellular sustained drug-release vectors. J Biomater Sci. 2010;21:127–40.
Provencher SW. A constrained regulation method for inverting data represented by linear algebraic or integral equations. Comput Phys Commun. 1982;27:213–27.
Wei Y, Chen W, Huang C, Wu H, Sun Y, Lo C, Janarthanan O. Screening and evaluation of polyhydroxybutyrate-producing strains from indigenous isolate Cupriavidus taiwanensis strains. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:252–65.
Cortés AL, Landázuri AL, García-Maldonado JQ. Screening and isolation of PHB-producing bacteria in a polluted marine microbial mat. Microbial Ecol. 2008;56:112–20.
Arshad MU, Jamil N, Naheed N, Husnain S. Analysis of bacterial strains from contaminated and non-contaminated sites for the production of biopolymers. Afri J Biotechnol. 2007;6:1115–21.
Rehman S, Jamil N, Husnain S. Screening of different contaminated environments for polyhydroxyalkanoates-producing bacterial strains. Biologia. 2007;62:650–6.
Ojumu TV, Yu J, Solomon BO. Production of polyhydroxyalkonates, a bacterial biodegradable polymer. Afri J Biotechnol. 2004;3:18–24.
Yüksekdag ZN, Aslim B, Beyatli Y, Mercan N. Effect of carbon and nitrogen sources and incubation times on poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthesis by Bacillus subtilis 25 and Bacillus megaterium 12. Afri J Biotechnol. 2004;3:63–6.
Reddy SV, Thirumala M, Mahmood SK. A novel Bacillus sp. accumulating poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) from a single carbon substrate. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;36:837–43.
Anil-Kumar PK, Shamala TR, Kshama L, Prakash MH, Joshi GJ, Chandrashekar A, Kumari KSL, Divyashree MS. Bacterial synthesis of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) using carbohydrate-rich mahua (Madhuca sp.) flowers. J Appl Microbiol. 2007;103:204–9.
Liu H, Pancholi M, Stubbs J III, Raghavan D. Influence of hydroxyvalerate composition of polyhydroxybutyrate valerate (PHBV) copolymer on bone cell viability and in vitro degradation. J Appl Polym Sci. 2010;116:3225–31.
Bloembergen S, Holden DA, Hamer GK, Bluhm TL, Marchessault RH. Macromolecules. 1986;19:2865.
Allen AD, Anderson WA, Ayorinde FO, Eribo E. Biosynthesis and characterization of copolymer poly (3HB-co-3HV) from saponifed Jatropha curcas oil by Pseudomonas oleovorans. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;37:849–56.
Hahn SK, Keun CY, Lee SY. Recovery and characterization of poly-(3-hydroxybutyric acid) synthesized in Alcaligenes eutrophus and recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microb. 1995;61(1):34–9.
Feng S, Huang G. Effects of emulsifiers on the controlled release of paclitaxel (Taxol) from nanospheres of biodegradable polymers. J Controlled Release. 2001;71:53–69.
Duan Y, Sun X, Gong T, Wang Q, Zhang Z. Preparation of DHAQ-loaded mPEG-PLGA-mPEG nanoparticles and evaluation of drug release behaviors in vitro/in vivo. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17:509–16.
Mohanraj VJ, Chen Y. Nanoparticles-a review. Trop J Pharm Res. 2006;5:561–73.
Musumeci T, Ventura CA, Giannone I, Ruozi B, Montenegro L, Pignatello R, Puglisi G. PLA/PLGA nanoparticles for sustained release of docetaxel. Int J Pharm. 2006;325:172–9.
Danhier F, Lecouturier N, Vroman B, Jerome C, Marchand-Brynaert J, Feron O, Preat V. Paclitaxel-loaded PEGylated PLGA-based nanoparticles: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release. 2009;13:11–7.
Masood F, Chen P, Yasin T, Fatima N, Hasan F, Hameed A. Encapsulation of ellipticine in poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) nanoparticles and its in vitro application. Mater Sci Eng C. 2013;33:1054–60.
Singh MP, Hill GC, Péoch D, Rayner B, Imbach JL, Lown JW. High-field NMR and restrained molecular modeling studies on a DNA heteroduplex containing a modified apurinic abasic site in the form of covalently linked 9-aminoellipticine. Biochemistry. 1994;33:10271–85.
Froelich-Ammon SJ, Patchan MW, Osheroff N, Thompson RB. Topoisomerase II binds to ellipticine in the absence or presence of DNA. Characterization of enzyme-drug interactions by fluorescence spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:14998–5004.
Poljaková J, Dračínský M, Frei E, Hudeček J, Stiborová M. The effect of pH on peroxidase-mediated oxidation of and DNA adduct formation by ellipticine. Collect Czechoslov Chem Commun. 2009;71:1169–85.
Kılıçay E, Demirbilek M, Türk M, Güven E, Hazer B, Denkbas EB. Preparation and characterization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) (PHBHHX) based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Europ J Pharm Sci. 2011;44:310–20.
Hazer B. Amphiphilic poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate)s: potential candidates for medical applications. Int J Polym Sci 2010:1–8.
Acknowledgments
We thank Higher Education Commission (HEC) Pakistan for providing the financial assistance to complete this research work. We also thank to members of Prof. P. Chen research group especially the Lab Manager, Tatiana Sheinin, University of Waterloo, Canada for their helpful guidance. We are deeply indebted to Dr. Ihsan-ul-Haq and Dr. M. Imran, Quaid-i-Azam University (QAU), Pakistan, for providing their help in the data analysis in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masood, F., Chen, P., Yasin, T. et al. Synthesis of poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-12 mol % 3-hydroxyvalerate) by Bacillus cereus FB11: its characterization and application as a drug carrier. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 24, 1927–1937 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4946-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4946-x