Abstract
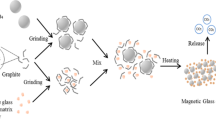
Magnetic bioactive glass ceramic (MG) in the system CaO–SiO2–P2O5–MgO–CaF2–MnO2–Fe2O3 for hyperthermia treatment of bone tumor was synthesized. The phase composition was investigated by XRD. The magnetic property was measured by VSM. The in vitro bioactivity was investigated by simulated body fluid (SBF) soaking experiment. Cell growth on the surface of the material was evaluated by co-culturing osteoblast-like ROS17/2.8 cells with materials for 7 days. The results showed that MG contained CaSiO3 and Ca5(PO4)3F as the main phases, and MnFe2O4 and Fe3O4 as the magnetic phases. Under a magnetic field of 10,000 Oe, the saturation magnetization and coercive force of MG were 6.4 emu/g and 198 Oe, respectively. After soaking in SBF for 14 days, hydroxyapatite containing CO3 2− was observed on the surface of MG. The experiment of co-culturing cells with material showed that cells could successfully attach and well proliferate on MG.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hench LL, Splinter RJ, Allen WC, Greenlee TK. Bonding mechanisms at the interface of ceramic prosthetic materials. J Biomed Mater Res. 1971;2:117–41.
Ohura K, Ikenaga M, Nakamura T, Yamamuro T, Ebisawa Y, Kokubo T, et al. A heat-generating bioactive glass-ceramic for hyperthermia. J Appl Biomater. 1991;2:153–9.
Ebisawa Y, Miyaji F, Kokubo T, Ohura, Nakamura T. Bioactivity of ferrimagnetic glass-ceramics in the system FeO-Fe2O3-CaO-SiO2. Biomaterials. 1997;18:1227–48.
Arcos D, Del Real RP, Vallet-Regì M. A novel bioactive and magnetic biphasic material. Biomaterials. 2002;23:2151–8.
Jiang Y, Jun O, Zhang Z, Qin Q-H. Preparation of magnetic and bioactive calcium zinc iron silicon oxide composite for hyperthermia treatment of bone cancer and repair of bone defects. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;22:721–9.
Singh R, Srinivasan A, Kothiyal GP. Evaluation of CaO-SiO2–P2O5-Na2O-Fe2O3 bioglass-ceramics for hyperthermia application. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20:S147–51.
Arcos D, Del Real RP, Vallet-Regi M. Biphasic materials for bone grafting and hyperthermia treatment of cancer. J Bio Med Mater Res. 2003;65A:71–8.
Lung Fung T, Kwok Chuen W, Shekhar Madhukar K, Lin H, Tsun Cheung C, James Francis G. Bisphosphonates reduce local recurrence in extremity giant cell tumor of bone: a case–control study. Bone. 2008;42:68–73.
Lee YK, Lee SB, Kim YU, Kim KN, Choi SY, Lee KH, et al. Effect of ferrite thermoseeds on destruction of carcinoma cells under alternating magnetic field. J Mater Sci. 2003;38:4221–33.
Luderer AA, Borrelli NF, Panzarino JN, Mansfield GR, Hess DM, Brown JL, et al. Glass-ceramic-mediated, magnetic-field-induced localized hyperthermia: response of a murine mammary carcinoma. Radiat Res. 1983;94:190–8.
Ebisawa Y, Sugimoto Y, Hayashi T, Kokubo T, Ohura K, Yamamuro T. Crystallization of (FeO-Fe2O3)-CaO-SiO2 glass and magnetic properties of their crystallized products. J Ceram Soc Jpn. 1991;99:7–13.
Bretcanu O, Spriano S, Verné E, Cöisson M, Tiberto P, Allia P. The influence on crystallised Fe3O4 on the magnetic properties of coprecipitation-derived ferrimagnetic glass-ceramics. Ata Biomater. 2005;1:421–9.
Singh R, Srinivasan A. Apatite-forming ability and magnetic properties of glass-ceramics containing zinc ferrite and calcium sodium phosphate phases. Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30:1100–6.
Shah SA, Hashmi MU, Alam S, Shamim A. Magnetic and bioactivity evaluation of ferrimagnetic ZnFe2O4 containing glass ceramics for the hyperthermia treatment of cancer. J Magn Magn Mater. 2010;322:375–81.
Chi-Shiung H, Huy-Zu C, Hui-Ju H, Yung-Sheng C, Moo-Chin W. Crystallization kinetics and magnetic properties of iron oxide contained 25Li2O–8MnO2–20CaO-2P2O5–45SiO2 glasses. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2007;27:3171–6.
Tzu-Wei W, Hsi-Chin W, Wei-Ren W, Feng-Huei L, Pei-Jen L, Ming-Jium S, et al. The development of magnetic degradable DP-Bioglass for hyperthermia cancer therapy. J Biomed Mater Res. 2007;83A:828–37.
Kokubo T. A-W Glass-ceramics: processing and properties. In: Hench LL, Wilson J, editors. An introduction to bioceramics. Singapore: World Scientific; 1993. p. 75–88.
Sharma K, Dixit A, Jagannath SS, Bhattacharya S, Prajapat CL, Sharma PK, et al. Preparation and studies on surface modifications of calcium-silico-phosphate ferrimagnetic glass-ceramics in simulated body fluid. Mater Sci Eng C. 2009;29:2226–33.
Guangda L, Dali Z, Ming X, Weizhong Y, Qin L, Bin C, et al. Study on the surface bioactivity of novel magnetic A-W glass ceramic in vitro. Appl Surf Sci. 2008;25:559–61.
Guang Da L, Da Li Z, Yun L, Tao Hua P, Guo Sheng C, Qiu Dan Y. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic bioactive glass-ceramics containing Mg ferrite for hyperthermia. Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30:148–53.
Culotta VC, Yang M, Hall MD. Manganese transport and trafficking: lessons learned from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eukaryot Cell. 2005;4:1159–65.
Paluszkiewicz C, Ślósarczyk A, Pijocha D, Sitarz M, Bućko M, Zima A, et al. Synthesis, structural properties and thermals stability of Mn-doped hydroxyapatite. J Mol Struct. 2010;976:301–9.
Mayer I, Gdalya S, Burghaus O, Reinen D, Cohen S. Crystal structure and EPR study of Mn-doped β-tricalcium phosphate. Mater Res Bull. 2008;43:447–52.
Bigi A, Bracci B, Cusinier F, Elkaim R, Fini M, Mayer I, et al. Human osteoblast response to pulsed laser deposited calcium phosphate coatings. Biomaterials. 2005;26:2381–9.
Sima F, Socol G, Axente E, Mihailescu IN, Zdrentu L, Petrescu SM, et al. Biocompatible and bioactive coatings of Mn2+-doped β-tricalcium phosphate synthesized by pulsed laser deposition. Appl Surf Sci. 2007;254:1155–9.
Khalid MB. Study of dielectric and impedance properties of Mn ferrites. Phys B Condens Matter. 2011;406:382–7.
Khalid MB, Shalendra K, Chan GL, Alimuddin. Study of dielectric and ac impedance properties of Ti doped Mn ferrites. Curr Appl Phys. 2009;9:1397–406.
Jyotsnendu G, Pallab P, Vaibhav S, Hitesh C, Shreerang C, Rinti B, Dhirendra B. Synthesis and characterizations of water-based ferrofluids of substituted ferrites [Fe1-x BxFe2O4, B = Mn, Co(x = 0–1)] for biomedical applications. J Magn Magn Mater. 2008;320:724–30.
Ming X, Dan-Ge F, Guang-Da L, Wei-Zhong Y, Da-Li Z. Preparation of porous apatite-wollastonite bioactive glass ceramic (AW-GC) by dipping with polymer foams. J Inorg Chem. 2007;23:708–12.
Kokubo T, Takadama H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials. 2006;27:2907–15.
Skelton KL, Glenn JV, Clarke SA, Georgiou G, Valappil SP, Knowles JC, et al. Effect of ternary phosphate-based glass compositions on osteoblast and osteoblast-like proliferation, differentiation and death in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2007;3:56372.
Gallego D, Higuita N, Garcia F, Ferrell N, Hansford DJ. Bioactive coatings on Portland cement substrates: Surface precipitation of apatite-like crystals. Mater Sci Eng C. 2008;28:347–52.
Yao L, Jiuxing J, Jiupeng Z. X-ray diffractionand Mössbauer studies of phase transformation in manganese ferrite prepared by combustion synthesis method. Mater Chem Phys. 2004;87:91–5.
Jong-Gyu P, Man-Jong L, Sang-Hoon H. Reaction kinetics and formation mechanism of magnesium ferrites. Thermochim Acta. 2005;425:131–6.
Zhigang Z. Ferrite magnetic material. BeiJing: Science Press; 1981.
Ohashi Y, Finger LW. The role of octahedral cations in pyroxenoid crystal chemistry I. Bustamite, wollastonite, and the pectolite-schizo-lite-serandite series. Am Mineral. 1978;63:274–88.
Wager LR, Mitchell RL. The distribution of trace elements during strong fractionation of basic magma-a further study of the Skaergaard intrusion, East Greenland. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1951;1:129–208.
Shokrollahi H, Janghorban K. Influence of additives on the magnetic properties, microstructure and densification of Mn–Zn soft ferrites. Mater Sci Eng B. 2007;141:91–107.
Chikazumi S, Taketomi S, Ukita M, Mizukami M, Miyajima H, Seto-gawa M, et al. Physics of magnetic fluids. J Magn Magn Mater. 1987;65:24551.
Langford JI, Wilson AJC. Scherrer after sixty years: A survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J Appl Cryst. 1978;11:102–13.
Singh R, Srinivasan A. Bioactivity of ferrimagnetic MgO-CaO-SiO2–P2O5-Fe2O3 glass-ceramics. Ceram Int. 2010;36:283–90.
Ruiz-Hernández E, Serrano MC, Arcos D, Vallet-Regí M. Glass–glass ceramic thermoseeds for hyperthermic treatment of bone tumors. J Biomed Mater Res. 2006;79A:533–43.
Šepelák V, Bergmann I, Menzel D, Feldhoff A, Heitjans P, Litterst FJ, et al. Magnetization enhancement in nanosized MgFe2O4 prepared by mechanosynthesis. J Magn Magn Mater. 2007;316:e764–7.
Abou Neel EA, Ahmed I, Blaker JJ, Bismarck A, Boccaccini AR, Lewis MP, et al. Effect of iron on the surface, degradation and ion release properties of phosphate-based glass micro-fibres. Acta Biomater. 2005;1:553–63.
Kokubo T, Matsushita T, Takadama H, Kizuki T. Development of bioactive materials based on surface chemistry. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2009;29:1267–74.
Xiaoxia Y, Xiaohui H, Chengzhong Y, Hexiang D, Yi W, Zhendong Z, et al. The in vitro bioactivity of mesoporous bioactive glasses. Biomaterials. 2006;27:3396–403.
Radin S, Ducheyne P, Rothman B, Conti A. The effect of in vitro modeling conditions on the surface reactions of bioactive glass. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;37A:363–75.
Liang H, Wan YZ, He F, Huang Y, Xu JD, Li JM, et al. Bioactivity of Mg-ion-implanted zirconia and titanium. Appl Surf Sci. 2007;253:3326–33.
Xiaoyan L, Xudong L, Hongsong F, Xiantao W, Jian L, Xingdong Z. In situ synthesis of bone-like apatite/collagen nano-composite at low temperature. Mater Lett. 2004;58:3569–72.
Inés B, Ingo H, Frank AM. Preparation of bioactive sodium titanate ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2007;27:4547–53.
Elbatal HA, Azooz MA, Khalil EMA, Monem AS, Hamdy YM. Characterization of some bioglass-ceramic. Mater Chem Phys. 2003;80:599–609.
Lopes PP, Leite Ferreira BJM, Almeida NAF, Fredel MC, Fernandes MHV, Correia RN. Preparation and study of in vitro bioactivity of PMMA-co-EHA composites filled with a Ca3(PO4)2-SiO2-MgO glass. Mater Sci Eng C. 2008;28:572–7.
Loty C, Forest N, Boulekbache H, Kokubo T, Sautier JM. Behavior of fetal rat chondrocytes cultured on a bioactive glass-ceramic. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;37A:137–49.
Nieves O, Ana IM, Antonio JS, Javier T, Vallet-Regì M, Lizarbe MA. Bioactive sol-gel glasses with and without a hydroxycarbonate apatite layer as substrates for osteoblast cell adhesion and proliferation. Biomaterials. 2003;24:3383–93.
Lüthen F, Bulnheim U, Müller PD, Rychly J, Jesswein H, Nebe JG. Influence of manganese ions on cellular behavior of human osteoblasts in vitro. Biomol Eng. 2007;54:531–6.
Hench LL. Genetic design of bioactive glass. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2009;29:1257–65.
Acknowledgment
Financial support from the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20060610024) from Education Ministry of China and Doctoral Research Fund from Henan University of Science and Technology are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Feng, S. & Zhou, D. Magnetic bioactive glass ceramic in the system CaO–P2O5–SiO2–MgO–CaF2–MnO2–Fe2O3 for hyperthermia treatment of bone tumor. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 22, 2197 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4417-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4417-1