Abstract
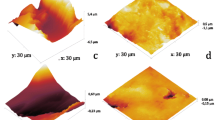
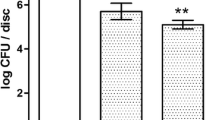
Dental implant failure is commonly associated to dental plaque formation. This problem starts with bacterial colonization on implant surface upon implantation. Early colonizers (such as Streptococcus sanguinis) play a key role on that process, because they attach directly to the surface and facilitate adhesion of later colonizers. Surface treatments have been focused to improve osseointegration, where shot-blasting is one of the most used. However the effects on bacterial adhesion on that sort of surfaces have not been elucidated at all. A methodological procedure to test bacterial adherence to titanium shot-blasted surfaces (alumina and silicon carbide) by quantifying bacterial detached cells per area unit, was performed. In parallel, the surface properties of samples (i.e., roughness and surface energy), were analyzed in order to assess the relationship between surface treatment and bacterial adhesion. Rather than roughness, surface energy correlated to physicochemical properties of shot-blasted particles appears as critical factors for S. sanguinis adherence to titanium surfaces.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisenbarth E, Meyle J, Nachtigall W, Breme J. Influence of the surface structure of titanium materials on the adhesion of fibroblasts. Biomaterials. 1996;17:399–1403.
Lincks J, Boyan BD, Blanchard CR, Lohmann CH, Liu Y, Cochran DL, Dean DD, Schwartz Z. Response of MG63 osteoblast-like cells to titanium and titanium alloy is dependent on surface roughness and composition. Biomaterials. 1998;19:2219–32.
Aparicio C, Gil FJ, Peraire C, Padròs A, Planell JA. Abstract Booklet Titanium, 99. 2000;2:1207–10.
Pegueroles M, Aparicio C, Bosio M, Engel E, Gil FJ, Planell JA, Altankov G. Spatial organization of osteoblast fibronectin matrix on titanium surfaces: effects of roughness, chemical heterogeneity and surface energy. Acta Biomater. 2009;6:291–301.
Weiger R, Decker E-M, Krastl G, Brecx M. Deposition and retention of vital and dead Streptococcus sanguinis cells on glass surfaces in a flow-chamber system. Arch Oral Biol. 1999;44:621–8.
Rickard A-H, Gilbert P, High N-J, Kolenbrander P, Handley P-S. Bacterial coaggregation an integral process in the development of multi-species biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:94–100.
Maeda K, Nagata H, Nonaka A, Kataoka K, Tanaka M, Shizukuishi S. Oral streptococcal glyceraldehydes-3phosphate dehydrogenase mediates interaction with Porphyromonas gingivalis frimbria. Microbes Infect. 2004;6:1163–70.
Norowski PA, Bumgardner JD. Review, Biomaterial and antibiotic strategies for Peri-implantitis. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 2009;88B:530–43.
Teughels W, van Assche N, Sliepen I, Quirynen M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17:68–81.
Elter C, Heuer W, Demling A, Hannig M, Heidenblut T, Bach F, Stiesch-Scholz M. Supra and subgingival biofilm formation on implant abutments with different surface characteristics. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23:327–34.
Bürgers R, Gerlach T, Hanhel S, Schwartz F, Handel G. Gosau. In vitro and in vivo biofilm formation on two different titanium implant surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21:156–64.
Mabboux F, Ponsonnet L, Morrier J-J, Jaffrezic N, Barsotti O. Surface free energy and bacterial retention to saliva-coated dental implant materials-an in vitro study. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2004;39:199–205.
Sissons CH. Artificial dental plaque biofilm model system. Adv Dent Res. 1997;11:110–26.
Steinberg D, Sela M, Klinger A, Kohavi D. Adhesion of periodontal bacteria to titanium and titanium alloy powders. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998;9:67–72.
Länge K, Herold M, Scheideler L, Geis-Gerstorfer J, Wendel HP, Gauglitz G. Investigation of initial pellicle formation on modified titanium dioxide (TiO2) surfaces by reflectometric interference spectroscopy (RIFS) in a model system. Dent Mater. 2004;20:814–22.
Gerber J, Wenaweser D, Mayfield-Heitz L, Niklaus L, Persson G. Comparison of bacterial plaque samples from titanium and tooth surfaces by different methods. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17:1–7.
Fürst M, Salvi G, Lang N, Persson G. Bacterial colonization immediately after installation on oral titanium implants. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2007;18:501–8.
Hauser-Gerspach I, Kulik E-M, Weiger R, Decker E-M, Von Ohle C, Meyer J. Adhesion of Streptococcus sanguinis to dental implant and restorative materials in vitro. Dent Mater J. 2007;26:361–6.
Schenkels L, Veerman E, Amerongen A. Biochemical composition of human saliva in relation to other mucosal fluids. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1995;6:161–75.
Stokes J, Davies G. Viscoelasticity of human whole saliva collected after acid and mechanical stimulation. Biorheology. 2007;44:141–60.
Cassie BD, Baxter S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans Faraday Soc. 1944;40:546–51.
Wenzel R. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind Eng Chem. 1936;28:988–94.
Owens D, Wendt R. Estimation of the surface energy of polymers. J Appl Polym Sci. 1969;13:1741–7.
Sharma P, Hanumantha R. Analysis of different approaches foe evaluation of surface energy of microbial cells by contact angle goniometry. Adv Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2002;98:341–463.
Pareta R, Reising A, Miller T, Storey D, Webster T. Increased endothelial cell adhesion on plasma modified nanostructured polymeric and metallic surfaces for vascular stent applications. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009;103:459–71.
Bellon-Fontaine M-N, Rault J, van Oss CJ. Microbial adhesion to solvents: a novel method to determine the electron donor/electron acceptor or Lewis acid-base properties of microbial cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 1996;7:47–53.
Quirynen M, van de Mei H, Bollen C, Schotte A, Marechal M, Doornbusch G, Naert I, Busscher H, van Steenberghe D. An in vivo study of the influence of the surface roughness of implants on the microbiology of supra- and subgingival plaque. J Dent Res. 1993;72:1304–9.
Größner-Schreiber B, Griepentrog M, Haustein I, Müller W, Lange K, Briedigkeit H, Göbel U. Plaque formation on surfaces modified dental implants, an in vitro study. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2001;12:543–51.
Poortinga A, Bos R, Busscher H. Charge transfer during staphylococcal adhesion to TiNOX® coatings with different specific resistivity. Biophys Chem. 2001;91:273–9.
Madar R. Silicon carbide in contention. Nature. 2004;430:974–5.
Acknowledgments
Rodriguez-Hernández appreciates the financial support from CONACYT-México (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología). This study was supported by MICINN (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación) from Spanish Government, project: MAT2009-13547.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Hernández, A.G., Juárez, A., Engel, E. et al. Streptococcus sanguinis adhesion on titanium rough surfaces: effect of shot-blasting particles. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 22, 1913–1922 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4366-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4366-8