Abstract
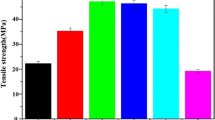
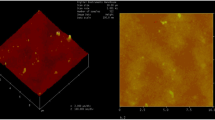
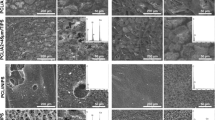
A homogenous membrane composed of chitosan (CS), sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC) and nano hydroxyapatite (n-HA) was prepared by a gradual electrostatic assembling (GEA) method. The physical and chemical properties of the membranes with different n-HA contents and CS/NaCMC ratios were characterized by Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and mechanical test. The schematic formation mechanism of the membrane was discussed. The results show that GEA is an effective method to prepare the polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) membrane, in which oppositely charged CS-NaCMC polysaccharides can assemble mildly and gradually through electrostatic interaction to form the membrane framework, while the filled n-HA crystals can regulate the structure stability of the composite membrane. The optimum preparation condition for the PEC membrane can be fixed to a content of 60 wt% n-HA, an equivalent amount of CS to NaCMC and a drying temperature of 60°C. The PEC membrane may have good prospect for guided bone regeneration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chellat F, Tabrizian M, Dumitriu S, Chornet E, Magny P, Rivard CH, Yahia L. In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of chitosan-xanthan polyionic complex. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(1):107–16.
Sæther HV, Holme HK, Maurstad G, Smidsrød O, Stokke BT. Polyelectrolyte complex formation using alginate and chitosan. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;74(4):813–21.
Böstman O, Pihlajamäki H. Clinical biocompatibility of biodegradable orthopaedic implants for internal fixation: a review. Biomaterials. 2000;21(24):2615–21.
Schwarz HH, Richau K, Paul D. Membranes from polyelectrolyte complexes. Polym Bull. 1991;25(1):95–100.
Thünemann AF, Müller M, Dautzenberg H, Joanny JF, Lowen H. Polyelectrolyte complexes. Adv Polym Sci. 2004;166:113–71.
Rinaudo M. Chitin and chitosan: properties and applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2006;31(7):603–32.
Czaja W, Krystynowicz A, Bielecki S, Brown RM. Microbial cellulose—the natural power to heal wounds. Biomaterials. 2006;27(2):145–51.
Malcolm Brown R, Saxena IM, Kudlicka K. Cellulose biosynthesis in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci. 1996;1(5):149–56.
Lal GS, Hayes ER. Determination of the amine content of chitosan by pyrolysis-gas chromatography. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 1984;6(2):183–93.
Berger J, Reist M, Mayer JM, Felt O, Peppas NA, Gurny R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydro gels for biomedical applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2004;57(1):19–34.
Peniche C, Argüelles-Monal W, de Biomateriales C. Chitosan based polyelectrolyte complexes. Macromol Symp. 2001;168(1):103–16.
Bernabé P, Peniche C, Argüelles-Monal W. Swelling behaviour of chitosan/pectin polyelectrolyte complex membranes. Effect of thermal cross-linking. Polym Bull. 2005;55(5):367–75.
Zhao Q, Qian J, An Q, Gao C, Gui Z, Jin H. Synthesis and characterization of soluble chitosan/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose polyelectrolyte complexes and the pervaporation dehydration of their homogeneous membranes. J Membr Sci. 2009;333(1–2):68–78.
Heinze T. New ionic polymers by cellulose functionalization. Macromol Chem Phys. 1998;199(11):2341–64.
Sinha VR, Singla AK, Wadhawan S, Kaushik R, Kumria R, Bansal K, Dhawan S. Chitosan microspheres as a potential carrier for drugs. Int J Pharm. 2004;274(1–2):1–33.
Gómez-Burgaz M, Garcia-Ochoa B, Torrado-Santiago S. Chitosan–carboxymethylcellulose inter polymer complexes for gastric-specific delivery of clarithromycin. Int J Pharm. 2008;359(1–2):135–43.
Feng Z, Shao Z, Yao J, Huang Y, Chen X. Protein adsorption and separation with chitosan-based amphoteric membranes. Polymer. 2009;50(5):1257–63.
Chen X, Liu J, Feng Z, Shao Z. Macroporous chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose blend membranes and their application for lysozyme adsorption. J Appl Polym Sci. 2005;96(4):1267–74.
Ren Y, Chen Z, Geng Y, Chen R, Zheng X. Usage of anisomeric square pulse with fluctuating frequency for electrochemical generation of FeO4 2− in CS–CMC bipolar membrane electrolysis cell. Chem Eng Process. 2008;47(4):708–15.
Haberska K, Ruzgas T. Polymer multilayer film formation studied by in situ ellipsometry and electrochemistry. Bioelectrochemistry. 2009;76(1–2):153–61.
Lee EJ, Shin DS, Kim HE, Kim HW, Koh YH, Jang JH. Membrane of hybrid chitosan–silica xerogel for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2009;30(5):743–50.
Jansen JA, De Ruijter JE, Janssen PTM, Paquay Y. Histological evaluation of a biodegradable polyactive (R)/hydroxyapatite membrane. Biomaterials. 1995;16(11):819–27.
Li W, Sun B, Wu P. Study on hydrogen bonds of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium film with two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;78(3):454–61.
Murugan R, Ramakrishna S. Development of nano composites for bone grafting. Compos Sci Technol. 2005;65(15–16):2385–406.
Jiang L, Li Y, Xiong C. A novel composite membrane of chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose polyelectrolyte complex membrane filled with nano-hydroxyapatite I. Preparation and properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20(8):1645–52.
Jiang LY, Li YB, Zhang L, Wang XJ. Preparation and characterization of a novel composite containing carboxymethyl cellulose used for bone repair. Mater Sci Eng C. 2009;29(1):193–8.
Wang X, Li Y, Wei J, de Groot K. Development of biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/poly (hexamethylene adipamide) composites. Biomaterials. 2002;23(24):4787–91.
Jayaraman M, Meyer U, Bühner M, Joos U, Wiesmann HP. Influence of titanium surfaces on attachment of osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Biomaterials. 2004;25(4):625–31.
Niederauer GG, McGee TD, Keller JC, Zaharias RS. Attachment of epithelial cells and fibroblasts to ceramic materials. Biomaterials. 1994;15(5):342–52.
Zhang L, Jin Y, Liu H, Du Y. Structure and control release of chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose microcapsules. J Appl Polym Sci. 2001;82(3):584–92.
Gómez-Burgaz M, Torrado G, Torrado S. Characterization and superficial transformations on mini-matrices made of inter polymer complexes of chitosan and carboxymethylcellulose during in vitro clarithromycin release. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;73(1):130–9.
Rosca C, Popa MI, Lisa G, Chitanu GC. Interaction of chitosan with natural or synthetic anionic polyelectrolytes. 1. The chitosan–carboxymethylcellulose complex. Carbohydr Polym. 2005;62(1):35–41.
Wei J, Li Y. Tissue engineering scaffold material of nano-apatite crystals and polyamide composite. Eur Polym J. 2004;40(3):509–15.
Kesting RE. Synthetic polymeric membranes: a structural perspective. New York: Wiley; 1985.
Hyder MN, Chen P. Pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol with chitosan–poly (vinyl alcohol) blend membranes: effect of CS–PVA blending ratios. J Membr Sci. 2009;340(1–2):171–80.
Bigi A, Cojazzi G, Panzavolta S, Ripamonti A, Roveri N, Romanello M, Noris Suarez K, Moro L. Chemical and structural characterization of the mineral phase from cortical and trabecular bone. J Inorg Biochem. 1997;68(1):45–51.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by China 973 fund (No. 2007CB936102) and China–Netherlands Program Strategic Alliances (No. 2008DFB50120).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Zuo, Y., Cheng, L. et al. A homogenous CS/NaCMC/n-HA polyelectrolyte complex membrane prepared by gradual electrostatic assembling. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 22, 289–297 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-4195-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-4195-1