Abstract
The suitability of zinc-based glass polyalkenoate cements (GPCs) for use in orthopaedics can be improved by the substitution of strontium into the glass phase which should impart improved radiopacity and bone forming properties to the cements without retarding strength. The purpose of this research was to produce novel GPCs based on calcium–strontium–zinc-silicate glasses and to evaluate their mechanical properties and biocompatibility with the ultimate objective of developing a new range of cements for skeletal applications. Three glass compositions, based on incremental substitutions of strontium for calcium, were synthesized; BT100 (0.16CaO, 0.36ZnO, 0.48SiO2), BT101 (0.04SrO, 0.12CaO, 0.36ZnO, 0.48SiO2) and BT102 (0.08SrO 0.08CaO, 0.36ZnO, 0.48SiO2). Each glass was then mixed with varying concentrations and molecular weights of polyacrylic acids in order to determine the working times, setting times, compressive strengths and biaxial flexural strengths of the novel cements. The maximum working time and setting time achieved was 29 and 110 s respectively; which, at present is inadequate for current clinical procedures. However, the optimum compressive and biaxial flexural strengths were up to 75 and 34 MPa respectively indicating that these formulations have potential in load bearing applications. Importantly, the substitution of Ca with Sr in the glasses did not have a deleterious effect on strengths or working times. Finally, the bioactivity of the best performing cements was determined in vitro using simulated body fluid. It was found that all cements facilitate the formation of an amorphous calcium phosphate at their surface which increases in density and coverage with time, indicating that these cement will bond directly to bone in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. M. KENNY and M. BUGGY, J. Mat. Sci. Mat. Med. 14 (2003) 923
G. LEWIS, J. Biomed. Mat. Res. 38 (1997) 155
K.-D. KHUN, Springer (2000) 141
N. J. DUNNE and J. F. ORR, ITBM-RBM 22(2) (2001) 88
M. DONKERWOLCKE, F. BURNY and D. MUSTER, Biomaterials 19 (1998) 1461
J. ORR and N. DUNNE, App. Mech. and Mat. 1–2 (2004) 127
M. J. DALBY, L. DISILVIO, E. J. HARPER and W. BONFIELD, Biomaterials 23 (2002) 569
J. PALUSSIERE, J. BERGE, A. GANGI, A. COTTEN, A. PASCO, R. BERTAGNOLI, H. JAKSCHE, P. CARPEGGIANI and H. DERAMOND, Eur. Spine. J. 14 (2005) 982
F. MONTICELLI, H.J. MEYER, and E. TUTSCH-BAUER, For.c Sci. Int. 149 (2005) 35
M.-A. CATTANI-LORENTE, C. GODIN, and J. M. MEYER, Dent. Mat. 9 (1993) 57
M. J. TYAS and M. F. BURROW, Aus. Dent. J. 49 (2004) 112
P. V. HATTON, K. HURRELL-GILLINGHAM and I. M. BROOK, J. Dent. 34 (2006) 598
D. BOYD and M. R. TOWLER, J. Mat. Sci. Mat. Med. 16 (2005) 843
J. W. NICHOLSON and A. D. WILSON, Acid-base Cements—Their Biomedical and Industrial Applications. (University Press Cambridge, 1993)
S. G. GRIFFIN and R. G. HILL, Biomaterials 20 (1999) 1579
M. A. A. DEBRUYNE and R. J. G. DEMOOR, Int. Endo. J. 37 (2004) 91
M. YAMAGUCHI and Z. J. MA, Calc. Tis. Int. 69 (2001) 158
S. POLIZZI, E. PIRA, M. FERRARA, M. BUGIANI, A. PAPALEO, R. ALBERA and S. PALMI, Neuro. Tox. 23 (2002) 761
E. REUSCHE, P. PILZ, G. OBERASCHER, B. LINDER, R. EGENSPERGER, K. GLOECKNER, E. TRINKA and B. IGLSEDER, Hum. Path. 32 (2001) 1136
J. SAWAI, S. SHINOBU, H. IGARASHI, A. HASHIMOTO, T. KOKUGAN, M. SHIMIZU and K. KOJIMA, J. Ferm. Bioeng. 86 (1998) 521
Toxilogical Profile for Strontium. Department of Health and Human Services ∼ Public Health Service (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). (2004) 23
A. BIGI, E. BOANINI, C. CAPUCCINI and M. GAZZANO, Inorg. Chim. Acta. 360 (2007) 1009
P. J. MARIE, Bone In Press, Accepted Manuscript
P. J. MARIE, Osteo. Int. 16 (2005) S7
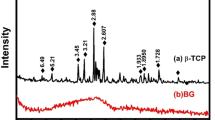
T. KOKUBO and H. TAKADAMA, Biomaterials 27 (2006) 2907
M. KAMITAKAHARA, M. KAWASHITA, T. KOKUBO and T. NAKAMURA, Biomaterials 22 (2001) 3191
International Standard 9917:1991(E). Dental Water Based Cements. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
J. A. WILLIAMS, R. W. BILLINGTON, and G. J. PEARSON, Dent. Mat. 18 (2002) 376
A. D. WILSON, R. G. HILL, C. P. WARRENS and B. G. LEWIS, J. Dent Res. 68(2) (1989) 89
S. G. GRIFFIN and R. G. HILL, Biomaterials 20(17) (1999) 1579
D. BOYD, M. R. TOWLER, S. WATTS, R. G. HILL, A. W. WREN and O. M. CLARKIN J. Mat. Sci. Mat. Med. In Press, Accepted Manuscript
D. BOYD, O. M. CLARKIN, A. W.WREN and M. R. TOWLER, Acta. Biomat. In Press, Accepted Manuscript
International Standard 5833:2002 (E). Implants for Surgery—Acrylic Resin Cements Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
C.-H. HSUEH, C. R. LUTTRELL, P. F. BECHER, Dent. Mater. 22 (2006) 460
J. A. WILLIAMS, R. W. BILLINGTON, and G. J. PEARSON, Dent. Mater. 18 (2002) 376
O. M. CLARKIN, M. R. TOWLER, G. M. INSLEY and M. E. MURPHY, J. Mat Sci. 42 (2007) 8357
N. KANZAKI, K. ONUMA, G. TREBOUX, S. TSUTSUMI and A. ITO, J. Phys. Chem. 104 (2000) 4189
Acknowledgements
The financial assistance of the Technology Development Fund, Enterprise Ireland (#TD/2005/327) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wren, A., Boyd, D. & Towler, M.R. The processing, mechanical properties and bioactivity of strontium based glass polyalkenoate cements. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 1737–1743 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3287-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3287-z