Abstract
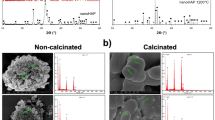
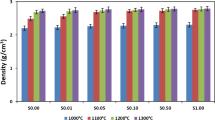
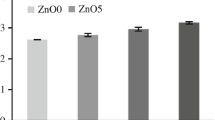
This study investigated doping titanium dioxide (TiO2) into phosphate glasses, 50 P2O5–30 CaO–20 Na2O, to control their degradation rate and enhance their biological response to be suitable scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. The thermal and structural properties were analysed using differential thermal analysis and X-ray powder diffraction. The effect of TiO2 incorporation on degradation rate, ion release, and pH changes was also carried out. In vitro cyto-biocompatibility was assessed through MG63 human osteosarcoma cells attachment and viability using scanning electron microscopy and confocal microscopy, respectively. The results showed that addition of TiO2 produced a significant increase in density and glass transition temperature. X-ray diffraction analysis showed the presence of NaCa(PO3)3 as a main phase of these glasses with titanium phosphate Ti–P2O7 only detected for 5 mol% TiO2 glasses. The degradation rate, however, was significantly reduced by one order of magnitude with incorporation of 5 mol% TiO2 which has been reflected in released ions (cations and anions) and the minimal pH changes. Moreover, addition of TiO2, 3 and 5 mol% in particular, supported the MG63 cells attachment and maintained high cell viability up to 7 days culture comparable to Thermanox®. These results suggested that TiO2 containing phosphate glasses can be a promising substrate for bone tissue engineering applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. J. MARLER, J. UPTON, R. LANGER and J. P. VACANTI, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 33(1–2) (1998) 165
F. R. A. J. ROSE and R. O. C. OREFFO, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 292(1) (2002) 1
K.-J. WALGENBACH, M. VOIGT, A. W. RIABIKHIN, C. ANDREE, D. J. SCHAEFER and G. B. STARK, Anatom. Rec. 263(4) (2001) 372
D. C. CLUPPER, J. E. GOUGH, P. M. EMBANGA, I. NOTINGHER and L. L. HENCH, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15 (2004) 803
J. E. GOUGH, I. NOTTINGHER and L. L. HENCH, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 66A (2004) 640
R. M. DAY and A. R. BOCCACCINI, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 73A(1) (2005) 73
M. CERUUTI, D. GREENSPAN and K. POWERS, Biomaterials 26 (2005) 1665
J. C. KNOWLES, J. Mater. Chem. 32 (2003) 395
I. AHMED, C. A. COLLINS, M. LEWIS, I. OLSEN and J. C. KNOWLES, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 3223
E. A. ABOU NEEL, I. AHMED, J. PRATTEN, S. N. NAZHAT and J. C. KNOWLES, Biomaterials 26 (2005) 2247
E. A. ABOU NEEl, I. AHMED, J. J. BLAKER, A. BISMARCK, A. R. BOCCACCINI, M. P. LEWIS, S. N. NAZHAT and J. C. KNOWLES, Acta Biomater. 1 (2005) 553
J. E. GOUGH, P. CHRISTIAN, C. A. SCOTCHFORD and I. A. JONES, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 66A (2003) 233
M. BITAR, V. SALIH, V. MUDERA, J. C. KNOWLES and M. LEWIS, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 2283
V. SALIH, K. FRANKS, M. JAMES, G. W. HASTINGS and J. C. KNOWLES, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 11 (2000) 615
N. MORTIZ, E. VEDEL, H. YLANEN, M. JOKINEN and M. HUPA, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15 (2004) 787
P. K. BROW, D. R. TALLANT, W. L. WARREN, A. MCINTYRE and D. E. DAY, Phys. Chem. Glasses 38(6) (1997) 300
V. RAJENDRAN, A. V. GAYATHRI DEVI, M. AZOOZ and F. H. EL-BATAL, J, Non-Cryst. Solids 353(1) (2006) 77
T. KASUGA and Y. ABE, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 243 (1999) 70
J. R. V. WAZER and K. A. HOLST, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 72 (1950) 639
J. J. BLAKER, J. E. GOUGH, V. MAQUET, I. NOTINGHER and A. R. BOCCACCINI, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 67A (2003) 1401
L.-L. TSENG, C.-J. HUANG, S.-S. HSU, J.-S. CHEN, H.-H. CHENG, H.-T. CHANGE, B.-P. JIANN and C.-R. JAN, Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 31 (2004) 732
S. J. LEE, J. S. CHOI, K. S. PARK, G. KHANG, Y. M. LEE and H. B. LEE, Biomaterials 25, (2004) 4699
M. NAVARRO, S. D. VALLE, S. MARTINEZ, S. ZEPPETELLI, L. AMBROSIO, J. A. PLANELL and M. P. GINEBRA, Biomaterials 25, (2004) 4233
M. NAVARRO, S. D. VALLE, S. MARTINEZ, S. ZEPPETELLI, L. AMBROSIO, J. A. PLANELL and M. P. GINEBRA, Biomaterials 25, (2004) 4233
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge the EPSRC for providing the funding to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abou Neel, E.A., Knowles, J.C. Physical and biocompatibility studies of novel titanium dioxide doped phosphate-based glasses for bone tissue engineering applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 377–386 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3079-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3079-5