Abstract
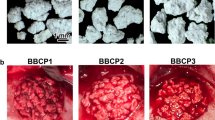
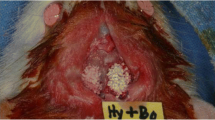
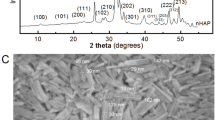
The purpose of this study was to investigate the bone regenerative effect of calcium phosphate glass in vivo. We prepared two different sizes of calcium phosphate glass powder using the system CaO-CaF2-P2O5-MgO-ZnO; the particle size of the powders were 400 μm and 40 μm. 8 mm calvarial critical-sized defects were created in 60 male Sprague-Dawley rats. The animals were divided into 3 groups of 20 animals each. Each defect was filled with a constant weight of 0.5 g calcium phosphate glass powder mixed with saline. As controls, the defect was left empty. The rats were sacrificed 2 or 8 weeks after postsurgery, and the results were evaluated using radiodensitometric and histological studies; they were also examined histomorphometrically. When the bigger powders with 400 μm particle were grafted, the defects were nearly completely filled with new-formed bone in a clean healing condition after 8 week. When smaller powders with 40 μm particle were transplanted, new bone formation was even lower than the control group due to a lot of inflammatory cell infiltration. It was concluded that the prepared calcium phosphate glass enhanced the new bone formation in the calvarial defect of Sprague-Dawley rats and it is expected to be a good potential materials for hard tissue regeneration. The particle size of the calcium phosphate was crucial; 400 μm particles promoted new bone formation, while 40 μm particles inhibited it because of severe inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.A. ZANDER, J Periodontol 47 (1976) 261.
S.G. JEFFREY, Comp Cont Educ Dent 18 (1997) 1013.
I. AUKHIL, J Perio Res. 18 (1983) 643.
M. R. DRAGOO, J Periodontol 44 (1973) 599.
B. J. SAMUEL, Int J Periodot Rest Dent. 17 (1997) 359.
R. A. YUKNA, J Periodontol 64 (1994) 2.
K. KURASHINA, Biomaterials 23 (2002) 407.
J. DONG, ibid 23 (2002) 4493.
M. JARCHO, J Bioeng 1 (1977) 78.
M. L. RABALIS, J Periodontol 52 (1981) 680.
R. A. YUKNA, ibid 65 (1994) 177.
S. J. FROUM, ibid 53 (1982) 719.
B. S. MOSKOW, ibid 54 (1983) 455.
Y. ABE, Bioceramics 1 (1988) 181.
S. KIHARA, J Am Ceram Soc. 67 (1984) C100.
R. Z. LEGEROS, J Mater Sci. 39 (2004) 5577.
Y. K. LEE, J Biomed Mater Res. 69 A (2004) 188.
J. P. SCHMITZ, Clin Orthop Rel Res. 205 (1986) 299.
E. FREEMAN, J Perio Res. 8 (1973) 229.
K. TAGAKI, Ann Surg. 196 (1982) 100.
L. J. MARDEN, J Biomed Mater Res. 28 (1994) 1127.
C. BOSCH, J Craniofac Surg. 9 (1998) 310.
J. P. SCHMITZ, Acta Anat 138 (1990) 185.
P. DUCHEYNE, J Biomed Mater Res. 19 (1985) 273.
F. B. BAGAMBISA, J Oral Maxillofac Implants 5 (1990) 217.
S. G. JEFFREY, Comp Cont Educ Dent. 18 (1997) 1013.
O. GAUTHIER, Biomaterial 19 (1998) 133.
M. H. MANKANI, Biotech Bioeng 72 (2001) 96.
J. D. BRUIJN, Abstract of the 28th annual meeting of the Biomaterials Society, 427, 2002.
S. KAMAKURA, J Dent Rer. 78 (1999) 1682.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, HJ., Kim, KN., Kim, KM. et al. Effect of calcium phosphate glass on bone formation in calvarial defects of Sprague-Dawley rats. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 17, 807–813 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-9839-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-9839-9