Abstract
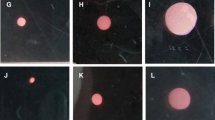
Understanding how a specific biomaterial may influence chondrocyte adhesion, proliferation and gene expression is important in cartilage tissue engineering. In this study several biodegradable polymers that are commonly used in tissue engineering were evaluated with respect to their influence on chondrocyte attachment, proliferation and gene expression. Primary cultures of porcine chondrocytes were performed in films made of poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), poly-D,L-lactic acid (PDLLA), poly-(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA), or polycaprolactone (PCL). Chondrocytes adhered to PDLLA or PLGA after 1-day incubation better than to PLLA or PCL. After 7 or 14 day culture, the cell numbers on PDLLA or PLGA was still higher than PLLA or PCL. The results suggested that cell attachment and growth might depend on degradation rate of biodegradable polymers. Along with the fact that PDLLA or PLGA supported expression of chondrocyte specific genes more than PLLA or PCL, the former two materials seemed to be more suitable for cartilage tissue engineering than the latter ones. Besides, we found that chondrocyte phenotype prior to seeding was important in the expression of ECM proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. I. CAPLAN, Sci Am 251 (1984) 84.
A. I. CAPLAN, M. ELYADERANI, Y. MOCHIZUKI, S. WAKITANI and V. M. GOLDBERG, Clin. Orthop. (1997) 254.
S. W. O’DRISCOLL, F. W. KEELEY and R. B. SALTER, J. Bone. Joint. Surg. Am. 68 (1986) 1017.
E. BELL, in “Principles of Tissue Engineering” (Academic Press, USA, 2000). p. xxxv.
J. A. HUBBELL, Bio-Technology 13 (1995) 565.
L. E. FREED, G. Vunjak-Novakovic, R. J. Biron, D. B. Eagles, D. C. Lesnoy and S. K. BARLOW, et al., Biotechnology (N Y) 12 (1994) 689.
L. G. CIMA, J. P. VACANTI, C. VACANTI, D. INGBER, D. MOONEY and R. LANGER, J. Biomech. Eng. 113 (1991) 143.
L. E. FREED, J. C. MARQUIS, A. NOHRIA, J. EMMANUAL, A. G. MIKOS and R. LANGER, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 27 (1993) 11.
N. A. PEPPAS and R. LANGER, Science 263 (1994) 1715.
S. PULAPURA and J. KOHN, J. Biomater. Appl. 6 (1992) 216.
D. A. GRANDE, C. HALBERSTADT, G. NAUGHTON, R. SCHWARTZ and R. MANJI, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 34 (1997) 211.
M. SITTINGER, D. Reitzel, M. Dauner, H. Hierlemann, C. Hammer and E. KASTENBAUER, et al., J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 33 (1996) 57.
S. L. ISHAUG-RILEY, L. E. OKUN, G. PRADO, M. A. APPLEGATE and A. RATCLIFFE, Biomaterials 20 (1999) 2245.
S. H. HSU, C. L. TSAI and C. M. TANG, Artif. Organs 26 (2002) 647.
K. VON DER MARK, V. GAUSS, H. VON DER MARK and P. MULLER, Nature 267 (1977) 531.
P. BENYA, J. SCHAFFER, Cell 30 (1982) 215.
K. ELIMA, E. VUORIO, FEBS Lett. 258 (1989) 195.
V. LEFEBVRE, C. PEETERS-JORIS and G. VAES, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1051 (1990) 266.
C. W. ARCHER, J. MCDOWELL, M. T. BAYLISS, M. D. STEPHENS and G. BENTLEY, J. Cell. Sci. 97 (Pt 2) (1990) 361.
A. L. AULTHOUSE, M. BECK, E. GRIFFEY, J. SANFORD, K. ARDEN and M. A. MACHADO, et al., In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 25 (1989) 659.
Y. J. KIM, R. L. SAH, J. Y. DOONG and A. J. GRODZINSKY, Anal. Biochem. 174 (1988) 168.
P. CHOMCZYNSKI and N. SACCHI, Anal. Biochem. 162 (1987) 156.
T. A. HORBETT and M. B. SCHWAY, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 22 (1988) 763.
M. D. EVANS and J. G. STEELE, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 40 (1998) 621.
S. I. ERTEL, B. D. RATNER and T. A. HORBETT, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 24 (1990) 1637.
T. A. HORBETT, J. J. WALDBURGER, B. D. RATNER and A. S. HOFFMAN, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 22 (1988) 383.
W.-B. TSAI, T.-C. WEI, M.-C. LIN, J.-Y. WANG and C.-H. CHENM, J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Edn. 16 (2005) 699.
C. G. PITT, T. A. Marks and A. SCHINDLER, in “Controlled Release of Bioactive Materials” (Academic Press, Inc., New York, 1980). p. 19.
S. KAY, A. THAPA, K. M. HABERSTROH and T. J. WEBSTER, Tissue Eng. 8 (2002) 753.
J. GAO, L. NIKLASON and R. LANGER, J. Biomed. Mater Res. 42 (1998) 417.
V. SALDANHA and D. A. GRANDE, Biomaterials 21 (2000) 2427.
B. DE CROMBRUGGHE, V. LEFEBVRE, R. R. BEHRINGER, W. BI, S. MURAKAMI and W. HUANG, Matrix Biol. 19 (2000) 389.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, WB., Chen, CH., Chen, JF. et al. The effects of types of degradable polymers on porcine chondrocyte adhesion, proliferation and gene expression. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 17, 337–343 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-8234-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-8234-x