Abstract
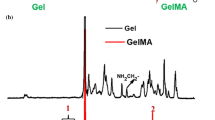
This study was conducted to understand the effects of aging methacrylated gelatin solutions on the properties of gelatin-HydroThaneTM Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN) films. The latter were prepared from methacrylated gelatin solutions that were either freshly made or stored at different concentrations and temperatures for various periods. The morphology, swelling stability and mechanical properties of the IPNs were then accordingly characterized. The IPNs prepared with aged solutions showed a reduced phase separation; changed from a network-like structure to a continuous phase structure; and demonstrated higher swelling stabilities and higher elasticity under optimal aging conditions, compared to the IPN prepared with a fresh methacrylated gelatin solution. An increase in viscosity and a change in phase transition of aged methacrylated gelatin solutions were also observed, presumably due to the physical structuring of methacrylated gelatin chains (e.g., by the formation of a helix structure), thus altering the resulting IPN characteristics. A better understanding of the effects of aging methacrylated gelatin solution on the formation and properties of gelatin-HydroThaneTM IPNs should enable us to further develop our composite biomaterials for different dressing applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. GUPTA and A. K. SRIVASTAVA, Polym. Int. 35 (1994) 109
S. H. TEOH, Z. G. TANG and S. RAMAKRISHNA, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 10 (1999) 343
D. S. JONES, D. W. J. MCLAUGHLIN, C. P. MCCOY and S. P. GORMAN, Biomaterials 26 (2005) 1761
X. HAN, B. CHEN and F. GUO, IPN around the World, edited by L.H. SPERLING, S. C. KIM (John Wiley & Sons, 1997), p.241
K. MURATA, J. SACHIN, E. ETORI and T. ANAZAWA, Polym. 43 (2002) 2845
B. L. LEE and S. C. KIM, Polym. Adv. Tech. 6 (1995) 402
K. MIMURA, H. ITO and H. FUJIOKA, Polym. 41 (2000) 4451
G. Y. WANG and C. P. HU, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 84 (2002) 1629
X. CAO and L. ZHANG, Biomacromolecules 6 (2005) 671
Y. LU, L. ZHANG, X. ZHANG and Y. ZHOU, Polym. 44 (2003) 6689
B. WANG, W. GONG, W. H. LIU, Z. F. WANG, N. QI, X. W. LI, M. J. LIU and S. J. LI, Polym. 44 (2003) 4047
S. M. TOSH, A. G. MARANGONI, F. R. HALLETT and I. J. BRITT, Food Hydrocolloids 17 (2003) 503
C. JOLY-DUHAMEL, D. HELLIO and M. DJABOUROV, Langmuir 18 (2002) 7208
http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/index.html
M. CHANGEZ, V. KOUL, B. KRISHNA, A. K. DINDA and V. CHOUDHARY, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 139
P. CEBE, J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 43 (2005) 629
H. L. FRISCH, Prog. Org. Coat. 27 (1996) 67
L. A. UTRACKI, J Rheol 35 (1991) 1615
H. TANAKA, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 (1996) 787
J. S. TURNER and Y.-L. CHENG, Macromol. 33 (2000) 3714
L. A. DE GRAAF, J. BEYER and M. MOLLER, J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 33 (1995) 1073
L. LIU, P. H. COOKE, D. R. COFFIN, M. L. FISHMAN and K. B. HICKS, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 92 (2004) 1893
H. -W. KANG, Y. TABATA and Y. IKADA, J. Bioactive Compatible Polym. 14 (1999) 331
Y. S. LIPATOV, Prog. Polym. Sci. 27 (2002) 1721
O. MIYAWAKI, Y. NORIMATSU, H. KUMAGAI, Y. IRIMOTO, H. KUMAGAI and H. SAKURAI, Biopolymers 70 (2003) 482
M. -W. WANG, C.-T. LEE, M.-S. LIN, Polym. Intern. 44 (1997) 503
P. V. KOZLOV, Polym. 24 (1983) 651
A. MÜHLEBACH, B. MÜLLER, C. PHARISA, M. HOFMANN, B. SEIFERLING and D. GUERRY, J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 35 (1997) 3603
F. H. SILVER, D. L. CHRISTIANSEN, P. S. SNOWHIL and Y. CHEN, Connect. Tissue Res. 41 (2000) 155
T.-T. HSIEH, K.-H. HSIEH, G. P. SIMON and C. TIU, Polym. 40 (1999) 3153
N. KURISAWA and N. YUI, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 199 (1998) 1547
P. GHOSH, A. CHAKRABARTI, S. B. KAR and R CHOWDHURY, Synthetic Metals 144 (2004) 241
K. MURATA and T. ANAZAWA, Polym. 43 (2002) 6575
F. J. HUA and C. P. HU, Euro. Polym. J. 35 (1999) 103
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Defence Research and Development Canada for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H.T., Mok, M., Martineau, L. et al. Hydrogel-elastomer composite biomaterials: 2. Effects of aging methacrylated gelatin solutions on the preparation and physical properties of interpenetrating polymer networks. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 18, 1025–1035 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0072-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0072-3