Abstract
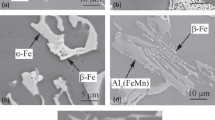
The mechanical properties of solution treated ASTM F-75 alloys with various carbon contents have been studied. Alloys cast under the same conditions were subjected to solution treatment for several periods and then their tensile properties were evaluated. In the as-cast conditions, the alloys exhibited higher strength values with increasing carbon content whereas their ductility was not significantly affected. For the solution treated alloys, the variation of the strength was characterized by a progressive increase for short treatment times until a maximum value was achieved, which was followed by a diminution in this property for longer treatment times. This behavior was more accentuated for the case of the alloys with medium carbon contents, which also exhibited the highest values of strength. Furthermore, the alloy’s ductility was enhanced progressively with increasing solution treatment time. This improvement in ductility was significantly higher for the medium carbon alloys compared with the rest of the studied alloys. Thus, high and low carbon contents in solution treated ASTM F-75 alloys did not produced sufficiently high tensile properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. R. MORRAL, J. Mater. 1 (1966) 384.
K. ASGAR and F. A. PEYTON, J. Dent. Res. 40 (1961) 63.
C. P. SULLIVAN, J. D. VARIN and M. J. DONACHIE, in “Cobalt-Base Superalloys” (Centre d’Information du Cobalt, Brussels, 1970) p. 11.
M. RIDDIHOUGH, Found. Trade. J. 5 (1959) 421.
M. GÓMEZ, H. MANCHA, J. RODRÍ GUEZ, J. ESCOBEDO, M. CASTRO and M. MÉNDEZ, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 34 (1997) 157.
J. B. VANDER SANDE, J. R. COKE and J. WULFF, Metall. Mater. Trans. A7 (1976) 389.
K. RAJAN and J. B. VANDER SANDE, J. Mater. Sci. 17 (1982) 769.
T. KILNER, W. M. LAANEMAE, R. PILHAR, G. C. WEATHERLY and S. R. MACEWEN, ibid. 21 (1986) 1349.
H. S. DOBBS and J. L. M. ROBERTSON, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 18 (1983) 391.
T. KILNER, R. M. PILLIAR and G. C. WEATHERLY, ibid. 16 (1982) 63.
J. COHEN and R. M. ROSE, ibid. 12 (1978) 935.
C. O. MONTERO, M. TALAVERA and H. F. LÓPEZ, Metall. Mater. Trans. A30 (1999) 614.
Z. GARZA, M. HERRERA, M. CASTRO, E. RAMÍ REZ, M. MÉNDEZ and J. MÉNDEZ, J. Mat. Eng. Perf. 10 (2001) 153.
H. MANCHA, E. CARRANZA, I. ESCALANTE, G. MENDOZA, M. MÉNDEZ, F. CEPEDA and E. VALDÉS, Metall. Mater. Trans. A32 (2001) 979.
M. CAUDILLO, M. HERRERA, M. CASTRO, E. RAMÍ REZ, C. GONZALEZ and J. ISLAS, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 59 (2002) 378.
E. RAMÍ REZ, M. CASTRO, M. MÉNDEZ, J. LACAZE, M. HERRERA and G. LESOULT, Scrip. Mater. 47 (2002) 811.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera, M., Espinoza, A., Méndez, J. et al. Effect of C content on the mechanical properties of solution treated as-cast ASTM F-75 alloys. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 16, 607–611 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-005-2530-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-005-2530-8