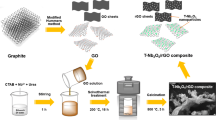
Abstract
The formation of a solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer and Li2O species at an anode driven by thermodynamic spontaneity not only consumes the active Li-ions (Li+), but also generates battery capacity loss. The unstable SEI layer growth directly degrades both battery efficiency and cycling stability. Thereby, prelithiated materials were prepared to militate against the enlargement of Li consumption for Li-ion batteries (LIBs). Here, we demonstrated the hydrothermal synthesis of lithium metasilicate (Li2SiO3), a prelithiated material, with physical characterizations exposing the microflower-like clusters evolved from the attachment of their high-purity primary plates. The electrochemical performance of the pristine Li2SiO3 provided a poor cycling capability in a half coin-cell test with a final discharge capacity of 17 mAh g−1 over 200 cycles, while the silica on reduced graphene oxide (SiO2/rGO) composite represented only ~ 290 mAh g−1. Conversely, the Li2SiO3–SiO2/rGO composite exhibited excellent cyclability over the pristine and SiO2/rGO with final discharge specific capacity up to ~ 470 mAh g−1 at the 200th cycle. Despite the revealed similar electrochemical patterns of the obtained cyclic voltammograms (CVs) for these materials, the curiosity of continuously increased capacity for the Li2SiO3–SiO2/rGO composite and Li+ compensation mechanisms upon cycling of Li2SiO3 were still clearly unsolved. The cycling capacities of the composite were distinctly observed as a great improvement after composite formation between Li2SiO3 and SiO2/rGO.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data in this research article will be made available on request.
Abbreviations
- SEI:
-
Solid electrolyte interface
- rGO:
-
Reduced graphene oxide
- LIBs:
-
Lithium-ion batteries
- ICE:
-
Initial coulombic efficiency
- CE:
-
Coulombic efficiency
- EC:
-
Ethylene carbonate
- DMC:
-
Dimethyl carbonate
- NMP:
-
N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
- DI water:
-
Deionized water
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- SAED:
-
Selected area electron diffraction
- CV:
-
Cyclic voltammetry
References
N. Mahmood, T. Tang, Y. Hou, Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1600374 (2016)
W. Qi, J.G. Shapter, Q. Wu, T. Yin, G. Gao, D. Cui, J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 19521 (2017)
L. He, Z. Gu, Y. Zhang, H. Jing, P. Li, Energ Fuel 37, 4835 (2023)
Z.-L. Xu, X. Liu, Y. Luo, L. Zhou, J.-K. Kim, Prog. Mater. Sci. 90, 1 (2017)
B.S. Parimalam, A.D. MacIntosh, R. Kadam, B.L. Lucht, J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 22733 (2017)
S.J. An, J. Li, C. Daniel, D. Mohanty, S. Nagpure, D.L. Wood, Carbon 105, 52 (2016)
H. Adenusi, G.A. Chass, S. Passerini, K.V. Tian, G. Chen, Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 1 (2023)
X. Lan, X. Zhou, Z. Jiao, K. Wang, B. Liu, P. Zhang, B. Xu, Mater. Lett. 353, 135300 (2023)
C. Sun, X. Zhang, C. Li, K. Wang, X. Sun, Y. Ma, Energy Storage Mater. 32, 497 (2020)
X. Li, H. Yang, CrystEngComm 16, 4501 (2014)
A. Alemi, S. Khademinia, Int. Nano Lett. 5, 15 (2014)
Y. Zhu, W. Hu, J. Zhou, W. Cai, Y. Lu, J. Liang, X. Li, S. Zhu, Q. Fu, Y. Qian, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Interfaces 11, 18305 (2019)
Y. Zhou, S. Feng, P. Zhu, H. Guo, G. Yan, X. Li, M. Su, Y. Liu, Z. Wang, J. Wang, Chem. Eng. J. 415, 128998 (2021)
N. Kuganathan, L.H. Tsoukalas, A. Chroneos, Solid State Ion. 335, 61 (2019)
X. Guo, K. Xie, Y. Wang, Z. Kang, W. Zhou, S. Cheng, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13, 5645 (2018)
R. Raccichini, A. Varzi, S. Passerini, B. Scrosati, Nat. Mater. 14, 1 (2015)
V. Laokawee, T. Autthawong, B. Chayasombat, A. Yu, T. Sarakonsri, Solid State Phenom. 302, 51 (2020)
O. Namsar, T. Autthawong, V. Laokawee, R. Boonprachai, M. Haruta, H. Kurata, A. Yu, T. Chairuangsri, T. Sarakonsri, Sustain. Energ. Fuels 4, 4625 (2020)
H. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Yang, Sci. Rep. 10, 5545 (2020)
N. Mahamai, T. Autthawong, W. Yodying, C. Yodbunork, O. Namsar, T. Sarakonsri, Microflower-Like Lithium Metasilicate for Li-Ion Battery Anode, (The Microscopy Society of Thailand (MST) (Pathum Thani, Thailand, 2022), p.52
M. Nie, D. Chalasani, D.P. Abraham, Y. Chen, A. Bose, B.L. Lucht, J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 1257 (2013)
C. Cao, I.I. Abate, E. Sivonxay, B. Shyam, C. Jia, B. Moritz, T.P. Devereaux, K.A. Persson, H.-G. Steinrück, M.F. Toney, Joule 3, 762 (2019)
A. Wang, S. Kadam, H. Li, S. Shi, Y. Qi, NPJ Comput. Mater. 4, 15 (2018)
E. Peled, S. Menkin, J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, A1703 (2017)
W. Li, F. Wang, M. Ma, J. Zhou, Y. Liu, Y. Chen, RSC Adv. 8, 33652 (2018)
S. Hao, Z. Wang, L. Chen, Mater. Des. 111, 616 (2016)
K.W. Schroder, H. Celio, L.J. Webb, K.J. Stevenson, J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 19737 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This research work was partially supported by Chiang Mai University, and the authors would like to express their gratitude to the Renewable Energy Laboratory-Advanced Battery Research Unit, Chiang Mai University, for sample preparation, battery cell fabrication, and electrochemical measurements. Also, the authors appreciate the characterizations and facility support provided by the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai University. This research project was financially supported by the Fundamental Fund 2023, Center of Excellence in Materials Science and Technology under the Administration of Materials Science Research Center of Chiang Mai University. This research has received funding support from the NSRF via the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research and Innovation [Grant No. B37G660018].
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Naruephon Mahamai. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Naruephon Mahamai and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahamai, N., Autthawong, T., Namsar, O. et al. Composite design for electrochemical improvement through prelithiated Li2SiO3 in rice husk-derived SiO2/rGO as lithium-ion battery anode. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 657 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12422-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12422-w