Abstract
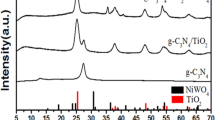
In this study a ternary composite MgO–TiO2@g-C3N4 was synthesized via a simplistic ultrasonic route and then it was characterized using various techniques. The development of tri-phased nanostructure was revealed by the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. The X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) study confirmed the presence of the constituent elements while the bonding patterns were investigated by the Fourier transform infrared (FTIR). The as-acquired MgO–TiO2@g-C3N4 heterojunction exhibited an optimal competence (94%) and enhanced photo-degradation rate constant towards the Alizarin Red S (ARS) dye in just 60 min under visible-light illumination. The heterostructured combined interfaces assembly of g-C3N4 and MgO–TiO2 NPs, have efficiently prompted the photo-excited charges separation, and blocked the recombination incidence. Henceforth, the prolonged lifetime has led to incessant generation of photoactive− species that ultimately upgraded the photo-degradation process. Furthermore, the fabricated hybrid photocatalysts showed superior recycling stability. A plausible photocatalytic reaction mechanism based on the S-scheme has been proposed. The advanced photocatalytic competence to degrade the AR dye under visible light irradiation makes MgO–TiO2@g-C3N4 a favorable photocatalyst for the dye-containing wastewater treatment.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This report encompasses all the facts and information that have been documented or analyzed during this study.
References
H.B. Hassan, A. Hashim, H.M. Abduljalil, Tailoring structural, optical characteristics of CuO/In2O3 nanoparticles-doped organic material for photodegradation of dyes pollutants. Polym. Bull. 80, 9059 (2022)
F. Wang et al., Preparation of high-strength dynamic polysaccharide nanocomposite hydrogels and their application towards dye adsorption. Ind. Crops Prod. 189, 115704 (2022)
O. Sacco et al., Behavior of N-doped TiO2 and N-doped ZnO in photocatalytic Azo dye degradation under UV and visible light irradiation: a preliminary investigation. Catalysts 12(10), 1208 (2022)
S.A. Moghadam, F. Farzaneh, Synthesis and investigation of template effects on nanoporous Bi2O3 morphologies by sol gel method as photocatalysts for degradation of some organic dyes as water pollutants. J. Cluster Sci. 33(2), 495–502 (2022)
N.U.D. Mir et al., Simpler is better: A heterometallic (Mn-Na) metal organic framework (MOF) with a rare myc topology synthesized from bench chemicals for selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 146, 110046 (2022)
Z. Abaker et al., Superior uptake of Cu (II) from aquatic media via Y2O3-ZnO nanostructures. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 30, 100879 (2022)
S. Aravindhan et al., Delonix regia biomass as an eco-friendly biosorbent for effective Alizarin Red S textile dye removal: characterization, kinetics, and isotherm studies. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 25, 101721 (2023)
S. Zaman et al., Synthesis of mediator free hollow BiFeO3 spheres/porous g-C3N4 Z-scheme photocatalysts for CO2 conversion and Alizarin Red S degradation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 162, 107534 (2023)
J. Zhou et al., Polyaniline/carbon hybrids: Synthesis and application for alizarin red S removal from water. Colloids Surf. A 676, 132204 (2023)
J. Fu et al., g-C3N4-Based heterostructured photocatalysts. Adv. Energy Mater. 8(3), 1701503 (2018)
J. Wen et al., A review on g-C3N4-based photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 391, 72–123 (2017)
X. Liu et al., Recent developments of doped g-C3N4 photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51(8), 751–790 (2021)
A. Modwi et al., Effect of annealing on physicochemical and photocatalytic activity of Cu5% loading on ZnO synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(12), 12974–12984 (2016)
A. Modwi et al., Structural and electrical characterization of Ba/ZnO nanoparticles fabricated by co-precipitation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30(7), 2633–2644 (2020)
A. Modwi et al., Fabrication and adsorption studies of paste/TiO2 nanocomposites through recycling of spent dry batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33(32), 24869 (2022)
A. Kerrami et al., Efficient photodegradation of azucryl red by copper-doped TiO2 nanoparticles—experimental and modeling studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28(41), 57543–57556 (2021)
A. Toghan, A. Modwi, Boosting unprecedented indigo carmine dye photodegradation via mesoporous MgO@ g-C3N4 nanocomposite. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 419, 113467 (2021)
A. Toghan et al., Mesoporous TiO2@ g-C3N4 composite: construction, characterization, and boosting indigo carmine dye destruction. Diam. Relat. Mater. 118, 108491 (2021)
Y. Zhao et al., Fabrication of a Sb2MoO6/g-C3N4 photocatalyst for enhanced RhB degradation and H2 generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 124(25), 13771–13778 (2020)
K.N. Van et al., Facile construction of S-scheme SnO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst for improved photoactivity. Chemosphere 289, 133120 (2022)
Z. Zhu et al., Construction of high-dispersed Ag/Fe3O4/g-C3N4 photocatalyst by selective photo-deposition and improved photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B 182, 115–122 (2016)
A. Modwi et al., Superior removal of dyes by mesoporous MgO/g-C3N4 fabricated through ultrasound method: adsorption mechanism and process modeling. Environ. Res. 205, 112543 (2022)
J. Feng et al., Improvement of g-C3N4 photocatalytic properties using the Hummers method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 479, 1–6 (2016)
I. Troppová et al., Unconventionally prepared TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalysts for photocatalytic decomposition of nitrous oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 430, 335–347 (2018)
G. Sui et al., Preparation and characterization of g-C3N4/Ag–TiO2 ternary hollowsphere nanoheterojunction catalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance. J. Alloys Compds. 823, 153851 (2020)
S. Obregón, Y. Zhang, G. Colón, Cascade charge separation mechanism by ternary heterostructured BiPO4/TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B 184, 96–103 (2016)
N. Ghane, S. Sadrnezhaad, Combustion synthesis of g-C3N4/Fe2O3 nanocomposite for superior photoelectrochemical catalytic performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 534, 147563 (2020)
Y. Chen et al., Construction of heterostructured g-C3N4/Ag/TiO2 microspheres with enhanced photocatalysis performance under visible-light irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(16), 14405–14414 (2014)
Y.R. Girish et al., Facile and rapid synthesis of solar-driven TiO2/g-C3N4 heterostructure photocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices 7(2), 100419 (2022)
N. Madima et al., TiO2-modified g-C3N4 nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes in aqueous solution. Heliyon 8(9), 10683 (2022)
Z. Zhang et al., A nonmetal plasmonic Z-scheme photocatalyst with UV-to NIR-driven photocatalytic protons reduction. Adv. Mater. 29(18), 1606688 (2017)
S. Ghattavi, A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, GC-MASS detection of methyl orange degradation intermediates by AgBr/g-C3N4: Experimental design, bandgap study, and characterization of the catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 45(46), 24636–24656 (2020)
E. Fathi, P. Gharbani, Modeling and optimization removal of reactive Orange 16 dye using MgO/g-C3N4/zeolite nanocomposite in coupling with LED and ultrasound by response surface methodology. Diam. Relat. Mater. 115, 108346 (2021)
S. Tamin et al., Mg 2–x Mn x SiO 4 compound obtained via sol–gel method: structural, morphological and electrochemical properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 86, 24–33 (2018)
J. Liu et al., Effect of ionic radius on colossal permittivity properties of (A, Ta) co-doped TiO2 (A= alkaline-earth ions) ceramics. Ceram. Int. 46(8), 12059–12066 (2020)
S. Mahanty, S. Roy, S. Sen, Effect of Sn doping on the structural and optical properties of sol–gel TiO2 thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 261(1), 77–81 (2004)
N. Bayal, P. Jeevanandam, Synthesis of TiO2− MgO mixed metal oxide nanoparticles via a sol− gel method and studies on their optical properties. Ceram. Int. 40(10), 15463–15477 (2014)
C. Yang et al., 2D/2D Ti3C2 MXene/g-C3N4 nanosheets heterojunction for high efficient CO2 reduction photocatalyst: dual effects of urea. Appl. Catal. B 268, 118738 (2020)
R. Dholam et al., Hydrogen production by photocatalytic water-splitting using Cr-or Fe-doped TiO2 composite thin films photocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 34(13), 5337–5346 (2009)
N. Nithya, S. Gopi, G. Bhoopathi, An amalgam of Mg-Doped TiO 2 nanoparticles prepared by Sol-Gel method for effective antimicrobial and photocatalytic activity. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 4594–4607 (2021)
S. Yousefi, B. Ghasemi, M.P. Nikolova, Morpho/Opto-structural characterizations and XRD-assisted estimation of crystallite size and strain in MgO nanoparticles by applying Williamson-Hall and size–strain techniques. J. Cluster Sci. 33(5), 2197–2207 (2022)
S.V.G. Kumari, K. Pakshirajan, G. Pugazhenthi, Synthesis and characterization of MgO nanostructures: a comparative study on the effect of preparation route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 294, 127036 (2023)
D. Guo et al., Facile fabrication of g-C3N4/MIL-53 (Al) composite with enhanced photocatalytic activities under visible-light irradiation. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 29(10), 690–697 (2015)
C.F. Toncón-Leal et al., Characterization of mesoporous region by the scanning of the hysteresis loop in adsorption–desorption isotherms. Adsorption 27(7), 1109–1122 (2021)
F.J. Sotomayor, K.A. Cychosz, M. Thommes, Characterization of micro/mesoporous materials by physisorption: concepts and case studies. Acc. Mater. Surf. Res. 3(2), 34–50 (2018)
C.V. Tran et al., Effective removal of Pb (II) from aqueous media by a new design of Cu–Mg binary ferrite. ACS Omega 5(13), 7298–7306 (2020)
M. Kapilashrami et al., Experimental evidence for ferromagnetism at room temperature in MgO thin films. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22(34), 345004 (2010)
P. Mei et al., The enhanced photodegradation of bisphenol A by TiO2/C3N4 composites. Environ. Res. 182, 109090 (2020)
M. Alcudia-Ramos et al., Fabrication of g-C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction composite for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production. Ceram. Int. 46(1), 38–45 (2020)
L. Lin et al., A highly efficient TiO 2@ ZnO n–p–n heterojunction nanorod photocatalyst. Nanoscale 5(2), 588–593 (2013)
P.M. Sherwood, Paul van der Heide: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: an introduction to principles and practices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 405(8), 2415–2416 (2013)
X. Guo et al., Synergistic photocatalytic and Fenton-like degradation of organic contaminants using peroxymonosulfate activated by CoFe2O4@ g-C3N4 composite. Environ. Technol. 42(14), 2240–2253 (2021)
M. Morales-Luna et al., Effect of a CdSe layer on the thermo-and photochromic properties of MoO3 thin films deposited by physical vapor deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 123(28), 17083–17091 (2019)
M. Pérez-González, S. Tomás, Surface chemistry of TiO2-ZnO thin films doped with Ag. Its role on the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Catal. Today (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.08.009
J. Lei et al., An inverse opal TiO 2/gC 3 N 4 composite with a heterojunction for enhanced visible light-driven photocatalytic activity. Dalton Trans. 48(10), 3486–3495 (2019)
L. Cui et al., Facile preparation of Z-scheme WO3/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 391, 202–210 (2017)
Z. Zhao et al., In situ preparation of WO3/g-C3N4 composite and its enhanced photocatalytic ability, a comparative study on the preparation methods. Eng. Sci. 7(4), 52–58 (2019)
Y.-J. Sun et al., Simultaneous construction of dual-site phosphorus modified g-C3N4 and its synergistic mechanism for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 517, 146192 (2020)
X. Zhang et al., One-step synthesis of bN-TiO2/C nanocomposites with high visible light photocatalytic activity to degrade Microcystis aeruginosa. Catalysts 10(5), 579 (2020)
C. Wang et al., Improved photocatalytic oxidation performance of gaseous acetaldehyde by ternary g-C3N4/Ag-TiO2 composites under visible light. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 602, 699–711 (2021)
H. Abbasi-Asl, M.M. Sabzehmeidani, M. Ghaedi, Efficient degradation of metronidazole antibiotic by TiO2/Ag3PO4/g–C3N4 ternary composite photocatalyst in a continuous flow-loop photoreactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9(5), 105963 (2021)
J. Zhang et al., Synthesis of novel ternary dual Z-scheme AgBr/LaNiO3/g-C3N4 composite with boosted visible-light photodegradation of norfloxacin. Molecules 25(16), 3706 (2020)
Y. Feng et al., Can Tauc plot extrapolation be used for direct-band-gap semiconductor nanocrystals? J. Appl. Phys. 117(12), 125701 (2015)
P. Jubu et al., Tauc-plot scale and extrapolation effect on bandgap estimation from UV–vis–NIR data–a case study of β-Ga2O3. J. Solid State Chem. 290, 121576 (2020)
B.D. Viezbicke et al., Evaluation of the Tauc method for optical absorption edge determination: ZnO thin films as a model system. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 252(8), 1700–1710 (2015)
J. Lu et al., One-step synthesis of g-C3N4 hierarchical porous structure nanosheets with dramatic ultraviolet light photocatalytic activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 214, 19–25 (2016)
P. Niu et al., Graphene-like carbon nitride nanosheets for improved photocatalytic activities. Adv. Func. Mater. 22(22), 4763–4770 (2012)
A.P. Alivisatos, Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271(5251), 933–937 (1996)
B. Zhang et al., Molten salt assisted in-situ synthesis of TiO2/g-C3N4 composites with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity and adsorption ability. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 362, 1–13 (2018)
N. Omrani, A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A novel quadripartite Cu2O-CdS-BiVO4-WO3 visible-light driven photocatalyst: Brief characterization and study the kinetic of the photodegradation and mineralization of sulfasalazine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 400, 112726 (2020)
Y. Zou et al., Controllable interface-induced co-assembly toward highly ordered mesoporous Pt@ TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Adv. Func. Mater. 28(50), 1806214 (2018)
E. El-Mossalamy, Potentiometric and spectroscopic studies of sulfonamide azo-dye complexes with some transition metal ions and uranium. Port. Electrochim. Acta 27(2), 143–152 (2009)
K. Santhi, C. Rani, S. Karuppuchamy, Degradation of alizarin red S dye using Ni doped WO 3 photocatalyst. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 5033–5038 (2016)
J.P. Shubha et al., Facile green synthesis of semiconductive ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of dyes from the textile industry: a kinetic approach. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 34(5), 102047 (2022)
N. Ali et al., Characterization and deployment of surface-engineered cobalt ferrite nanospheres as photocatalyst for highly efficient remediation of alizarin red S dye from aqueous solution. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 5063–5073 (2020)
S. Senobari, A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A novel ternary nano-composite with a high photocatalyitic activity: characterization, effect of calcination temperature and designing the experiments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 394, 112455 (2020)
C.-K. Huang et al., Enhanced photocatalytic performance of BiVO4 in aqueous AgNO3 solution under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 399, 10–19 (2017)
E. Djatoubai et al., engineered cobalt single-atoms@ BiFeo3 heteronanostructures for highly efficient solar water oxidation. Small (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202206293
M. Althamthami et al., Influence of hole-scavenger and different withdrawn speeds on photocatalytic activity of Co3O4 thin films under sunlight irradiation. Ceram. Int. 48(21), 31570–31578 (2022)
L. Zhao et al., Fe2WO6 coupling on cube-like SrTiO3 as a highly active S-scheme heterojunction composite for visible light photocatalysis and antibacterial applications. Environ. Technol. Innov. 28, 102941 (2022)
B. Van den Bogaert et al., Photochemical recycling of europium from Eu/Y mixtures in red lamp phosphor waste streams. Green Chem. 17(4), 2180–2187 (2015)
J. Korpanty, L.R. Parent, N.C. Gianneschi, Enhancing and mitigating radiolytic damage to soft matter in aqueous phase liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy in the presence of gold nanoparticle sensitizers or isopropanol scavengers. Nano Lett. 21(2), 1141–1149 (2021)
R. Senthil et al., Synthesis and characterization of low-cost g-C3N4/TiO2 composite with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible-light irradiation. Opt. Mater. 64, 533–539 (2017)
R.G. Pearson, Absolute electronegativity and hardness: application to inorganic chemistry. Inorg. Chem. 27(4), 734–740 (1988)
Z. Yang et al., Solid-state, low-cost, and green synthesis and robust photochemical hydrogen evolution performance of ternary TiO2/MgTiO3/C photocatalysts. Iscience 14, 15–26 (2019)
J. Liu, Origin of high photocatalytic efficiency in monolayer g-C3N4/CdS heterostructure: a hybrid DFT study. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(51), 28417–28423 (2015)
T. Mazzo et al., Controlling the electronic, structural, and optical properties of novel MgTiO3/LaNiO3 nanostructured films for enhanced optoelectronic devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2(5), 2612–2620 (2019)
L. Fu et al., Probing charge transfer under external bias at Cu/SrTiO3 heterojunction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 592, 153269 (2022)
L. Zhang et al., Emerging S-scheme photocatalyst. Adv. Mater. 34(11), 2107668 (2022)
X. Li et al., Enhanced photocatalytic degradation and H2/H2O2 production performance of S-pCN/WO2. 72 S-scheme heterojunction with appropriate surface oxygen vacancies. Nano Energy 81, 105671 (2021)
B. Li et al., Novel synthesis of Z-scheme α-Bi2O3/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst and its enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance: influence of calcination temperature. Chin. Chem. Lett. 31(10), 2705–2711 (2020)
S. Kohtani, A. Kawashima, H. Miyabe, Reactivity of trapped and accumulated electrons in titanium dioxide photocatalysis. Catalysts 7(10), 303 (2017)
M. Baruah et al., Batch sorption–photodegradation of alizarin Red S using synthesized TiO 2/activated carbon nanocomposite: an experimental study and computer modelling. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 5, 1–13 (2020)
S. Sood et al., The visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of alizarin red S using Bi-doped TiO 2 nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 38(7), 3127–3136 (2014)
S. Siva Kumar, V.R. Rao, G.N. Rao, Efficient photocatalytic degradation of alizarin red S by silver-impregnated zinc oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India Sect. A: Phys. Sci. 83, 309–315 (2013)
S.D. Abraham et al., Eco-friendly and green synthesis of BiVO4 nanoparticle using microwave irradiation as photocatalayst for the degradation of Alizarin Red S. J. Mol. Struct. 1113, 174–181 (2016)
V. Rodríguez-González et al., Photocatalytic decomposition of synthetic alizarin red S by nickel doped TiO 2. Top. Catal. 54, 490–495 (2011)
A. Gul et al., Incorporation of anatase tio2 to highly porous silica (bmms) for photo-degradation of alizarin red dye in aqueous solution. ChemistrySelect 6(26), 6816–6825 (2021)
H. Bouchaaba, B. Bellal, M. Trari, Removal of a commercial dye, alizarin red, by solar Photocatalysis involving the Heterosystem ZnO–SnO 2. Theoret. Exp. Chem. 53, 417–422 (2018)
F. Anjum et al., Photo-degradation, thermodynamic and kinetic study of carcinogenic dyes via zinc oxide/graphene oxide nanocomposites. J. Market. Res. 15, 3171–3191 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU- RG23101).
Funding
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU- RG23101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in the study’s design, preparation of materials, data collection, and analysis. Each author submitted feedback on earlier article draughts. All authors read and authorized the completed manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors indicate no financial or personal affiliations that could have influenced their work in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alqarni, L.S., Alghamdi, M.D., Alhussain, H. et al. S-scheme MgO–TiO2@g-C3N4 nanostructures as efficient photocatalyst for alizarin red S photodegradation. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 239 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-11996-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-11996-9