Abstract
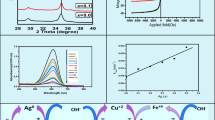
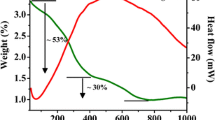
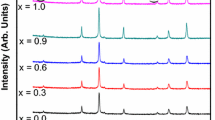
The Ag–Cr doped Zn nanoferrite series (Zn(1-2x)AgxCrxFe2O4, where x = 0.0 to 0.25) has been prepared using the co-precipitation method. The spinel ferrite nanoparticles structure, magnetic and catalytic properties were investigated. X-ray diffraction showed that the synthesized samples contained a single cubic spinel structure, and crystallite size was in the nano-range (7–15 nm). Fourier-transform infrared spectra showed two significant absorption bands at 600 cm−1 and 400 cm−1, which belonged to the tetrahedral (A) and octahedral (B) sites, respectively. These samples transformed from the paramagnetic phase into the superparamagnetic phase as the Ag–Cr doping increased. Based on what they were like before, these samples could be used as catalysts to speed up the breakdown of different dyes when H2O2 is present. When our group used these materials with the malachite green dye, the oxidation process proceeded according to first-order kinetics. This research showed that the dye concentration, H2O2 concentration, pH, catalyst dose, and temperature all affect how catalytically active they are.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
R. Jarariya, A review based on spinel ferrite nanomaterials-MgFe2O4-synthesis of photocatalytic dye degradation in visible light response. J. Environ. Treat. Tech. 10(2), 149–56 (2022)
Y. Xu, J. Ai, H. Zhang, The mechanism of degradation of bisphenol A using the magnetically separable CuFe2O4/peroxymonosulfate heterogeneous oxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 309, 87–96 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.023
A.K.S. Rocha, L.B. Magnago, J.J. Santos, V.M. Leal, A.A.L. Marins, V.C.B. Pegoretti, S.A.D. Ferreira, M.F.F. Lelis, M.B.J.G. Freitas, Copper ferrite synthesis from spent Li-ion batteries for multifunctional application as catalyst in photo Fenton process and as electrochemical pseudocapacitor. Mater. Res. Bull. 113, 231–240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.02.007
R. Jasrotia, A. Verma, R. Verma, J. Ahmed, S.K. Godara, G. Kumar, A. Mehtab, T. Ahmad, S. Kalia, Photocatalytic dye degradation efficiency and reusability of Cu-substituted Zn-Mg spinel nanoferrites for wastewater remediation. J. Water Process Eng. 1(48), 102865 (2022)
M. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Akbari, T. Gholami, Removal of malachite green (a toxic dye) from water by cobalt ferrite silica magnetic nanocomposite: herbal and green sol-gel autocombustion synthesis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 42, 24846–24860 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.08.077
K.C. Das, S.S. Dhar, Rapid catalytic degradation of malachite green by MgFe2O4 nanoparticles in presence of H2O2. J. Alloys Compd. 828, 154462 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154462
G. Katoch, J. Prakash, R. Jasrotia, A. Verma, R. Verma, S. Kumari, T. Ahmad, S.K. Godara, J. Ahmed, A. Kandwal, M. Fazil, P.K. Maji, S. Kumar, G. Kumar, Sol-gel auto-combustion developed Nd and Dy co-doped Mg nanoferrites for photocatalytic water treatment, electrocatalytic water splitting and biological applications. J. Water Process Eng. 53, 103726 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.103726
M. Verma, M. Mitan, H. Kim, D. Vaya, Efficient photocatalytic degradation of Malachite green dye using facilely synthesized cobalt oxide nanomaterials using citric acid and oleic acid. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1(155), 110125 (2021)
A.M. El-Sawy, M.A. Salem, I.A. Salem, M.M. Hydara, A.B. Zaki, Sonophotocatalytic degradation of malachite green in aqueous solution using six competitive metal oxides as a benchmark. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 22(3), 579–94 (2023)
B. Arora, S. Sharma, S. Dutta, S. Yadav, P. Rana, R.K. Sharma, Fabrication of a recyclable magnetic halloysite-based cobalt nanocatalyst for the efficient degradation of bisphenol A and malachite green. Mater. Adv. 3(15), 6373–84 (2022)
P. Kotwal, R. Jasrotia, J. Prakash, J. Ahmed, A. Verma, R. Verma, A. Kandwal, S.K. Godara, S. Kumari, P.K. Maji, M. Fazil, T. Ahmad, M.S. Tamboli, N. Sharma, R. Kumar, Magnetically recoverable sol-gel auto-combustion developed Ni(1–x)Cu(x)Dy(y)Fe(2-y)O(4) magnetic nanoparticles for photocatalytic, electrocatalytic, and antibacterial applications. Environ. Res. 231, 116103 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116103
N.M. Mahmoodi, Zinc ferrite nanoparticle as a magnetic catalyst: synthesis and dye degradation. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 4255–4260 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.06.070
A. Tawfik, M.G. Alalm, H.M. Awad, M. Islam, M.A. Qyyum, A.A. Al-Muhtaseb, A.I. Osman, M. Lee, Solar photo-oxidation of recalcitrant industrial wastewater: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 20(3), 1839–62 (2022)
S.K. Ray, D. Dhakal, S.W. Lee, Visible light driven Ni–BaMo3O10 photocatalyst for Indigo Carmine degradation: Mechanism and pathways. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 105, 104697 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104697
T. Zhou, G. Zhang, P. Ma, X. Qiu, H. Zhang, H. Yang, G. Liu, Novel magnetically separable Ag3PO4@CuFe2O4 micro-nanocomposite with highly enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 210, 271–274 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.09.044
M. Su, C. He, V.K. Sharma, M. Abou Asi, D. Xia, X. Zhong Li, H. Deng, Y. Xiong, Zinc ferrite: synthesis, characterization, and mesoporous photocatalytic activity with H2O2/visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 211–212, 95–103 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.006
K. Mohit, V.R. Gupta, N. Gupta, S.K. Rout, Structural and microwave characterization of Ni0.2Co xZn0.8-xFe2O4 for antenna applications. Ceram. Int. 40, 1575–1586 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.07.045
H.B. Desai, A. Kumar, A.R. Tanna, Structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles synthesis through auto combustion technique. Eur. Chem. Bull. 10(3), 186–190 (2021)
M. Mozaffari, H. Masoudi, Zinc ferrite nanoparticles: new preparation method and magnetic properties. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 2563–2567 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2625-x
R. Sharma, S. Singhal, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of zinc doped nickel ferrite and their application in photo catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Physica B 414, 83–90 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2013.01.015
R.M. Sebastian, S. Xavier, E.M. Mohammed, Dielectric behavior and AC conductivity of Mg2+ doped zinc ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel technique. Ferroelectrics 481, 48–56 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2015.1049491
S.M. Chavan, M.K. Babrekar, S.S. More, K.M. Jadhav, Structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Zn ferrite thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 507, 21–25 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.07.171
G. Satyanarayana, G. Nageswara Rao, K.V. Babu, G.V. Santosh Kumar, G. Dinesh Reddy, Effect of Cr 3+ substitution on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Ni 0.7 Zn 0.2 Cu 0.1 Fe 2–x Cr x O 4 Ferrites. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 74, 684–694 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.74.684
E.E. Ateia, M. Farag, Synthesis of cobalt/calcium nanoferrites with controllable physical properties. Appl. Phys. A 125, 1–10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2593-x
A. Goyal, S. Bansal, S. Singhal, Facile reduction of nitrophenols: comparative catalytic efficiency of MFe2O4 (M = Ni, Cu, Zn) nano ferrites. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 39, 4895–4908 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.01.050
M.A. Ansari, A. Baykal, S. Asiri, S. Rehman, Synthesis and characterization of antibacterial activity of spinel chromium-substituted copper ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical application. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28, 2316–2327 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0889-5
M.R. Bhandare, H.V. Jamadar, A.T. Pathan, B.K. Chougule, A.M. Shaikh, Dielectric properties of Cu substituted Ni0.5-xZn 0.3Mg0.2Fe2O4 ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 113–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.11.173
K.M. Batoo, M.S.A. El-Sadek, Electrical and magnetic transport properties of Ni-Cu-Mg ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 566, 112–119 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.02.129
M. Madhukara Naik, H.S. Bhojya Naik, G. Nagaraju, M. Vinuth, H. RajaNaika, K. Vinu, Green synthesis of zinc ferrite nanoparticles in Limonia acidissima juice: characterization and their application as photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Microchem. J. 146, 1227–1235 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.02.059
F. Majid, J. Rauf, S. Ata, I. Bibi, M. Yameen, M. Iqbal, Hydrothermal synthesis of zinc doped nickel ferrites: evaluation of structural, magnetic and dielectric properties. Z. Phys. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2018-1305
A.A. Ati, A.H. Abdalsalam, A.S. Hasan, Thermal, microstructural and magnetic properties of manganese substitution cobalt ferrite prepared via co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(3), 3019–37 (2021)
N. Amin, M. Sajjad, U. Hasan, Z. Majeed, Z. Latif, M. Ajaz, K. Mahmood, A. Ali, K. Mehmood, M. Fatima, M. Akhtar, M. Imran, A. Bibi, M. Zahir, F. Jabeen, N. Bano, Structural, electrical, optical and dielectric properties of yttrium substituted cadmium ferrites prepared by Co-Precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 46(13), 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.079
A.I. Borhan, P. Samoila, V. Hulea, A.R. Iordan, M.N. Palamaru, Photocatalytic activity of spinel ZnFe2-xCrxO4 nanoparticles on removal Orange I azo dye from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45, 1655–1660 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.12.002
M. Hashim, S. Alimuddin, S.E. Kumar, R.K. Shirsath, J. Kotnala, R. Shah, Kumar, Influence of Cr3+ ion on the structural, ac conductivity and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Mg ferrite. Ceram. Int. 39, 1807–1819 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.08.028
S.J. Haralkar, R.H. Kadam, S.S. More, S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, S. Patil, D.R. Mane, Substitutional effect of Cr 3+ ions on the properties of Mg-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Physica B 407, 4338–4346 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2012.07.030
M.A. Gabal, Y.M. AlAngari, A. Saaed, Properties of Co 1 − x Zn x Fe 2 O 4 Nanocrystalline Auto-Combustion Method, (2017) 1–12.
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, M. Ahmad, M.S. Nazir, M. Imran, A. Ali, A. Sattar, G. Murtaza, Evaluation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of CuZnNi (CuxZn0.5−xNi0.5Fe2O4) nanocrystalline ferrites for core, switching and MLCI’s applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 260–268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.08.035
D.S. Nair, M. Kurian, Chromium-zinc ferrite nanocomposites for the catalytic abatement of toxic environmental pollutants under ambient conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 344, 925–941 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.045
P. Samoila, L. Sacarescu, A.I. Borhan, D. Timpu, M. Grigoras, N. Lupu, M. Zaltariov, V. Harabagiu, Magnetic properties of nanosized Gd doped Ni-Mn-Cr ferrites prepared using the sol-gel autocombustion technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 92–97 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.10.174
T.R. Tatarchuk, N.D. Paliychuk, M. Bououdina, B. Al-Najar, M. Pacia, W. Macyk, A. Shyichuk, Effect of cobalt substitution on structural, elastic, magnetic and optical properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 731, 1256–1266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.103
R. Sagayaraj, S. Aravazhi, C. Selva kumar, S. Senthil kumar, G. Chandrasekaran, Tuning of ferrites (CoxFe3-xO4) nanoparticles by co-precipitation technique. SN Appl. Sci. 1, 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0244-7
H. Zhu, H. Zou, Ultra-efficient catalytic degradation of malachite green dye wastewater by KMnO 4-modified biochar (Mn/SRBC). RSC Adv. 12(41), 27002–11 (2022)
F. Meshkani, M. Rezaei, Preparation of nanocrystalline metal (Cr, Al, Mn, Ce, Ni, Co and Cu) modified ferrite catalysts for the high temperature water gas shift reaction. Renew. Energy. 74, 588–598 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.08.037
P.A. Vinosha, B. Xavier, S. Krishnan, S.J. Das, Investigation on zinc substituted highly porous improved catalytic activity of NiFe2O4 nanocrystal by co-precipitation method. Mater. Res. Bull. 101, 190–198 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.01.026
P. Thakur, R. Sharma, M. Kumar, S.C. Katyal, N.S. Negi, N. Thakur, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Super paramagnetic la doped Mn-Zn nano ferrites: dependence on dopant content and crystallite size. Mater. Res. Express. 3, 075001 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/3/7/075001
Y. Khan, E. Kneller, Structure and magnetic moment of zinc-substituted γ iron oxide. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 7, 9–11 (1978)
Z.Ž Lazarević, Č Jovalekić, V.N. Ivanovski, A. Rečnik, A. Milutinović, B. Cekić, N.Ž Romčević, Characterization of partially inverse spinel ZnFe2O4 with high saturation magnetization synthesized via soft mechanochemically assisted route. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 75, 869–877 (2014)
S. Torkian, A. Ghasemi, R. Shoja Razavi, Cation distribution and magnetic analysis of wideband microwave absorptive CoxNi1−xFe2O4 ferrites. Ceram. Int. 43, 6987–6995 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.124
R.E. El Shater, E.H. El-Ghazzawy, M.K. El-Nimr, Study of the sintering temperature and the sintering time period effects on the structural and magnetic properties of M-type hexaferrite BaFe12O19. J. Alloys Compd. 739, 327–334 (2018)
Y. Yafet, C. Kittel, Antiferromagnetic arrangements in ferrites. Phys. Rev. 87, 290 (1952)
M. Sugimoto, The past, present, and future of ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 269–280 (1999)
M. Ergüt, D. Uzunoğlu, A. Özer, Efficient decolourization of malachite green with biosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles loaded carbonated hydroxyapatite as a reusable heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 54(8), 786–800 (2019)
H. Zhang, G. Li, L. Deng, H. Zeng, Z. Shi, Heterogeneous activation of hydrogen peroxide by cysteine intercalated layered double hydroxide for degradation of organic pollutants: Performance and mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 543, 183–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.02.059
R. Qu, B. Xu, L. Meng, L. Wang, Z. Wang, Ozonation of indigo enhanced by carboxylated carbon nanotubes: performance optimization, degradation products, reaction mechanism and toxicity evaluation. Water Res. 68, 316–327 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.017
F.F. Mohamed, P.M. Allah, A.P. Mehdi, M. Baseem, Photoremoval of Malachite Green (MG) using advanced oxidation process. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 15(3), 65–70 (2011)
Y. Hu, Y. Li, J. He, T. Liu, K. Zhang, X. Huang, L. Kong, J. Liu, EDTA-Fe(III) Fenton-like oxidation for the degradation of malachite green. J. Environ. Manag. 226, 256–263 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.029
S. Hashemian, Fenton-like oxidation of malachite green solutions: Kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Chem. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/809318
A. Bellal, Wet hydrogen peroxide catalytic oxidation of malachite green over Fe2O3/Kaolin catalyst: optimization of reaction parameters, (2021) 1–7. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355467298 Wet.
A. Serrano-Martínez, M.T. Mercader-Ros, I. Martínez-Alcalá, C. Lucas-Abellán, J.A. Gabaldón, V.M. Gómez-López, Degradation and toxicity evaluation of azo dye Direct red 83:1 by an advanced oxidation process driven by pulsed light. J. Water Process. Eng. 37, 101530 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101530
A. Verma, S. Thakur, G. Mamba, Prateek, R.K. Gupta, P. Thakur, V.K. Thakur, Graphite modified sodium alginate hydrogel composite for efficient removal of malachite green dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 148, 1130–1139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.142.
I. Hasan, A. Bassi, K.H. Alharbi, I.I. Binsharfan, R.A. Khan, A. Alslame, Sonophotocatalytic degradation of malachite green by nanocrystalline chitosan-ascorbic acid@nife2 o4 spinel ferrite. Coatings. 10, 1–19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121200
M.S.C. Sandeep Thakur, Removal of Malachite Green Dye from aqueous solution by Fenton Oxidation, (2016) 254–259.
G.H. Dang, T.T. Le, A.K. Ta, T.N. Ho, T.V. Pham, T.V. Doan, T.H. Luong, Removal of Congo red and malachite green from aqueous solution using heterogeneous Ag/ZnCo-ZIF catalyst in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Green Process Synth. 9(1), 567–77 (2020)
M. Yuan, X. Fu, J. Yu, Y. Xu, J. Huang, Q. Li, D. Sun, Green synthesized iron nanoparticles as highly efficient fenton-like catalyst for degradation of dyes. Chemosphere. 261, 127618 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127618
A.H. Gemeay, M.E. El-halwagy, R.G. El-sharkawy, A.B. Zaki, Chelation mode impact of copper ( II ) -aminosilane complexes immobilized onto graphene oxide as an oxidative catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 2761–2772 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.020
Z. Harrache, M. Abbas, T. Aksil, M. Trari, Thermodynamic and kinetics studies on adsorption of Indigo Carmine from aqueous solution by activated carbon. Microchem. J. 144, 180–189 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.09.004
K.C. Das, S.S. Dhar, Remarkable catalytic degradation of malachite green by zinc supported on hydroxyapatite encapsulated magnesium ferrite (Zn/HAP/MgFe2O4) magnetic novel nanocomposite. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 4592–4606 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04294-x
S. Jauhar, S. Singhal, M. Dhiman, Manganese substituted cobalt ferrites as efficient catalysts for H2O2 assisted degradation of cationic and anionic dyes: their synthesis and characterization. Appl. Catal. A 486, 210–218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.08.020
D. Badmapriya, I.V. Asharani, Dye degradation studies catalysed by green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 9, 409–416 (2016)
Z.H. Jaffari, S.M. Lam, J.C. Sin, H. Zeng, Boosting visible light photocatalytic and antibacterial performance by decoration of silver on magnetic spindle-like bismuth ferrite. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 1(101), 103–15 (2019)
E.M. Mostafa, E. Amdeha, Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye by highly stable visible-light-responsive Fe-based tri-composite photocatalysts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 69861–69874 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20745-6
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AHG: conceptualization, supervision, investigation reviewing, and editing. ESS: methodology, writing—original drafts preparation. AHM: conceptualization, supervision. MMA-G: investigation formal analysis, reviewing. REE-S: investigation formal analysis, reviewing, and editing. RK: reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Shater, R.E., Abdel-Galeil, M.M., Gemeay, A.H. et al. Synthesis and structural, magnetic, and catalytic characteristics Ag–Cr doped Zn nanoferrite series for dye degradation utilizing advanced oxidation processes. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 271 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-11964-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-11964-3