Abstract
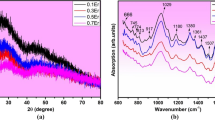
In this paper, a vitreous matrix 65TeO2–15Li2O–20ZnO (TLZ) doped with different concentrations of Sm2O3 (0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.35, 0.5, and 1.0 mol%) was produced via melt-quenching technique. The influence of the concentration of Sm2O3 ions on physical and thermal properties, and the Raman gain coefficient of TLZ glass samples, has been investigated. From the X-ray diffractograms, it was obtained that adding Sm2O3 ions had no discernible effect on the overall properties of the TLZ glass samples, keeping the amorphous nature of the glass structure. In addition, it was observed that the density of the samples increased with the incorporation of the Sm3+ ions. Furthermore, the molar volume of the TLZ glass samples increased and the oxygen packing density (OPD) decreased, with the insertion of the Sm2O3. These results indicated that the Sm3+ ions are actively involved in the glass structure by forming bonds with the non-bridging oxygen (NBO) species. Another important result was the investigated sample thermal stability (ΔT) that remains constant up to a concentration of 0.15 mol% of Sm2O3 and then increases with the additional Sm2O3. In addition, the Raman analyses, for an excitation at 532 nm, revealed that the incorporation of Sm3+ ions does not significantly affect the Te–O–Te bonding environment. The refractive index of the samples was determined, and it was obtained that the refractive index increased with the incorporation of Sm3+ ions. Finally, the Raman gain coefficient was also investigated for the peaks centered at 988 and 2091 cm−1, and it exhibited a minimum value at a Sm2O3 concentration of approximately 0.5 mol%. In conclusion, these results indicate that the TLZ glass samples are good candidates for high-speed optical communications due to their interesting properties and higher Raman cross-section compared to other glassy systems.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analyzed during the current work are included.
References
A. Murali, R.P. Sreekanth Chakradhar, J. Lakshmana Rao, EPR studies of Gd3 + ions in lithium tetra boro-tellurite and lithium lead tetra boro-tellurite glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 364, 142–149 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2005.04.002
S. Rada, E. Culea, M. Rada, The experimental and theoretical investigations on the structure of the gadolinium-lead-tellurate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 128, 464–469 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.03.032
D. Tang, Y. Tian, D. Dorosz, X. Wang, X. Yang, Y. Liu, X. Zhang, J. Zhang, S. Xu, 2–3 μm mid-infrared luminescence of Ho3+/Yb3+ co-doped chloride-modified fluorotellurite glass. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 285, 121833 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.121833
P. Vani, G. Vinitha, R. Praveena, M. Durairaj, T.C.S. Girisun, N. Manikandan, Influence of holmium ions on the structural and optical properties of barium tellurite glasses. Opt. Mater. (Amst) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2023.113438
J. Ding, C. Li, L. Xia, Y. Zhang, J. Li, Y. Zhou, A new Nd3+/Tm3+/Ho3 + tri-doped tellurite glass for multifunctional applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 150, 111777 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2022.111777
D. Souri, H. Zaliani, E. Mirdawoodi, M. Zendehzaban, Thermal stability of sb-V2O5–TeO2 semiconducting oxide glasses using thermal analysis. Measurement 82, 19–25 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2015.12.026
D. Souri, Physical and thermal characterization and glass stability criteria of amorphous silver-vanadate-tellurate system at different heating rates: inducing critical Ag2O/V2O5 ratio. J. Non Cryst. Solids 475, 136–143 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.09.008
S.F. Hosseini, D. Souri, Optical properties of tellurovanadate—molybdate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 13506–13515 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08285-8
P. Patra, K. Annapurna, Progress in materials science transparent tellurite glass-ceramics for photonics applications: a comprehensive review on crystalline phases and crystallization mechanisms. Prog Mater. Sci. 125, 100890 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2021.100890
M. Kubliha, M. Çelikbilek, A. Erçin, O. Bo, P. Kostka, Thermal, optical, structural, and electrical properties of ZnO–MoO3–TeO2 glasses. Ceram. Int. 49, 12950–12958 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.12.166
S. Bairagi, K.S. Bartwal, G.F. Ansari, Materials today: proceedings investigations on optical and photoluminescence properties of Dy3 + doped zinc tellurite glass. Mater. Today? Proc. 80, 799–805 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.11.131
N.M. Yusoff, M.R. Sahar, S.K. Ghoshal, Sm3+:Ag NPs assisted modification in absorption features of magnesium tellurite glass. J. Mol. Struct. 1079, 167–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.09.039
E.S. Yousef, H.H. Hegazy, M.M. Elokr, Y.M. Aboudeif, Raman spectroscopy and Raman gain coefficient of telluroniobium-zinc-lead oxyglasses doped with rare earth. Chalcogenide Lett. 12, 653–663 (2015)
A. Gonçalves, M.A. Ribeiro, J.V. Gunha, A. Somer, V.S. Zanuto, N.G.C. Astrath, D.T. Dias, M.A.F. Santos, C. Jacinto, E.K. Lenzi, A. Novatski, A generalized Drude–Lorentz model for refractive index behavior of tellurite glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 16949–16955 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01696-0
A. Wagh, Y. Raviprakash, M.P. Ajithkumar, V. Upadhyaya, S.D. Kamath, Effect of Sm2O3 on structural and thermal properties of zinc fluoroborate glasses. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed.) 25, 1185–1193 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63714-1
V. Rodriguez, G. Guery, M. Dussauze, F. Adamietz, T. Cardinal, K. Richardson, Raman gain in tellurite glass: how combination of IR, Raman, hyper-Raman and hyper-Rayleigh brings new understandings. J. Phys. Chem. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b07627
K. Damak, E. Sayed, A.S. Al-shihri, H.J. Seo, C. Rüssel, R. Maâlej, Quantifying Raman and emission gain coefficients of Ho3 + doped TeO2–ZnO–PbO–PbF2–Na2O (TZPPN) tellurite glass. J. Solid State Sci. 28, 74–80 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2013.12.012
R.F. Muniz, V.S. Zanuto, M.S. Gibin, J.V. Gunha, A. Novatski, J.H. Rohling, A.N. Medina, M.L. Baesso, Down- and up-conversion processes in Nd3/Yb3+ co-doped sodium calcium silicate glasses with concomitant Yb2+ assessment. J. Rare Earths 41, 342–348 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2022.01.020
A. Gonçalves, V.S. Zanuto, G.A.S. Flizikowski, A.N. Medina, F.L. Hegeto, A. Somer, J.L. Gomes, J.V. Gunha, G.K. Cruz, C. Jacinto, N.G.C. Astrath, A. Novatski, Luminescence and upconversion processes in Er3+-doped tellurite glasses. J. Lumin. 201, 110–114 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.04.031
F. Aouaini, A. Maaoui, N. Bel, H. Mohamed, M.M. Alanazi, L. Abu, E. Maati, Visible to infrared down conversion of Er3 + doped tellurite glass for luminescent solar converters. J. Alloys Compd. 894, 162506 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162506
D. Said, M.F. Malek, H. Nurhafizah, E.S. Sazali, A.L. Anis, R. Hisam, Influence of vanadium in sensitized luminescence mechanism and Judd–Ofelt analysis in Er3+/Ho3 + doped mixed ionic-electronic glass system. Opt. Mater. (Amst) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2023.114169
G. Eryurek, S. Tabanli, T. Buhari, M. Erdem, B.-Z. Glasses, Color tuning and optical temperature sensing properties of upconversion emission in Yb3+/Er3+/Tm3+ doped boro-zinctellurite glasses. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 12, 076005 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ace550
F. Ren, C. Song, Y. Cong, Y. Wu, Y. Bai, D. Zhou, Near-infrared luminescence enhancement in Yb3+/Ho3 + co-doped bismuth-tellurite glass by tailoring glass network. Ceram. Int. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.07.257
M. Sheoran, P. Sehrawat, M. Kumar, R.K. Malik, Crystal structure and optical analysis of new reddish-orange Sm3+ doped BaGd2ZnO5 nano-crystalline materials for multifunctional applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 145, 111522 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111522
A. Tarafder, A.R. Molla, S. Mukhopadhyay, B. Karmakar, Fabrication and enhanced photoluminescence properties of Sm3+-doped ZnO–Al2O3–B2O3–SiO2 glass derived willemite glass–ceramic nanocomposites. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 36, 1463–1470 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2014.03.035
M. Li, D. Li, E.Y.B. Pun, H. Lin, Excitability remodeling in Sm3+-doped aluminosilicate glass phosphors. J. Alloys Compd. 966, 171652 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.171652
B. Mu, J. Huang, R. Song, Y. Dong, B. Qi, Optical analysis of Dy3+/Sm3 + co-doped NaY(MoO4)2 phosphors for warm white LED. J. Alloys Compd. 945, 168916 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.168916
I. Ullah, C.S. Sarumaha, A. Angnanon, I. Khan, M. Shoaib, S.A. Khattak, S. Kothan, N. Sangwaranatee, G. Rooh, J. Kaewkhao, Spectral features of Gd2O3 modified Sm3+ doped lithium strontium borate glasses for solid-state laser applications. Ceram. Int. 49, 13774–13782 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.12.255
M.R. Chandana, B.R.R. Krushna, J. Malleshappa, K. Manjunatha, T.-E. Hsu, S.Y. Wu, S.C. Sharma, B.D. Prasad, B. Subramanian, H. Nagabhushana, Simple fabrication of novel Sm3 + doped BaGd2ZnO5 nanophosphors for flexible displays, improved data security applications, and solid-state lighting applications. Mater. Today Sustain. 22, 100397 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100397
S.G.M. Mushtaque, A.R. Kadam, S.J. Dhoble, High color purity and color tunability in Sm3+/Eu3 + activated/co-activated Sr6Ca4(PO4)6F2 phosphor for WLED and display devices application. J. Mol. Struct. 1274, 134510 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134510
J.Y. Chen, J.Q. Chen, L.J. Li, W.N. Zhang, L.P. Chen, H. Guo, A four-mode high-sensitive optical thermometer based on Ca3LiZnV3O12:Sm3+ phosphors. Mater. Today Chem. 29, 101409 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2023.101409
S. Sailaja, C. Nageswara Raju, C. Adinarayana Reddy, B. Deva Prasad Raju, Y.-D. Jho, B. Sudhakar Reddy, Optical properties of Sm3+-doped cadmium bismuth borate glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 1038, 29–34 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.01.052
S.N.F. Zalamin, M.H.M. Zaid, K.A. Matori, M.K.A. Karim, Y. Yaakob, W.M. Cheong, Z.W. Loh, M.I. Sayyed, Role of Sm3 + ions as network-modifying on elastic, mechanical, and radiation shielding properties of MgO–B2O3–TeO2 glasses. Prog Nucl. Energy. 161, 104752 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2023.104752
A. Novatski, A. Somer, A. Gonçalves, R.L.S. Piazzetta, J.V. Gunha, A.V.C. Andrade, E.K. Lenzi, A.N. Medina, N.G.C. Astrath, R. El-Mallawany, Thermal and optical properties of lithium-zinc-tellurite glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 231, 150–158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.03.078
D.T. Dias, A. Gonçalves, A. Somer, V.S. Zanuto, R.A. dos Santos, J.V. Gunha, N.G.C. Astrath, A. Novatski, Raman gain coefficient of Er3 + doped TeO2–Li2O–ZnO glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 16917–16921 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01633-1
S.V. Sagar, S. Babu, K.V. Rao, Emission spectroscopy of Sm3 + ion-activated zinc phosphate glass for reddish–orange lighting applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11608-y
J.V. Gunha, T. de Sales, R.F. Muniz, W. Ferreira, G.C. Astrath, A. Novatski, Spectroscopic studies of TeO2-based glasses doped with Sm3+ ions and its use as an optical temperature sensor, Preprint. (2024)
L. Bolundut, E. Culea, G. Borodi, R. Stefan, C. Munteanu, P. Pascuta, Influence of Sm3+:Ag codoping on structural and spectroscopic properties of lead tellurite glass ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41, 2931–2939 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.10.119
M. Sq, A. Mm, R.M.D. Sahar, A. Kf, Influence of Sm2O3 ion concentration on structural and thermal. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-873.1000222
B. Eraiah, Optical properties of samarium doped zinc–tellurite glasses. Bull. Mater. Sci. 29, 375–378 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704138
R. Mondal, D. Biswas, A. Sundar, R.K.N. Ningthemcha, D. Deb, S. Bhattacharya, S. Kabi, Influence of samarium content on structural, thermal, linear and non-linear optical properties of ZnO–TeO2–P2O5 glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123561
S.O. Baki, L.S. Tan, C.S. Kan, H.M. Kamari, A.S.M. Noor, M.A. Mahdi, Structural and optical properties of Er3+–Yb3 + codoped multicomposition. J. Non Cryst. Solids 362, 156–161 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.11.042
S.A. Bassam, K.A. Naseer, A.J. Prakash, K.A. Mahmoud, C.S. Suchandsangeeth, M.I. Sayyed, M.S. Alqahtani, E. El Sheikh, M. Uddin, Effect of Tm2O3 addition on the physical, structural, elastic, and radiation-resisting attributes of tellurite-based glasses. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 209, 110988 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2023.110988
N. Elkhoshkhany, S.Y. Marzouk, S. Shahin, Synthesis and optical properties of new fluoro-tellurite glass within (TeO2–ZnO–LiF–Nb2O5–NaF) system. J. Non Cryst. Solids 472, 39–45 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.07.012
J. De Clermont-gallerande, S. Saito, M. Colas, P. Thomas, T. Hayakawa, New understanding of TeO2 e ZnO e Na2O ternary glass system. J. Alloys Compd. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157072
J.V. Gunha, R.F. Muniz, A. Somer, A. Gonçalves, R. Denkiewicz, G. De Souza, T.O. Sales, C. Jacinto, R. El-mallawany, A. Novatski, Characterization of oxyfluorotellurite glasses with TeO2–Li O–ZnO–LiF composition. Ceram. Int. 48, 4302–4311 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.224
S. Gafar, S. Krishna, K. Hamzah, S. Aishah, Tailored spectroscopic characteristics of sm 3+ -imbued zinc-sodium tellurite glasses: influence of Dy3 + co-doping. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 139, 113774 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2023.113774
S.Q. Mawlud, M.M. Ameen, M.R. Sahar, N.M. Yusof, K.F. Ahmed, Y.A. Tanko, Absorption and luminescence spectral properties study of Sm3+ doped TeO2–Na2O glasses, Proceedings of 4th International Science Postgraduate Conference 2016. (2016)
T. Sekiya, N. Mochida, A. Ohtsuka, M. Tonokawa, Raman spectra of MO1/2–TeO2 (M = Li, na, K, Rb, Cs and Tl) glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids. 144, 128–144 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(05)80393-X
V. Dimitrov, T. Komatsu, An interpretation of optical properties of oxides and oxide glasses in terms of the electronic ion polarizability and average single bond strength. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 45, 219–250 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.11.014
N. Alfryyan, Z.A. Alrowaili, R.F. Muniz, E. Zainab Mufarreh, J.V. Gunha, A. Novatski, J.L. Gomes Junior, F.C. Serbena, I.O. Olarinoye, M.S. Al-Buriahi, Design synthesis and characterization of Pb-free tellurite glasses for radiation shielding applications. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2023.110969
U.P.M. Serdang, H.A. Sidek, S. Rosmawati, Z.A. Talib, M. Halimah, W.M. Daud, Synthesis and optical properties of ZnO–TeO2 glass system. J. Appl. Sci. 6, 1489–1494 (2009)
R. El-Mallawany, The optical properties of tellurite glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 1774–1777 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351649
S.K. Ahmmad, M.A. Samee, A. Edukondalu, S. Rahman, Physical and optical properties of zinc arsenic tellurite glasses. Results Phys. 2, 175–181 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2012.10.002
I. Jlassi, H. Elhouichet, M. Ferid, Thermal and optical properties of tellurite glasses doped erbium. J. Mater. Sci. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4820-x
B. Eraiah, Optical properties of lead-tellurite glasses doped with samarium trioxide. Bull. Mater. Sci. 33, 391–394 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0059-z
J. Fellman, T. Westerlund, Determination of the complex indices of refraction of glasses using Kramers–Krönig transformation. J. Non Cryst. Solids 146, 165–174 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(05)80489-2
C. Rivero, K. Richardson, R. Stegeman, G. Stegeman, T. Cardinal, E. Fargin, M. Couzi, V. Rodriguez, Quantifying Raman gain coefficients in tellurite glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids. 346, 396–401 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2004.08.051
R. Jose, G. Qin, Y. Arai, Y. Ohishi, Tailoring of Raman gain bandwidth of tellurite glasses for designing gain-flattened fiber Raman amplifiers. J. Opt. Sco Am. B 25, 373–382 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.25.000373
E.S. Yousef, H.H. Hegazy, S. Almojadah, M. Reben, Absorption spectra and Raman gain coef fi cient in near-IR region of Er3 + ions doped TeO2–Nb2O5–Bi2O3–ZnO glasses. Opt. Laser Technol. 74, 138–144 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2015.06.002
Y.A.N.Z. Hang, Y.X.U. Insheng, C.H.Y. Ou, D.X.U. Ong, J.U.T. Ang, P.E.Z. Hang, S.H.D. Ai, Raman gain and femtosecond laser induced damage of Ge–As–S chalcogenide glasses. Opt. Express 25, 8886–8895 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.25.008886
R.H. Stolen, C. Lee, Development of the stimulated Raman spectrum in single-mode silica fibers. J. Opt. Sco Am. B 1, 652–657 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.1.000652
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude for the support provide by Brazilian agencies CAPES, CNPq, Fundação Araucária, FINEP and FAPEAL. Special thanks to C-LABMU/UEPG and LAPTO-UTFPR/PG for their invaluable technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by Fundação Araucária, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JVG: data curation, methodology, validation, investigation, writing—original draft. RFM: writing—review and editing, supervision. AS: conceptualization, writing—original draft. TdeOS: methodology, investigation, data curation. WfdaS: conceptualization, investigation, writing—review and editing. DTD: methodology, investigation, data curation. RE-M: writing—review and editing. CJdaS: methodology, investigation, data curation NGCA: writing—review and editing. AN: conceptualization, investigation, resources, writing—original draft, funding acquisition, supervision. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analysis and manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gunha, J.V., Muniz, R.F., Somer, A. et al. Influence of Sm2O3 ion concentration on physical and thermal properties, and Raman gain coefficient of TeO2–Li2O–ZnO vitreous system. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 240 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11895-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11895-5