Abstract
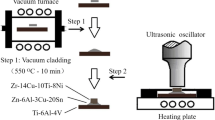
The joining processes of many devices, such as sensor photonic, MEMS, and biomedical devices, must be entirely flux free. This research presents a direct ultrasonic-assisted active soldering (UAAS) technology for a flux-free glass/substrate (glass, Si wafer, sapphire) bonding process using In49Sn active solder at low temperature in air. The joint microstructures were examined by optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled with energy-dispersive spectrometry (EDS). Results showed that the joints were nearly void-free. The active Lutetium element (Lu) was found to be segregated at the interface of the active solder/substrate joint and played an important role in reliable joining at low temperature. The shear strengths were 3.87 ± 0.50 MPa for glass/glass, 2.76 ± 0.59 MPa for glass/Si wafer, and 3.02 ± 0.43 MPa for glass/sapphire joints. The failure mode of the joints was a mixture of cohesive failure and adhesive fracture.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated or analyzed during current study are included in this paper.
References
J.J. Li, X. Yu, T.L. Shi, C.L. Cheng, J.H. Fan, S.Y. Cheng, G.L. Liao, Z.R. Tang, Low temperature and low-pressure Cu–Cu bonding buy highly sinterable Cu nanoparticle paste. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 255 (2017)
K.N. Tu, H.Y. Hsiao, C. Chen, Transition from flip chip solder joint to 3D IC microbump: its effect on microstructure anisotropy. Microelectron. Reliab. 53, 2–6 (2013)
K.N. Tu, Reliability challenges in 3D IC packaging technology. Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 517–523 (2011)
R.I. Made, C.L. Gan, L.L. Yan, A. Yu, S.W. Yoon, J.H. Lau, C. Lee, Study of low-temperature thermocompression bonding in Ag-In solder for packaging applications. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 365–371 (2009)
N. Belov, T.K. Chou, J. Heck, K. Kornelsen, D. Spicer, S. Akhlaghi, M. Wang, T. Zhu, Thin-layer Au–Sn solder bonding process for wafer-level packaging, electrical interconnections and MEMS applications. IEEE Int. Interconnect Technol. Conf. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/IITC.2009.5090361
C.T. Ko, K.N. Chen, Low temperature bonding technology for 3D integration. Microelectron. Reliab. 52, 302–311 (2012)
C. Wei, S.Q. Li, Microstructure and mechanical performance of composite joints of sapphire by ultrasonic-assisted brazing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 257, 1–6 (2018)
M. Ali, K.M. Knowles, P.M. Mallinson, J.A. Fernie, Interfacial reactions between sapphire and Ag–Cu–Ti-based active braze alloys. Acta Mater. 103, 859–869 (2016)
M.K. Pal, G. Gergely, D. Koncz-Horváth, Z. Gácsi, Characterization of the interface between ceramics reinforcement and leadfree solder matrix. Surf. Interfaces. 20, 100576 (2020)
L.X. Cheng, X.J. Yue, J. Xia, Z.Z. Wu, G.Y. Li, Adsorption and interface reaction in direct active bonding of GaAs to GaAs using Sn–Ag–Ti solder filler. J. Mater. Sci. : Mater. Electron. 32, 21248–21261 (2021)
L.X. Cheng, K.B. Ma, X.J. Yue, Z.L. Li3, G.Y. Li, Role of Ti in direct active bonding of SiC substrate using Sn–Ag–Ti alloy filler. J. Mater. Sci. : Mater. Electron. 33, 3331–3347 (2022)
L.C. Tsao, Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of microplasma oxidized TiO2/Ti joints soldered using Sn3.5Ag4Ti(ce) active filler. J. Mater. Sci. : Mater. Electron. 25, 233–243 (2014)
L.C. Tsao, S.Y. Chang, Y.C. Yu, Direct active soldering of Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 high entropy alloy to 6061-Al using Sn–Ag–Ti active solder. T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 28, 748–756 (2018)
F. Weber, M. Rettenmayr, Joining of SiO2 glass and 316L stainless steel using Bi– Ag-based active solders. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 3444–3454 (2021)
R. Koleňák, I. Kostolný, J. Drápala, M. Sahul, J. Urminský, Characterizing the soldering alloy type In–Ag–Ti and the study of direct soldering of SiC ceramics and copper. Metals. 8, 274 (2018)
S. Bao, W. Li, Y. He, Y. Zhong, L. Zhang, D. Yu, On the optimization of molding warpage for wafer-level glass interposer packaging. J. Mater. Sci. : Mater. Electron. 34, 1061 (2023)
T. Mouratidis, The effect of joint thickness on intermetallic growth in the In52Sn48(liquid)/Cu(solid) diffusion couple. J. Electron. Mater. 53, 418–431 (2024)
B.J. Lee, C.S. Oh, J.H. Shim, Thermodynamic assessments of the Sn–In and Sn–Bi binary systems. J. Electron. Mater. 25, 983–991 (1996)
B. Belan, M. Manyako, R. Gladyshevskii, R. Černý, XIV International Conference on Crystal Chemistry of Intermetallic Compounds (Lviv, 2019), p. 124
H. Mavoori, A.G. Ramirezm, S. Jin, Lead-free universal solders for optical and electronic devices. J. Electron. Mater. 31, 1160–1165 (2002)
A.G. Ramirez, H. Mavoori, S. Jin, Bonding nature of rare-earth-containing lead-free solders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 398–400 (2002)
H. Mavoori, A.G. Ramirez, S. Jin, Universal solders for direct and powerful bonding on semiconductors, diamond, and optical materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 2976–2978 (2001)
C.W. Bale, E. Bélisle, P. Chartrand, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, A.E. Gheribi, K. Hack, I.H. Jung, Y.B. Kang, J. Melançon, A.D. Pelton, S. Petersen, C. Robelin, J. Sangster, M.-A. Van Ende, (2023) FTlite-FACT light alloy databases. https://www.crct.polymtl.ca/fact/phase_diagram.php?file=Lu-Si.jpg&dir=FTlite
R.W. Olesinski, N. Kanani, G.J. Abbaschian, The In–Si (indium–silicon) system. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams 6, 128–130 (1985)
R.W. Olesinski, G.J. Abbaschian, The Si–Sn (Silicon–Tin) system, bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams 5, 273–276 (1984)
W. Guo, Z. She, S. Yang, H. Xue, X. Zhang, Understanding the influence of Lu, La and Ga active elements on the bonding properties of Sn/SiO2 interfaces from first principle calculations. Ceram. Int. 46, 24737–24743 (2020)
A. Navrotsky, W. Lee, A. Mielewczyk-Gryn, S.V. Ushakov, A. Anderko, H. Wu, R.E. Riman, Thermodynamics of solid phases containing rare earth oxides. J. Chem. Thermodynamics. 88, 126–141 (2015)
A. Kostov, B. Friedrich, Selection of crucible oxides in molten titanium and titanium aluminum alloys by thermo-chemistry calculations. J. Min. Metall. B 41, 113–125 (2005)
Acknowledgements
Thank C. P. Chu for useful discussion and specimen preparation. SEM was performed by the Precision Instrument Center of National Pingtung University of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
Funding
Project supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under Project No. MOST 106-2221-E-020-015, MOST 111-2221-E-020-017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.C.: contributed to conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, writing of the original draft, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript. Both Y.S. and C.H.: contributed to shear measurements and equation analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or Personal relationships that could appear to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsao, L.C., Chia, YS. & Li, MC. Joining of SiO2 glass and substrate using In49Sn active solder in air. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 81 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11816-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11816-6