Abstract
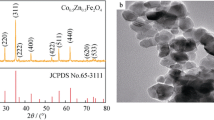
The agglomeration phenomenon of ZnFe2O4(ZFO) nanoparticles limits its application in microwave absorption. Although some work attempts to solve it, they usually only focus on screening the types of dispersants and do not explore the dosage of dispersants. In this work, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was selected as dispersant to synthesis ZFO particles through co-precipitation technology, and the micromorphology, structure, electromagnetic parameters, and microwave absorption property of material were influenced by the content of SDS and detected by XRD, SEM, TEM, VSM, and VNA. The results show that the prepared samples were all spherical ZFO particles and were relatively pure. The ZFO-15 particles with a uniform particle size of 27 nm are most dispersed and have the best impedance matching performance mainly due to the formation of considerable micelles in the solution to guide the dispersion of precipitates. The minimum reflection loss of ZFO-15 with a thickness of 7.5 mm can reach − 33.44 dB at 12.24 GHz and the effective absorption width is 5.1 GHz (8.6–12.6 GHz and 16.5–17.6 GHz). This is mainly attributed to the well-dispersed particles promoting the better performance of ZFO material in terms of dielectric and magnetic loss characteristics. It has potential reference value in the industrial application field of ferrite absorbing materials.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings of the present report cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
J. Cui, L. Huang, J.W. Ma et al., Carbon-encapsulated core-shell structure ZnFe2O4 sphere composites coupled with excellent microwave absorption and corrosion resistance. RSC 14, 15393 (2022)
L. Chai, Y.Q. Wang, N.F. Zhou et al., In-situ growth of core-shell ZnFe2O4 @ porous hollow carbon microspheres as an efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interf Sci. 581, 475–484 (2021)
A. Iqbal, F. Shahzad, K. Hantanasirisakul et al., Anomalous absorption of electromagnetic waves by 2D transition metal carbonitride Ti3CNTx (MXene). Science. 369, 446–450 (2020)
X.Z. Zhang, Y.C. Zhang, J. He et al., ZnFe2O4 nanospheres decorated residual carbon from coal gasification fine slag as an ultra-thin microwave absorber. Fuel. 331, 125811 (2023)
H.L. Lv, Z.H. Yang, P.L.Y. Wang et al., A voltage boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. 30(15), 1706343 (2018)
Z.G. Gao, Xu. Electrostatic self-assembly synthesis of ZnFe2O4 quantum dots (ZnFe2O4 @ C) and electromagnetic microwave absorption. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 179, 107417 (2019)
Y. Li, X.F. Liu, X.Y. Nie et al., Multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid aerogel for self-cleaning, heat-insulating, and highly efficient microwave absorbing material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(10), 1–9 (2019)
B. Quan, W. Shi, S.J.H. Ong et al., Defect engineeting in two common types of dielectric materials for electromagnetic absorption applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(28), 1901236–1901245 (2019)
J.N. Hu, C.Y. Liang, J.D. Li et al., Flexible reduced graphene oxide @ Fe3O4/silicone rubber composites for enhanced microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 570, 151270 (2021)
T.E. Balaji, H.T. Das, T. Maiyalagan, Recent trends in bimetallic oxides and their composites as electrode materials for supercapacitor applications. Chemeletrochem. 8, 1723–1746 (2021)
N. Tiwari, S. Kadam, S. Kulkarni, Synthesis and characterization of ZnCo2O4 electrode for high-performance supercapacitor application. Mater. Lett. 298, 130039 (2021)
J.S. Xue, H.Z. Zhang, J.H. Zhao et al., Characterization and microwave absorption of spinel MFe2O4(M = mg, Mn, Zn) nanoparticles prepared by a facile oxidation-precipitation process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 514, 167168 (2020)
K.L. Xu, L. Jiao, C.Q. Wang et al., Nonylphenol photodegradation by novel ternary MIL-100(Fe)/ZnFe2O4/PCN composite under visible light irradiation via double charge transfer process. J. Environ. Sci. 111, 93–103 (2022)
J.X. He, Y. Yang, P. Zhou et al., Preparation and electrochemical performances of ZnMoO4–ZnFe2O4 composite electrode materials. Ionics 28(3), 1285–1294 (2022)
B. Bhujn, M.T.T. Tan, A.S. Shanmugam, Study of mixed ternary transition metal ferrites as potential electrodes for supercapacitor applications. Results Phys. 7, 345–353 (2017)
M.B. Askari, P. Salarizadeh, M. Seifi et al., ZnFe2O4 nanorods on reduced graphene oxide as advanced supercapacitor electrodes. J. Alloy Compd. 860, 158479 (2021)
L. Vaisman, H.D. Wagner, G. Marom, The role of surfactants in dispersion of carbon nanotubes. J. Colloid Interf Sci. 37, 128–130 (2006)
W.H. Duan, Q. Wang, F. Collins, Dispersion of carbon nanotubes with SDS surfactants: a study from a binding energy perspective. Chem. Sci. 2, 1407 (2011)
J.H. Chen, Kinetics and Mechanism Studies on Dispersion of CNT in SDS Aqueous Solutions. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 61, 481–489 (2014)
X.X. Li, W.J. Wang, Z.G. Hu, Preparation of uniformly dispersed Yag Ultrafine powders by Coprecipitation Method with SDS treatment. Powder Metall. Met. C+. 48, 7–8 (2009)
P. Zhang, I. Lo, D. Connor et al., High efficiency removal of methylene blue using SDS surface-modified ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interf Sci. 508, 39–48 (2017)
Y.C. Wu, R.X. Guo, H.T. Xia et al., Effects of different dispersants on mechanical and electrical properties of GO/CNFs cement-based composites. Bull. Chin Ceram Soc. 40(3), 732–739 (2021)
C.F. Jia, M.B. Xing, H.F. Zhang et al., Preparation study of water-based MWCNT-Fe3O4 magnetic nanofluids with high stability. Funct. Mater. 11(52), 11023–11030 (2021)
G.L. Chen, J. Liu, R.Q. Liu et al., Simple Preparation of ZnFe2O4 with different precipitants by co-precipitation for microwave absorption material. J. Electron. Mater. 52(10), 6391–6402 (2023)
X.Y. Wang, B. Wang, S.C. Wei, Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure, magnetic, and microwave absorption properties of Mtype barium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 34, 1045 (2023)
S. Feng, M.G. Yu, T.P. Xie et al., MoS2/CoFe2O4 heterojunction for boosting photogenerated carrier separation and the dominant role in enhancing peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134467 (2022)
X.G. Huang, Y.S. Qin, Y.B. Ma et al., Preparation and electromagnetic properties of nanosized ZnFe2O4 with various shapes. Ceram. Int. 45, 18389–18397 (2019)
Y. Ruiz-Morales, A. Romero-Martinez, Coarse-Grain Molecular Dynamics Simulations to investigate the bulk viscosity and critical micelle concentration of the ionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 14(122), 3931–3943 (2018)
W.J. Feng, H.L. Liu, P.F. Hui et al., Preparation and properties of SrFe12O19/ZnFe2O4 Core/Shell Nano-Powder Microwave Absorber. Integr. Ferroelectr. 152, 120–126 (2014)
D. Li, Y. Feng, D.S. Pan et al., Negative imaginary parts of complex permeability and microwave absorption performance of core double-shelled FeCo/Fe2.5Cr0.5Se4 nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 6, 73020 (2016)
J.T. Zhou, B. Wei, M.Q. Wang et al., Three dimensional flower like ZnFe2O4 Ferrite loaded graphene: Enhancing microwave absorption performance by constructing microcircuits. J. Alloy Compd. 889, 161734 (2021)
J.S. Deng, Q.B. Wang, Y.Y. Zhou et al., Facile design of a ZnO nanorod-Ni core-shell composite with dual peaks to tune its microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv. 7(15), 9294–9302 (2017)
A. Aharoni, Exchange resonance modes in a ferromagnetic sphere. J. Appl. Phys. 69(11), 7762–7764 (1991)
Y.B. Li, R. Yi, A.G. Yan et al., Facile synthesis and properties of ZnFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4/polypyrrole core-shell nanoparticles. Solid State Sci. 11, 1319–1324 (2009)
H.S. Liang, L.M. Zhang, Wu. Exploration of Twin-Modified Grain Boundary Engineering in Metallic Copper Predominated Electromagnetic Wave Absorber. Small. 18, 2203620 (2022)
Q. Zhou, T.T. Shi, B. Xue et al., Multi-scale integrated design and fabrication of ultra-broadband electromagnetic absorption utilizing multi-walled carbon nanotubes-based hierarchical metamaterial. Compos. Sci. Technol. 232, 109877 (2023)
Funding
This work is supported by Applied Basic Research Project of Liaoning Province in 2022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DF: design of the work, acquired data and wrote the manuscript; GC and RL: interpreted the results; DF: agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, D., Chen, G. & Liu, R. Influence of SDS dispersant on the preparation and microwave absorption properties of ZnFe2O4 materials. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2330 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11746-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11746-3