Abstract
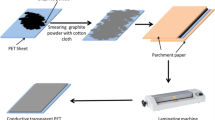
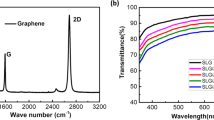
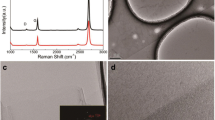
Graphene is an excellent material for transparent conductive electrodes due to its high electrical conductivity, transparency, flexibility, and mechanical strength. On the other hand silver nanowires (AgNWs) have also been considered as an excellent material for transparent conductive electrodes due to their high electrical conductivity, high aspect ratio, good transparency and other properties suitable for transparent electronics. Herein, we have presented a simple approach to combine the properties of graphene and silver nanowires to develop a good transparent and flexible conductive electrode on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) sheet. The transmittance of the as-prepared graphene/AgNWs electrode was found to be 82.6% at 550 nm, which is comparable to the transmittance of commercial transparent conductive electrodes. The sheet resistance of the electrode was determined to be 212.59 kΩ/sq (measured by four point-probe method). The low sheet resistance of the graphene/AgNW electrode makes it suitable for use in a variety of electronic devices, including solar cells, supercapacitors, flexible displays, and touch sensitive screens. The proposed approach is highly scalable and can boost the fabrication of low cost and highly transparent electrodes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or used in the study are presented in the submitted article.
References
T.-B. Song, N. Li, Emerging transparent conducting electrodes for organic light emitting diodes. Electronics. 3(1), 190–204 (2014)
K.-H. Ok, J. Kim, S.-R. Park, Y. Kim, C.-J. Lee, S.-J. Hong, M.-G. Kwak, N. Kim, C.J. Han, J.-W. Kim, Ultra-thin and smooth transparent electrode for flexible and leakage-free organic light-emitting diodes. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 1–8 (2015)
C. Wang, K. Xia, H. Wang, X. Liang, Z. Yin, Y. Zhang, Advanced carbon for flexible and wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 31(9), 1801072 (2019)
S.K. Maurya, H.R. Galvan, G. Gautam, X. Xu, Recent progress in transparent conductive materials for photovoltaics. Energies. 15(22), 8698 (2022)
H. Jang, Y.J. Park, X. Chen, T. Das, M.S. Kim, J.H. Ahn, Graphene-based flexible and stretchable electronics. Adv. Mater. 28(22), 4184–4202 (2016)
J.-H. Ahn, B.H. Hong, Graphene for displays that bend. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9(10), 737–738 (2014)
F. Bonaccorso, Z. Sun, T. Hasan, A.C. Ferrari, Graphene photonics and optoelectronics. Nat. Photonics. 4(9), 611–622 (2010)
S.J. Kim, K. Choi, B. Lee, Y. Kim, B.H. Hong, Materials for flexible, stretchable electronics: graphene and 2D materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 45, 63–84 (2015)
J.A. Rogers, T. Someya, Y. Huang, Materials and mechanics for stretchable electronics. Science 327(5973), 1603–1607 (2010)
H. Li, Y. Liu, A. Su, J. Wang, Y. Duan, Promising hybrid graphene-silver nanowire composite electrode for flexible organic light-emitting diodes. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 17998 (2019)
M.J. Nikzad, N. Mohamadbeigi, S.K. Sadrnezhaad, S.M. Mahdavi, Fabrication of a highly flexible and affordable transparent electrode by aligned u-shaped copper nanowires using a new electrospinning collector with convenient transferability. ACS Omega. 4(25), 21260–21266 (2019)
H. Essaidi, L. Cattin, Z. El Jouad, S. Touihri, M. Blais, E. Ortega, G. Louarn, M. Morsli, T. Abachi, T. Manoubi, Indium free electrode, highly flexible, transparent and conductive for optoelectronic devices. Vacuum. 153, 225–231 (2018)
H.T. Dao, H. Makino, Improving electrical conductivity and its thermal stability of Al-doped ZnO polycrystalline films using ultrathin Al film as a passivation layer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 203, 110159 (2019)
S. Lu, Y. Sun, K. Ren, K. Liu, Z. Wang, S. Qu, Recent development in ITO-free flexible polymer solar cells. Polymers. 10(1), 5 (2017)
E.J. López-Naranjo, L.J. González-Ortiz, L.M. Apátiga, E.M. Rivera-Muñoz, A. Manzano-Ramírez, Transparent electrodes: a review of the use of carbon-based nanomaterials. J. Nanomater. 2016 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4928365
S. Huang, Y. Liu, F. Yang, Y. Wang, T. Yu, D. Ma, Metal nanowires for transparent conductive electrodes in flexible chromatic devices: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 20(5), 3005–3037 (2022)
Y. Zhou, R. Azumi, Carbon nanotube based transparent conductive films: progress, challenges, and perspectives. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 17(1), 493–516 (2016)
Y.S. Woo, Transparent conductive electrodes based on graphene-related materials. Micromachines. 10(1), 13 (2018)
Z. Wang, C.P. Puls, N.E. Staley, Y. Zhang, A. Todd, J. Xu, C.A. Howsare, M.J. Hollander, J.A. Robinson, Y. Liu, Technology ready use of single layer graphene as a transparent electrode for hybrid photovoltaic devices. Phys. E: Low-dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 44(2), 521–524 (2011)
M.A. Shinde, K. Mallikarjuna, J. Noh, H. Kim, Highly stable silver nanowires based bilayered flexible transparent conductive electrode. Thin Solid Films. 660, 447–454 (2018)
T.K. Lahane, J. Agrawal, V. Singh, Optimization of polyol synthesized silver nanowires for transparent conducting electrodes application. Mater. Today Proc. 59, 257–263 (2022)
M.R. Azani, A. Hassanpour, T. Torres, Benefits, problems, and solutions of silver nanowire transparent conductive electrodes in indium tin oxide (ITO)-free flexible solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 10(48), 2002536 (2020)
A. Madeira, M. Plissonneau, L. Servant, I.A. Goldthorpe, Tréguer-Delapierre, increasing silver nanowire network stability through small molecule passivation. Nanomaterials 9(6), 899 (2019)
R. Zhang, M. Engholm, Recent progress on the fabrication and properties of silver nanowire-based transparent electrodes. Nanomaterials. 8(8), 628 (2018)
C. Choi, E. Schlenker, H. Ha, J.Y. Cheong, B. Hwang, Versatile applications of silver nanowire-based electrodes and their impacts. Micromachines. 14(3), 562 (2023)
S. Iravani, H. Korbekandi, S.V. Mirmohammadi, B. Zolfaghari, Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 9(6), 385 (2014)
H. Sim, C. Kim, S. Bok, M.K. Kim, H. Oh, G.-H. Lim, S.M. Cho, B. Lim, Five-minute synthesis of silver nanowires and their roll-to-roll processing for large-area organic light emitting diodes. Nanoscale. 10(25), 12087–12092 (2018)
K.S. Lau, S.X. Chin, S.T. Tan, F.S. Lim, W.S. Chang, C.C. Yap, M.H.H. Jumali, S. Zakaria, S.W. Chook, C.H. Chia, Silver nanowires as flexible transparent electrode: role of PVP chain length. J. Alloys Compd. 803, 165–171 (2019)
S. Kumar, J.K. Goswamy, P. Kumar, S. Kumar, Chemically derived graphene nanoribbons from carbon nanotubes for supercapacitor application. Mater. Today Proc. 50, 1511–1515 (2022)
S. Rattan, S. Kumar, J.K. Goswamy, Graphene oxide reduction using green chemistry. Mater. Today Proc. 26, 3327–3331 (2020)
S. Kumar, R.R. Nair, P.B. Pillai, S.N. Gupta, M.A. Iyengar, A.K. Sood, Graphene oxide-MnFe2O4 magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6(20), 17426–17436 (2014)
S. Rattan, M. Kaur, S. Kumar, J.K. Goswamy, Synergistic effect of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes for improved supercapacitive performance electrodes. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33(36), 26841–26851 (2022)
Y. Lei, T. Zhang, Y.-C. Lin, T. Granzier-Nakajima, G. Bepete, D.A. Kowalczyk, Z. Lin, D. Zhou, T.F. Schranghamer, A. Dodda, Graphene and beyond: recent advances in two-dimensional materials synthesis, properties, and devices. ACS Nanosci. Au (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnanoscienceau.2c00017
S. Sharma, K. Singh, S. Kumar, K. Bhatt, Y. Dwivedi, A. Rana, C.C. Tripathi, Fabrication of reduced graphene oxide modified poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate based transparent conducting electrodes for flexible optoelectronic application. SN Appl. Sci. 3, 1–8 (2021)
X. An, T. Simmons, R. Shah, C. Wolfe, K.M. Lewis, M. Washington, S.K. Nayak, S. Talapatra, S. Kar, Stable aqueous dispersions of noncovalently functionalized graphene from graphite and their multifunctional high-performance applications. Nano Lett. 10(11), 4295–4301 (2010)
S.V. Kumar, A.P. Bafana, P. Pawar, A. Rahman, S.A. Dahoumane, C.S. Jeffryes, High conversion synthesis of < 10 nm starch-stabilized silver nanoparticles using microwave technology. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 5106 (2018)
Funding
Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MK: investigation, methodology, experimentation and writing original draft. PB: data validation and characterization. T: data curation and experimentation. A: data curation experimentation. SK: conceptualization, editing and supervision. JKG: supervision and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not involve any studies with human participants and/or animals.
Informed consent
Informed consent was received from all authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, M., Bhatt, P., Twinkle et al. Graphene-silver nanowires hybrid electrode on PET sheet for improved-performance transparent electronics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2287 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11703-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11703-0