Abstract
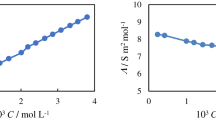
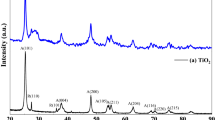
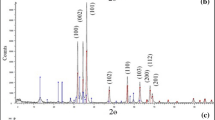
Industrial wastewater treatment using solid phase extraction has emerged as one of the most effective approaches. In this paper, TiO2–g-C3N4 nanocomposite was prepared by a simple one-step ultrasonic method and used as an adsorbent for the elimination of Rhodamine B (RhB) dye. X-ray powder diffraction XRD, Transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectrometer and RAMAN were utilized to characterize the TiO2–g-C3N4 nanocomposite. The impacts of initial RhB dye concentration, contact time, and pH were investigated. The adsorption capacity for the elimination of RhB dye was 148.46 mg g−1. The analyses of the kinetic model demonstrate that the process exhibited pseudo-second-order kinetics. The suitability and applicability of the Sips model are demonstrated by fitting experimental equilibrium data to various isotherm models. The examination of TiO2–g-C3N4 nanocomposite as a suitable adsorbent for several dyes [Rhodamine B (RhB), basic fuchsin, malachite green, congo red, and indigo carmine] demonstrated the nanocomposite’s overall high potential for removal of dyes from industerial wastewater. The adsorption process was found to be spontaneous, thermodynamically favorable and physisorption of RhB molecule onto TiCN nanocomposites.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Upon reasonable request, the corresponding author will provide the datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study.
References
V. Katheresan, J. Kansedo, S.Y. Lau, Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6(4), 4676–4697 (2018)
D. Bhatia et al., Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(19), 1836–1876 (2017)
H. Mahdizadeh et al., Hybrid UV/COP advanced oxidation process using ZnO as a catalyst immobilized on a stone surface for degradation of acid red 18 dye. MethodsX. 7, 101118 (2020)
S. Mondal, M.K. Purkait, S. De, Advances in dye removal technologies (Springer, Cham, 2018)
Y. Zhou et al., Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: a review. Environ. Pollut. 252, 352–365 (2019)
M.R. Elamin et al., Application of synthesized vanadium–titanium oxide nanocomposite to eliminate rhodamine-B dye from aqueous medium. Molecules 28(1), 176 (2022)
T. Xu et al., Construction of large-pore crystalline covalent organic framework as high-performance adsorbent for rhodamine B dye removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59(17), 8315–8322 (2020)
G. Kumar, D.T. Masram, Sustainable synthesis of MOF-5@ GO nanocomposites for efficient removal of rhodamine B from water. ACS Omega. 6(14), 9587–9599 (2021)
A. Toghan et al., Mesoporous TiO2@g-C3N4 composite: construction, characterization, and boosting indigo carmine dye destruction. Diam. Relat. Mater. 118, 108491 (2021)
A. Toghan, A. Modwi, Boosting unprecedented indigo carmine dye photodegradation via mesoporous MgO@g-C3N4 nanocomposite. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 419, 113467 (2021)
A. Modwi et al., Adsorption kinetics and photocatalytic degradation of malachite green (MG) via Cu/ZnO nanocomposites. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5(6), 5954–5960 (2017)
A. Moumen et al., Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution by catalytic wet oxidation technique using Ni/kaolin as catalyst. Molecules 27(21), 7528 (2022)
E.S. Mansor, H. Ali, A. Abdel-Karim, Efficient and reusable polyethylene oxide/polyaniline composite membrane for dye adsorption and filtration. Colloid and Interface Science Communications. 39, 100314 (2020)
K.A. Omar, R. Sadeghi, Novel nonanol-based deep eutectic solvents: thermophysical properties and their applications in liquid–liquid extraction and amino acid detection. J. Mol. Liq. 336, 116359 (2021)
A. Modwi et al., Flower buds like MgO nanoparticles: from characterisation to indigo carmine elimination. Z. für Naturforschung A 73(11), 975–983 (2018)
S. Rahali et al., Adsorption behavior of Congo red onto barium-doped ZnO nanoparticles: correlation between experimental results and DFT calculations. Langmuir. 37(24), 7285–7294 (2021)
A. Modwi et al., Superior removal of dyes by mesoporous MgO/g-C3N4 fabricated through ultrasound method: adsorption mechanism and process modeling. Environ. Res. 205, 112543 (2022)
B. Aissa et al., Yttrium oxide-doped ZnO for effective adsorption of basic fuchsin dye: equilibrium, kinetics, and mechanism studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19(10), 9901–9914 (2022)
N. Sharifi et al., Synthesis of Fe3O4@activated carbon to treat metronidazole effluents by adsorption and heterogeneous fenton with effluent bioassay. J. Photochem. Photobiol. a 427, 113845 (2022)
A. Nasiri, S. Rajabi, M. Hashemi, CoFe2O4@methylcellulose/AC as a new, green, and eco-friendly nano-magnetic adsorbent for removal of reactive red 198 from aqueous solution. Arab. J. Chem. 15(5), 103745 (2022)
A. Nasiri et al., New efficient and recyclable magnetic nanohybrid adsorbent for the metronidazole removal from simulated wastewater. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33(33), 25103–25126 (2022)
I. Anastopoulos et al., Use of nanoparticles for dye adsorption. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 39(6), 836–847 (2018)
A. Hamzezadeh et al., Application of low-cost material for adsorption of dye from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 102(1), 254–269 (2022)
N. Kumar et al., Bionanocomposite hydrogel for the adsorption of dye and reusability of generated waste for the photodegradation of ciprofloxacin: a demonstration of the circularity concept for water purification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(12), 17011–17025 (2018)
S. Moosavi et al., Application of efficient magnetic particles and activated carbon for dye removal from wastewater. ACS Omega. 5(33), 20684–20697 (2020)
A. Nasiri et al., CuCoFe2O4@MC/AC as a new hybrid magnetic nanocomposite for metronidazole removal from wastewater: bioassay and toxicity of effluent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 296, 121366 (2022)
S. Rajabi, A. Nasiri, M. Hashemi, Enhanced activation of persulfate by CuCoFe2O4@MC/AC as a novel nanomagnetic heterogeneous catalyst with ultrasonic for metronidazole degradation. Chemosphere 286, 131872 (2022)
G. Yazdanpanah et al., Heterogeneous Sono-Fenton like catalytic degradation of metronidazole by Fe3O4@HZSM-5 magnetite nanocomposite. Heliyon 9(6), e16461 (2023)
L. Zheng, X. Wang, X. Wang, Reuse of reverse osmosis concentrate in textile and dyeing industry by combined process of persulfate oxidation and lime-soda softening. J. Clean. Prod. 108, 525–533 (2015)
S. Mallakpour, S. Rashidimoghadam, Carbon nanotubes for dyes removal. Compos. Nanoadsorbents (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814132-8.00010-1
C. Wang et al., Enhancing light emission efficiency without color change in post-transition metal chalcogenides. Nanoscale. 8(11), 5820–5825 (2016)
A. Modwi et al., Scalable fabrication and characterization of Y2O3@g-C3N4 nanocomposite for the enhancement of photocatalytic removal of Congo red dye under visible light. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 34(4), 298 (2023)
R.A. AbuMousa et al., Efficient mesoporous MgO/g-C3N4 for heavy metal uptake: modeling process and adsorption mechanism. Nanomaterials 12(22), 3945 (2022)
C. Lu, X. Chen, Nanostructure engineering of graphitic carbon nitride for electrochemical applications. ACS Nano 15(12), 18777–18793 (2021)
A. Modwi, Exfoliated g-C3N4 as efficient sorbent for Pb ions removal from synthetic wastewaters. Z. für Naturforschung A (2023). https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-2022-0293
R.B. Said et al., Uptake of BF dye from the Aqueous phase by CaO-g-C3N4 nanosorbent: construction, descriptions, and recyclability. Inorganics 11(1), 44 (2023)
A. Bessadok-Jemai et al., Hybrid CaO@MgO@g-C3N4 nanostructure as a cost-effective sorbent for hazardous organic dyes activated by additives. Diam. Relat. Mater. 133, 109757 (2023)
A. Modwi, A. Albadri, K.K. Taha, High Malachite Green dye removal by ZrO2-g-C3N4 (ZOCN) meso-sorbent: characteristics and adsorption mechanism. Diam. Relat. Mater. 132, 109698 (2023)
O. Aldaghri et al., Cleanup of Cd II from water media using Y2O3@gC3N4 (YGCN) nanocomposite. Diam. Relat. Mater. 129, 109315 (2022)
A. Modwi et al., Effect of annealing on physicochemical and photocatalytic activity of Cu5% loading on ZnO synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(12), 12974–12984 (2016)
A. Modwi et al., Excellent adsorption of dyes via MgTiO3@g-C3N4 nanohybrid: construction, description and adsorption mechanism. Inorganics 10(11), 210 (2022)
I. Troppová et al., Unconventionally prepared TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalysts for photocatalytic decomposition of nitrous oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 430, 335–347 (2018)
A. Tripathi, S. Narayanan, Impact of TiO2 and TiO2/g-C3N4 nanocomposite to treat industrial wastewater. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 10, 280–291 (2018)
L. Khezami et al., Harmonizing the photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4 nanosheets by ZrO2 stuffing: from fabrication to experimental study for the wastewater treatment. Biochem. Eng. J. 182, 108411 (2022)
X. Bai et al., Photocatalytic activity enhanced via g-C3N4 nanoplates to nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 117(19), 9952–9961 (2013)
M. Karimi-Nazarabad, E.K. Goharshadi, Highly efficient photocatalytic and photoelectrocatalytic activity of solar light driven WO3/g-C3N4 nanocomposite. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 160, 484–493 (2017)
Z. Wu et al., Synthesis and characterization of Ni-doped anatase TiO2 loaded on magnetic activated carbon for rapidly removing triphenylmethane dyes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28(3), 3475–3483 (2021)
H. Lin, L. Zhao, Novel g-C3N4/TiO2 nanorods with enhanced photocatalytic activity for water treatment and H2 production. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(19), 18191–18199 (2019)
H. Berger, H. Tang, F. Lévy, Growth and Raman spectroscopic characterization of TiO2 anatase single crystals. J. Cryst. Growth. 130(1–2), 108–112 (1993)
M.A. Ben Aissa et al., Dependency of crystal violet dye removal behaviors onto mesoporous V2O5-g-C3N4 constructed by simplistic ultrasonic method. Inorganics 11(4), 146 (2023)
A.E. Albadri et al., Synthesis of mesoporous Ru-ZnO@ g-C3N4 nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity for methylene blue degradation. Water 15(3), 481 (2023)
H. Lin, L. Zhao, Novel gC3N4/TiO2 nanorods with enhanced photocatalytic activity for water treatment and H2 production. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 18191–18199 (2019)
S. Rahdar et al., Synthesis and characterization of MgO supported Fe–Co–Mn nanoparticles with exceptionally high adsorption capacity for rhodamine B dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8(5), 3800–3810 (2019)
X. Gao et al., Ultra-high-capacity adsorption of rhodamine B in a carboxyl-functionalized metal–organic framework via surface adsorption. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 66(1), 669–676 (2020)
L. Khezami et al., Efficient removal of organic dyes by Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02952-w
M. Ben Aissa et al., Yttrium oxide-doped ZnO for effective adsorption of basic fuchsin dye: equilibrium, kinetics, and mechanism studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03816-y
K. Kuśmierek, J. Fronczyk, A. Świątkowski, Adsorptive removal of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solutions using mineral materials as low-cost adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 234(8), 531 (2023)
Y. Yu et al., Benzene carboxylic acid derivatized graphene oxide nanosheets on natural zeolites as effective adsorbents for cationic dye removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 260, 330–338 (2013)
C.A. Matias et al., Biosorption of rhodamine b from aqueous solution using Araucaria angustifolia sterile bracts. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 36(1), 97–104 (2020)
M.R.R. Kooh, M.K. Dahri, L.B. Lim, The removal of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution using Casuarina equisetifolia needles as adsorbent. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2(1), 1140553 (2016)
Z. Abaker et al., Superior uptake of Cu (II) from aquatic media via Y2O3-ZnO nanostructures. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 30, 100879 (2022)
L. Khezami et al., Mesoporous Sn@TiO2 nanostructures as excellent adsorbent for Ba ions in aqueous solution. Ceram. Int. 48(4), 5805–5813 (2022)
B. Oladipo, E. Govender-Opitz, T.V. Ojumu, Kinetics, thermodynamics, and mechanism of Cu (II) Ion sorption by biogenic iron precipitate: using the lens of wastewater treatment to diagnose a typical biohydrometallurgical problem. ACS Omega 6(42), 27984–27993 (2021)
B. Mustafa et al., Adsorption performance and kinetics study of pb (II) by RuO2–ZnO nanocomposite: construction and recyclability. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19(1), 327–340 (2022)
Y. Sun et al., Methylene blue removed from aqueous solution by encapsulation of bentonite aerogel beads with cobalt alginate. ACS Omega 7(45), 41246–41255 (2022)
S. Kohzadi et al., Removal of RhB from water by Fe-modified hydrochar and biochar–An experimental evaluation supported by genetic programming. J. Mol. Liq. 369, 120971 (2023)
J. Yang, S. Shojaei, S. Shojaei, Removal of drug and dye from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide: adsorption studies and chemometrics methods. NPJ Clean. Water. 5(1), 5 (2022)
E. Wierzbicka et al., Efficient rhodamine b dye removal from water by acid-and organo-modified halloysites. Minerals. 12(3), 350 (2022)
S. Zghal et al., Adsorptive removal of rhodamine B dye using carbon graphite/cnt composites as adsorbents: kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic study. Materials. 16(3), 1015 (2023)
A. Kausar et al., Experimental and theoretical studies of rhodamine B direct dye sorption onto clay-cellulose composite. J. Mol. Liq. 328, 115165 (2021)
S. Shakeri, Z. Rafiee, K. Dashtian, Fe3O4-based melamine-rich covalent organic polymer for simultaneous removal of auramine O and rhodamine B. J. Chem. Eng. Data 65(2), 696–705 (2020)
F. Motahari, M.R. Mozdianfard, M. Salavati-Niasari, Synthesis and adsorption studies of NiO nanoparticles in the presence of H2acacen ligand, for removing rhodamine B in wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 93, 282–292 (2015)
S.K. Lagergren, About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handingarl. 24, 1–39 (1898)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU), Saudi Arabia for funding and supporting this work through Research Partnership Program (grant number IMSIU-RP23086).
Funding
This work was funded by Deanship of Scientific Research, Imam Mohammed Ibn Saud Islamic University (Grant No.: IMSIU-RP23086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Preparation of materials, data collection, and analysis were achieved by MK, MABA, KMD and EAA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MK, AM, RBS and MEK. Funding acquisition MK and MEK. Each author provided feedback on prior drafts of the article. The methodology, some explanations and response to reviewers’ comments in revision stage MK, MABA, NR and MEK. The final manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khairy, M., Khalifa, M.E., Abdelrahman, E.A. et al. Performance of mesoporous TiO2–g-C3N4 prepared by simple ultrasonic method for removal of organic dyes from waste water. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11694-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11694-y