Abstract
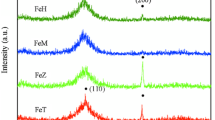
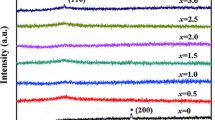
The effect of Si/Fe ratio on glass-forming ability, crystallization behavior, formed phase, and soft magnetic properties of Fe74−xSixBCuNbNiCo (X = 3, 4, 5, and 6) alloy ribbons is investigated. With decreasing the ratio of Si/Fe, the glass-forming abilities of Fe74−xSixBCuNbNiCo alloys decrease, the as-quenched X = 6 and 5 alloy ribbons are amorphous state, the X = 4 and 3 alloy samples precipitate FeNi3 in the amorphous precursors during melt-spinning technique. The as-quenched Fe74−xSixBCuNbNiCo (X = 3, 4, 5, and 6) alloy ribbons show two-stage crystallization behaviors; with X reducing, the onset temperature of the first crystallization decreases from 442 to 402 °C, and the temperature interval of onset crystallization of α-Fe and boride phases is 121–147 °C. After annealing at appropriate temperatures, with decreasing Si/Fe, the annealed Fe74−xSixBCuNbNiCo alloy samples show a significant decrease in Br and µ, which make the linearity of B–H hysteresis loop more pronounced. By comparison with X = 6 alloy, the annealed X = 3 alloy sample annealed at 480 °C × 60 min shows a great B–H linearity with a constant µ of 2.3k and higher Ms of 181 emu/g (Bs ≈ 1.7 T), leading to good resistance to DC bias in current transformers. The iron core with low µ and high Bs can enable current transformers to be used at high current power without saturation failure. Finally, we discussed that a high Bs and low constant µ in annealed X = 3 alloy could attribute to the coupling effect between α-Fe and FeNi3 nanocrystalline phases.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
T.C. Batista, B.A. Luciano, R.C.S. Freire, W.B. Castro, E.M. Araújo, J. Alloys Compd. 615, S228–S230 (2014)
E. So, D. Bennett, IEEE T. Instrum. Meas. 56, 584–587 (2007)
P. Ripka, M. Mirzaei, P. Mlejnek, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 563, 170019 (2022)
G. Herzer, Acta Mater. 61, 718–734 (2013)
D. Azuma, N. Ito, M. Ohta, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 501, 166373 (2020)
J.M. Silveyra, E. Ferrara, D.L. Huber, T.C. Monson, Science (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0195
Y. Yoshizawa, S. Oguma, K. Yamauchi, J. Appl. Phys. 64, 6044–6046 (1988)
J. Xu, X. Liu, Y. Wang, Q. Shi, J. Wang, K. Li, Y. Yang, J. Alloys Compd. 902, 163887 (2022)
T. Luo, Y. Yang, C. Fan, F. Hou, G. Wang, J. Xu, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 576, 121286 (2022)
T. Luo, J. Xu, G. Wang, W. Cai, Y. Yang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 505, 166714 (2020)
M. Jiang, M. Cai, J. Zhou, S. Di, X. Li, Q. Luo, B. Shen, Mater. Today Nano (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtnano.2023.100307
D.A. Shishkin, Mater. Res. Express (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaed5f
Y. Yoshizawa, S. Fujii, D.H. Ping, M. Ohnuma, K. Hono, Scr. Mater. 48, 863–868 (2003)
Q. Luo, D. Li, M. Cai, S. Di, Z. Zhang, Q. Zeng, Q. Wang, B. Shen, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 116, 72–82 (2022)
S. Flohrer, R. Schafer, J. McCord, S. Roth, L. Schultz, F. Fiorillo, W. Gunther, G. Herzer, Acta Mater. 54, 4693–4698 (2006)
T. Gheiratmand, H.R.M. Hosseini, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 408, 177–192 (2016)
H.R. Lashgari, D. Chu, S. Xie, H. Sun, M. Ferry, S. Li, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 391, 61–82 (2014)
F. Hou, Y. Yang, T. Luo, G. Wang, C. Fan, Z. Xie, Phys. B 595, 412293 (2020)
W. Li, C.X. Xie, C.L. Yao, H.Y. Liu, K.W. Wang, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 505, 87–91 (2019)
M.A.W. Michael, E. McHenry, E. David, Prog Mater. Sci. 44, 291–433 (1999)
G.V. Raynor, V.G. Rivlin, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 2, 102–102 (1981)
Y. Waseda, S. Ueno, M. Hagiwara, K.T. Aust, Prog. Mater. Sci. 34, 149–260 (1990)
X. Jia, W. Zhang, Y. Dong, A. He, J. Li, R.-W. Li, J. Mater. Sci. 56, 2539–2548 (2020)
F. Pfeifer, C.M. Radeloff, M. Materials, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 19, 190–207 (1980)
R. Madugundo, O. Geoffroy, B. Frincu, S. Kodjikian, S. Rivoirar, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 422, 475–478 (2017)
Funding
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52071089), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2019A1515010886).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL: methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft. HL: project administration, supervision, writing—review & editing. CH: resources, data curation. GY: resources, investigation. FH: software, formal analysis. YY: conceptualization, funding acquisition, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, T., Liu, H., Huang, C. et al. The effect of composition on glass-forming ability, crystallization behavior, and soft magnetic properties of FeSiBCuNbNiCo amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11607-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11607-z