Abstract
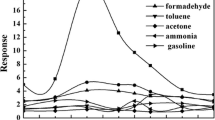
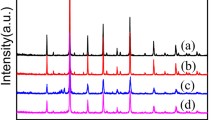
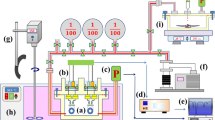
Isopropanol is one of the most important chemical raw materials and organic solvents, but a large amount of isopropanol will do harm to human health. Therefore, it is essential to monitor isopropanol. In this work, high-performance isopropanol gas sensors were fabricated with SnO2 molecularly imprinted polymers (SnO2 MIPs). All the samples were characterized for performance evaluation. The results show that with molecular imprinting (MI) modification, gas sensors based on SnO2 MIPs have better gas sensing performance for isopropanol compared with pure SnO2. Especially, when the molar ratio of methacrylic acid (MAA) to isopropanol was 6:10, excellent gas sensing performance was achieved. At the optimum working temperature of 300 °C, the response of this sensor to isopropanol of 500 ppm was 33.87, and the response and recovery times were 10 s and 3 s, respectively. In addition, it is proven that MI modification could significantly improve the selectivity of gas sensors to the target gas due to the specific recognition sites. Therefore, SnO2 MIPs with the molar ratio of MAA to isopropanol of 6:10 would be a promising isopropanol sensing material.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
R.J. Slaughter, R.W. Mason, D.M.G. Beasley, J.A. Vale, L.J. Schep, Isopropanol poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 52, 470–478 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3109/15563650.2014.914527
Y. Lu, X.X. Liu, Z.Q. Zhao, X.Y. Ou, Y.R. Yang, Q. Wei, J.L. Chen, J. Jiang, Y. Sun, H.P. Zhao et al., Telomere length in peripheral leukocytes is a sensitive marker for assessing genetic damage among workers exposed to isopropanol, lead and noise: the case of an electronics manufacturer. Genes Environ. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41021-021-00226-x
D.W. Cao, S.M. Xia, P. Pan, H.Y. Zeng, C.J. Li, Y. Peng, Light-driven MPV-type reduction of aryl ketones/aldehydes to alcohols with isopropanol under mild conditions. Green Chem. 23, 7539–7543 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc02449c
H. Zhan, Environmentally friendly pesticide emulsifier composition useful to produce pesticides comprises acrylic acid, acrylic ester, surfactant, vegetable oil, crosslinking agent, dimethylbenzene, sodium hydroxide, isopropanol, camphor and water. CN107853296-A.
K. Sakurai, K. Uehama, K. Ezaki, Mfg. odourless isopropanol for cosmetics - by reacting propylene and sulphuric acid, distilling to provide high and low boiling fractions etc. JP60224646-A; JP93040736-B.
Z. Hua, Printing ink comprises e.g. pigment, alcohol-soluble polyurethane solution, isopropanol, diluent, polyurethane resin, propyl acetate, and water. CN112480735-A.
H.R. Greene, M.D. Krasowski, Correlation of osmolal gap with measured concentrations of acetone, ethylene glycol, isopropanol, methanol, and propylene glycol in patients at an academic medical center. Toxicol. Rep. 7, 81–88 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.12.005
K.L. Edelen, A. Barton, W. Banner, Sustained low-efficiency dialysis (SLED) therapy following ingestion of isopropanol in a pediatric patient. Clin. Toxicol. 58, 208–211 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2019.1616094
C. Lupu, Separation of ethanol methanol acetone and isopropanol by gas chromatography. Clin. Chem. 12, 537 (1966)
L. Rowbottom, C. Workman, N.B. Roberts, Evaluation of selected-ion flow-tube mass spectrometry for the measurement of ethanol, methanol and isopropanol in physiological fluids: effect of osmolality and sample volume. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 23, 2763–2767 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.4165
J.P. Zhu, M.T. Yao, Y.J. Lia, C.C. Chan, In situ thermal degradation of isopropanol under typical thermal desorption conditions for GC-MS analysis of volatile organic compounds. Anal. Methods 6, 6116–6119 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ay00415a
A.M. Kutsyk, O.O. Ilchenko, Y.M. Yuzvenko, V.V. Obukhovsky, V.V. Nikonova, Vibration spectroscopy of complex formation in aqueous solutions of isopropanol. Ukr. J. Phys. 63, 506–512 (2018). https://doi.org/10.15407/ujpe63.6.506
C.Q. Han, Y. Yao, S.S. Lv, Y. Wu, A.X. Lu, C.C. Yan, Y. Liu, X.S. Luo, X.W. Ni, Study on the components of isopropanol aqueous solution. Optik 155, 307–314 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.10.164
L.J. Guo, W. Liu, C.Q. Wang, Nanoscale Ag-decorated hollow porous CuO/SnO2 heterojunctions for isopropanol detection. Acs Appl Nano Mater 6, 7830–7840 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.3c00959
K. Li, M.P. Chen, Q. Rong, Z.Q. Zhu, Q.J. Liu, J. Zhang, High selectivity methanol sensor based on Co-Fe2O3/SmFeO3 p-n heterojunction composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 765, 193–200 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.212
Y. Tan, J. Zhang, Highly sensitive ethanol gas sensors based on Co-doped SnO2 nanobelts and pure SnO2 nanobelts. Physica E-Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2022.115604
S.H. Li, Z. Chu, F.F. Meng, T. Luo, X.Y. Hu, S.Z. Huang, Z. Jin, Highly sensitive gas sensor based on SnO2 nanorings for detection of isopropanol. J. Alloy. Compd. 688, 712–717 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.248
Y.Q. Yu, S.T. Liu, Facile synthesis of Ni-doped SnO2 nanorods and their high gas sensitivity to isopropanol. Front. Mater. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-022-0585-9
Y.L. Kong, Y.X. Li, X.X. Cui, L.F. Su, D. Ma, T.R. Lai, L.J. Yao, X.C. Xiao, Y.D. Wang, SnO2 nanostructured materials used as gas sensors for the detection of hazardous and flammable gases: a review. Nano Materials Science 4, 339–350 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoms.2021.05.006
M.P. Chen, Y.M. Zhang, T.P. Lv, K.J. Li, Z.Q. Zhu, J. Zhang, R.H. Zhang, Q.J. Liu, Ag-LaFeO3 nanoparticles using molecular imprinting technique for selective detection of xylene. Mater. Res. Bull. 107, 271–279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.08.004
Q.J. Li, M. Wang, Y. Jin, Y.L. Lu, S.Q. Xiong, M.D. Wang, J.H. Xu, C.H. Wei, J.L. Li, Microfluidic synthesis of pH-responsive molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres for fluorescence sensing target glycoprotein. Food Chem. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136570
W.J. Cheng, Z.J. Liu, Y. Wang, Preparation and application of surface molecularly imprinted silica gel for selective extraction of melamine from milk samples. Talanta 116, 396–402 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.05.067
Q.Q. Zhou, Z.G. Xu, Z.M. Liu, Molecularly imprinting-aptamer techniques and their applications in molecular recognition. Biosensors-Basel (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080576
X.P. Fu, Y. Li, S. Gao, Y.Q. Lv, Selective recognition of tumor cells by molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Sep. Sci. 44, 2483–2495 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202100137
Y. Cheng, J.Y. Nie, Z.X. Li, Z. Yan, G.F. Xu, H.F. Li, D.K. Guan, A molecularly imprinted polymer synthesized using beta-cyclodextrin as the monomer for the efficient recognition of forchlorfenuron in fruits. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 409, 5065–5072 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0452-1
P.N. Zhao, M. Yan, C.C. Zhang, R.X. Peng, D.S. Ma, J.H. Yu, Determination of glyphosate in foodstuff by one novel chemiluminescence-molecular imprinting sensor. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 78, 1482–1486 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.01.037
Y.B. Hua, Y. Ahmadi, K.H. Kim, Molecularly imprinted polymers for sensing gaseous volatile organic compounds: opportunities and challenges*. Environ. Pollut. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119931
Q.T. Li, W. Zeng, Y.Q. Li, Core-shell NiO sphere prepared by a facile method with enhanced VOC gas sensing. J. Electrochem. Soc. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ac7a60
Q. Rong, K.J. Li, C. Wang, Y.M. Zhang, M.P. Chen, Z.Q. Zhu, J. Zhang, Q.J. Liu, Enhanced performance of an acetone gas sensor based on Ag-LaFeO(3)molecular imprinted polymers and carbon nanotubes composite. Nanotechnology (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab80f9
J.N. Zhang, G. Li, J. Liu, Y.M. Liu, R.Y. Yang, L. Li, Q.Y. Zhao, J.Z. Gao, G.Q. Zhu, B.P. Zhu et al., Metal-organic framework-derived mesoporous rGO-ZnO composite nanofibers for enhanced isopropanol sensing properties. Sensor. Actuat B-Chem. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.133108
A. Alhadi, S.Y. Ma, Synthesis of Sn doped-Bi2WO6 nanoslices for enhanced isopropanol sensing properties. Physica B-Condensed Matter. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2022.413819
C. Zhang, Y.C. Huan, Y. Li, Y.F. Luo, M. Debliquy, Low concentration isopropanol gas sensing properties of Ag nanoparticles decorated In2O3 hollow spheres. J. Adv. Ceram. 11, 379–391 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-021-0530-x
T.T. Yang, S.Y. Ma, P.F. Cao, X.L. Xu, L. Wang, S.T. Pei, T. Han, X.H. Xu, P.D. Yun, H. Sheng, Synthesis and characterization of ErFeO3 nanoparticles by a hydrothermal method for isopropanol sensing properties. Vacuum (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.110005
J.X. Wang, Q. Zhou, S.D. Peng, L.N. Xu, W. Zeng, Volatile organic compounds gas sensors based on molybdenum oxides: a mini review. Front. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00339
Z.T. Li, W. Zeng, Q.T. Li, SnO2 as a gas sensor in detection of volatile organic compounds: a review. Sensor Actuat a-Phys (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.113845
C.N. Wang, Y.L. Li, F.L. Gong, Y.H. Zhang, S.M. Fang, H.L. Zhang, Advances in doped ZnO nanostructures for gas sensor. Chem. Rec. 20, 1553–1567 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202000088
W.A. Song, M.X. Zhang, W.G. Zhao, Q.L. Zhao, H.S. Hao, H. Lin, W.Y. Gao, S. Yan, Nanostructured SnO2 microsphere-based gas sensor array enhanced by molecular imprinting for methanol and ethanol discriminative detection. Acs Appl Nano Mater 5, 12765–12777 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c02662
V. Shah, J. Bhaliya, G.M. Patel, P. Joshi, Room-temperature chemiresistive gas sensing of SnO2 nanowires: a review. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 32, 741–772 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02198-5
W.Y. Yang, H.L. Shen, J.W. Ge, B.B. Xu, Improving TiO2 gas sensing selectivity to acetone and other gases via a molecular imprinting method. Nanotechnology (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abd818
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Graduate Scientific Research and Innovation Foundation of Chongqing, China (No. CYS20001) and the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. KJQN201801320).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation, Experiments, Data processing, Writing-Original draft preparation, Z.Z.; Reviewing, WZ; Editing, YQL and WZ; Supervision, WZ; Conceptualization and Methodology, WZ and YL; Resources, WZ All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Li, Y. & Zeng, W. A novel sensitive gas sensor based on SnO2 molecularly imprinted polymers for monitoring isopropanol. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2091 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11582-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11582-5