Abstract
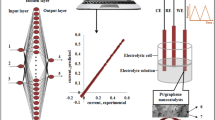
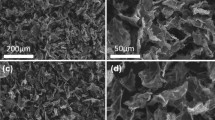
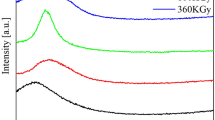
The ion permeation through graphene oxide (GO) membranes irradiated by electrons was studied in this paper. The effect of irradiation on the microstructure of GO membranes was investigated using various techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and Raman spectrum. FTIR results confirmed that no new chemical groups were formed during the electron beam irradiation process. XRD results indicated that the interlayer spacing shrunk with the irradiation dose. The ions permeation through the GO membrane was evaluated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. It was found that the inductive effect can be enhanced when the irradiation dose increased from 0 to 80 kGy and weakened at a higher irradiation dose. The machine learning method was further employed to explore the optimum parameters. The predicted data are highly consistent with the experimental data (results), which were verified by the testing phase in machine learning. The electron beam irradiation can be potentially applied to adjust the inhibition of ion permeation through the GO membrane.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
G. Liu, W. Jin, N. Xu, Graphene-based membrance. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 5016–5030 (2015)
D.M. Warsinger, S. CHakraborty, E.W. Tow, M.H. Plumlee et al., A review of polymeric membranes and processes for potable water reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 81, 209–237 (2018)
Z. Chen, K. Ito, H. Yanagishita, N. Oshima, Correlation study between free-volume holes and molecular separations of composite membranes for reverse osmosis processes by means of variable-energy positron annihilation techniques. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 18055–18060 (2011)
J.Y. Liu, Z. Chen, L. Yao, J.J. Li, Correlation between the ion permeation and free volume property in ethyl cellulose film during the acid treatment. Mater. Chem. Front. 3, 1518–1522 (2019)
L. Chen, G.S. Shi, J. Shen, B. Peng, Ion sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing. Nature. 550, 380–383 (2017)
H.B. Huang, Y.Y. Mao, Y.L. Ying, Y. Liu, Salt concentration, pH and pressure controlled separation of small molecules through lamellar graphene oxide membranes. Chem. Commun. 49, 5963–5965 (2013)
J.Q. Wang, P. Zhang, B. Liang, Y.X. Liu, Graphene oxide as an effective barrier on a porous nanofibrous membrane for water treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 6211–6218 (2016)
B. Mi, Graphene oxide membranes for ionic and molecular sieving. Science. 343, 740–742 (2014)
W.S. Huang, C.H. Tsou, M.D. Guzman, Q.F. An, Y.L. Liu, Y.M. Zhang, C.C. Hu, K.R. Lee, Cross-linking with diamine monomers to prepare composite graphene oxide-framework membranes with varying d-spacing. Chem. Mater. 26, 2983–2990 (2014)
H.D. Yang, H. Chen, Z. Chen, Y. Li, L. Yao, G.M. Wang, Q.R. Deng, P. Fu, Inductive effect of MXene membrane influenced by β-cyclodextrin intercalation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 101, 1874–1880 (2023)
N. Sahiner, Soft and flexible hydrogel templates of different sizes and various functionalities for metal nanoparticle preparation and their use in catalysis. Prog. Polym. Sci. 38, 1329–1356 (2013)
Y.J. Zhang, Z. Chen, L. Yao, X. Wang, P. Fu, Z.D. Lin, The graphene oxide membrane immersing in the aqueous solution studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Mater. Res. Express. 5, 045606 (2018)
Y.J. Zhang, Z. Chen, L. Yao, X. Wang, Q.M. Fu, Z.D. Lin, S.G. Wang, Study of ion permeation through the graphene oxide/polyether sulfone membranes. ChemElectroChem. 7, 493–499 (2020)
H. Chen, Z. Chen, G.M. Wang, Q.R. Deng, L. Yao, Wang, inductive effect in MXene/Poly (ether sulfone) membrane during ion diffusion. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 3, 4509–4516 (2021)
Z. Chen, S.T. Luo, L. Yao, Y. Zhang, Z.D. Lin, S.G. Wang, The inductive effect of montmorillonite/polyether sulfone membrane during the ion diffusion process. Appl. Clay Sci. 203, 106002 (2021)
T. Szabo, O. Berkesi, I. Dekany, DRIFT study ofdeuterium-exchanged graphene oxide. Carbon. 15, 3186–3189 (2005)
Y. Shen, H.B. Zhang, H. Zhang et al., Structural evolution of functionalized graphene sheet during solvothermal reduction. Carbon. 56, 132–138 (2013)
C. Zhang, D.M. Dabbs, L.M. Liu et al., Combined effects of functional groups, lattice defects, and edges in the infrared spectra of graphene oxide. J. Phy Chem. C 119, 18167–18176 (2015)
J. Bai, H. Sun, X. Yin et al., Oxygen-content-controllable graphene oxide from electron-beam-irradiated graphite: synthesis, characterization, and removal of aqueous lead [Pb(II)]. ACS Appl. Mater. & Interfaces. 8, 25289–25296 (2016)
F.M. Mohamed, A. Hamdy, Ohira, Y. Kobayashi, Free volume and oxygen permeability in polymers related to Polymer Electrolyte fuel cells. Mater. Sci. Forum. 607, 58–60 (2009)
E.E. Abdel-Hady, H.M. Abdel-Hamid, H.F.M. Mohamed, Electron beam and gamma irradiation effects on conducting polystyrene studied by positron annihilation technique. Radiat. Meas. 38(2), 211–216 (2004)
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China 12205089, 12375290, and 12075172 and the Scientific Research Foundation of Hubei University of Science and Technology, grant numbers, 2021ZX16, 2022ZX03, 2021KF06, BK202216, and 2021ZX18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LQ contributed to writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript, conceptualization, investigation, methodology, and funding acquisition. MW contributed to writing of the original draft, methodology, investigation, and formal analysis. HY contributed to investigation and formal analysis. ZL contributed to investigation and formal analysis. YH contributed to investigation and methodology, ZC contributed to formal analysis, methodology, and funding acquisition. CH contributed to formal analysis and funding acquisition. ZC contributed to writing of the original draft, resources, project administration, and funding acquisition. XT contributed to conceptualization, resources, writing of the original draft, and methodology.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, L., Wu, M., Yang, H. et al. Effect of the electron irradiation on the ion permeation through the GO membrane. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2139 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11542-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11542-z