Abstract
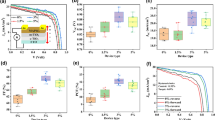
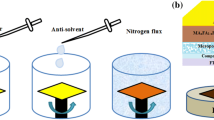
The performance of CH\(_{3}\)NH\(_{3}\)PbI\(_{3}\) based perovskite materials deposited on Al-doped ZnO film is correlated with carrier extraction, surface, and film qualities of the hole transporting layers(HTLs). Changing the surface properties of HTL with both EG and triton X-100 into PEDOT: PSS in the ratio of 2:1. This shows better conductivity, good film formation, higher hole mobility, and negligible hysteresis in halide perovskite-based solar cells. In this present work, 10% of efficiency has been achieved by adding co-dopants in PEDOT: PSS layer in the Al–ZnO/CH\(_{3}\)NH\(_{3}\)PbI\(_{3}\)/PEDOT: PSS heterostructure with a cost-effective method. Not only better hole extraction of PEDOT: PSS is observed after co-doped it with EG and triton X-100 but also higher efficiency is observed in the heterostructure.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets created and/or analyzed in the present study are available from the corresponding author upon affordable request.
References
Yohan Ko, Yechan Kim, Seong Young Kong, Sakeerali Cheeran Kunnan, Yongseok Jun, Improved performance of sol-gel ZnO-based perovskite solar cells via TiCl\(_{4}\) interfacial modification. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 183, 157–163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2018.04.021
M.A. Green, Thin-film solar cells: review of materials, technologies and commercial status. J. Mater. Sci.: MaterElectron 18, 15–19 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9177-9
A. Fakharuddin, R. Jose, T.M. Brown, F. Fabregat-Santiago, J. Bisquert, A perspective on the production of dye-sensitized solar modules. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3952–3981 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EE01724B
Abraha Tadese Gidey, Da-Wei. Kuo, Adane Desta Fenta, Chin-Ti. Chen, Chao-Tsen. Chen, First conventional solution sol-gel-prepared nano porous materials of nickel oxide for efficiency enhancing and stability extending MAPbI\(_{3}\) inverted perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 4(7), 6486–6499 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.1c00496
Piyali Chatterjee, Amit K. Chakraborty, Metal organic framework derived Ca\(_{4}\)Fe\(_{9}\)O\(_{17}\)as photocatalyst for degradation of organic dyes. Mater. Lett. 284, 129034 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.129034
B. Walker, C. Kim, T.-Q. Nguyen, Small molecule solution-processed bulk heterojunction solar cells. Chem. Mater. 23, 470–482 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm102189g
A. Al Ashouri, E. Köhnen, B. Li, A. Magomedov, H. Hempel et al., Monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell with \(>\)29% efficiency by enhanced hole extraction. Science 370(6522), 1300–1309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abd4016
S. Gu, R. Lin, Q. Han, Y. Gao, H. Tan et al., Tin and mixed lead-tin halide perovskite solar cells: progress and their application in tandem solar cells. Adv. Mater. 32(27), 1907392 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201907392
M. Green, E. Dunlop, J. Hohl-Ebinger, M. Yoshita, N. Kopidakis, X. Hao, Solar cell efficiency tables(version 57). Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3371
X. Luo, T. Wu, Y. Wang, X. Lin, H. Su et al., Progress of all-perovskite tandem solar cells: the role of narrow-bandgap absorbers. Sci. China Chem. 64, 218–227 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-020-9870-4
K. Xiao, R. Lin, Q. Han, Y. Hou, Z. Qin et al., All-perovskite tandem solar cells with 24.2% certifed efciency and area over 1cm\(^{2}\) using surface-anchoring zwitterionic antioxidant. Nat. Energy 5, 870–880 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-020-00705-5
Y. Deng, C.H. Van Brackle, X. Dai, J. Zhao, B. Chen et al., Tailoring solvent coordination for high-speed, room-temperature blading of perovskite photovoltaic flms. Sci. Adv. 5(12), eaax7537 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax7537
A. Dualeh, N. Tetreault, T. Moehl, P. Gao, M.K. Nazeeruddin, M. Gr-tzel, Effect of annealing temperature on film morphology of organic-inorganic hybrid pervoskite solid-state solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 3250–3258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201304022
Y. Chen, T. Chen, L. Dai, Layer-by-Layer Growth of CH\(_{3}\)NH\(_{3}\)PbI\(_{3-x}\)Cl\(_{x}\) for highly efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 27, 1053–1059 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201404147
C. Momblona, O. Malinkiewicz, C. Roldan-Carmona, A. Soriano, L. Gil-Escrig, E. Bandiello, M. Scheepers, E. Edri, H.J. Bolink, Efficient methylammonium lead iodide perovskite solar cells with active layers from 300 to 900 nm. APL Mater. 2, 081504 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4890056
W. Ke, G. Fang, Q. Liu, L. Xiong, P. Qin, H. Tao, J. Wang, H. Lei, B. Li, J. Wan, G. Yang, Y. Yan, Low-temperature solution-processed tin oxide as an alternative electron transporting layer for efficient perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137(21), 6730–6733 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b01994
D. Liu, T.L. Kelly, Perovskite solar cells with a planar heterojunction structure prepared using room-temperature solution processing techniques. Nat. Photonics 8(2), 133–138 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.342
K. Wang, Y. Shi, B. Li, L. Zhao, W. Wang, X. Wang, X. Bai, S. Wang, C. Hao, T. Ma, Amorphous inorganic electron-selective layers for efficient perovskite solar cells: feasible strategy towards room-temperature fabrication. Adv. Mater. 28(9), 1891–1897 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201505241
S.S. Shin, W.S. Yang, J.H. Noh, J.H. Suk, N.J. Jeon, J.H. Park, J.S. Kim, W.M. Seong, S.I. Seok, High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn\(_{2}\)SnO\(_{4}\) prepared in solution below 100\(^{0}\)C. Nat. Commun. 6, 7410 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8410
S. Wang, Y. Zhu, C. Wang, R. Ma, NH\(_{4}\)F as an interfacial modifier for high performance NiOx-based inverted perovskite solar cells. Org. Electron. 78, 105627 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2020.105627
Z. Li, B.H. Jo, S.J. Hwang, T.H. Kim, S. Somasundaram, E. Kamaraj, J. Bang, T.K. Ahn, S. Park, H.J. Park, Bifacial passivation of organic hole transport interlayer for NiOx-based p-i-n perovskite solar cells. Adv. Sci. 6, 1802163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201802163
Z. Zhu, Y. Bai, T. Zhang, Z. Liu, X. Long, Z. Wei, Z. Wang, L. Zhang, J. Wang, F. Yan, S. Yang, High-performance hole-extraction layer of sol-gel-processed NiO nanocrystals for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem.Int. Ed. 53, 1–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201405176
D. Koushik, M. Jost, A. Ducinskas, C. Burgess, V. Zardetto, C. Weijtens, M.A. Verheijen, W.M.M. Kessels, S. Albrecht, M. Creatore, Plasma-assisted atomic layer deposition of nickel oxide as hole transport layer for hybrid perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 12532–12543 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC04282B
A.M. Nardes, M. Kemerink, R.A.J. Janssen, J.A.M. Bastiaansen, N.M.M. Kiggen, B.M.W. Langeveld, A.J. van Breemen, M.M. de Kok, Microscopic understanding of the anisotropic conductivity of PEDOT:PSS thin films. Adv. Mater. 19, 1196–1200 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200602575
W. Hong, Y. Xu, G. Lu, C. Li, G. Shi, Transparent graphene/PEDOT-PSS composite films as counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 10, 1555–1558 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2008.08.007
C.K. Cho, W.J. Hwang, K. Eun, S.H. Choa, S.I. Na, H.K. Kim, Mechanical flexibility of transparent PEDOT:PSS electrodes prepared by gravure printing for flexible organic solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 19, 3269–3275 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2011.07.009
Y. Xia, J. Ouyang, PEDOT:PSS films with significantly enhanced conductivities induced by preferential solvation with cosolvents and their application in polymer photovoltaic cells. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 4927–4936 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM04177G
Y. Hou, H. Zhang, W. Chen, S. Chen, C.O.R. Quiroz, H. Azimi, A. Osvet, G.J. Matt, E. Zeira, J. Seuring, N. Kausch-Busies, W. Lovenich, C.J. Brabec, Inverted, environmentally stable perovskite solar cell with a novel low-cost and water-free PEDOT hole-extraction Layer. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1500543 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201500543
K. Sun, S. Zhang, P. Li et al., Review on application of PEDOTs and PEDOT:PSS in energy conversion and storage devices. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 4438–4462 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2895-5
Y. Xia, K. Sun, J. Chang, J. Ouyang, Effects of organic inorganic hybrid perovskite materials on the electronic properties and morphology of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly-(styrenesulfonate) and the photovoltaic performance of planar perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 15897–15904 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA03456F
S. Zhang, Z. Yu, P. Li, B. Li, F.H. Isikgor, D. Du, K. Sun, Y. Xia, J. Ouyang, Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrene sulfonate films with low conductivity and low acidity through a treatment of their solutions with probe ultrasonication and their application as hole transport layer in polymer solar cells and perovskite solar cells. Org. Electron. 32, 149–156 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2016.02.024
S.R. Jang et al., Voltage-enhancement mechanisms of an organic dye in high open-circuit voltage solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano. 5, 8267–8274 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2029567
A. Bera, S. Chattopadhyay, Violet-yellow light emission from a p-Si/Zn(Mg)O /ZnO/Zn(Fe)O Heterostructure. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 1615–1622 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09381-x
Hui Shi, Congcong Liu, Qinglin Jiang, Xu. Jingkun, Effective approaches to improve the electrical conductivity of PEDOT:PSS: a review. Adv.Electron. Mater. 1(4), 1500017 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.201500017
Muhammad Ans, Javed Iqbal, Bertil Eliasson, Muhammad Jawwad Saif, Hafiz Muhammad Asif. Javed, Khurshid Ayub, Designing of non-fullerene 3D star-shaped acceptors for organic solar cells. J. Mol. Model. 25, 129 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-019-3992-9
Muhammad Ans, Javed Iqbal, Ijaz Ahmad Bhatti, Khurshid Ayub, Designing dithienonaphthalene based acceptor materials with promising photovoltaic parameters for organic solar cells. RSC Adv. 9, 34496–34505 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA06345E
Muhammad Ans, Khurshid Ayub, Shabbir Muhammad, Javed Iqbal, Development of fullerene free acceptors molecules for organic solar cells: a step way forward toward efficient organic solar cells. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1161, 26–38 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comptc.2019.06.003
Muhammad Ans, Khurshid Ayub, Ijaz Ahmad Bhatti, Javed Iqbal, Designing indacenodithiophene based non-fullerene acceptors with a donor-acceptor combined bridge for organic solar cells. RSC Adv. 9, 3605–3617 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09292C
Muhammad Ans, Javed Iqbal, Bertil Eliasson, Muhammad Jawwad Saif, Khurshid Ayub, Opto-electronic properties of non-fullerene fused-undecacyclic electron acceptors for organic solar cells. Comput. Mater. Sci. 159, 150–159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2018.12.009
Muhammad Ans, Mahalingavelar Paramasivam, Khurshid Ayub, Ralf Ludwig, Muhammad Zahid, Xiudi Xiao, Javed Iqbal, Designing alkoxy-induced based high performance near infrared sensitive small molecule acceptors for organic solar cells. J. Mol. Liq 305, 112829 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112829
Acknowledgements
This experimental work was supported by Ramakrishna Mission Residential College under Vivekananda Centre For Research and financially supported by Govt.of West Bengal Science and Technology and Biotechnology Department, memo no.\(461(Sanc)/ST/P/S \& T/16G-19/2018\), West Bengal, India. We would like to thank Dr. A. Singha, Dept. of Physics, Bose Institute, Kolkata, India for providing the required facilities to perform this experimental work. We would also like to thank Dr. Sk Irsad Ali, Dept. of Physics, the University of Burdwan, WB, India for his valuable suggestions on experimental work.
Funding
This experimental work was supported by Ramakrishna Mission Residential College under Vivekananda Centre For Research and financially supported by Govt. of West Bengal Science and Technology and Biotechnology Department, memo no.\(461(Sanc)/ST/P/S \& T/16G-19/2018\), West Bengal, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The contributions of all authors are as follows RHS: Participated in the data curation, experimentation, software, methodology, and writing of the original draft. AB: Participated in the software, reviewing, and analysis. SC: Participated in the supervision, resources, reviewing, methodology, and editing of the manuscript. JCM: Participated in the reviewing and analysis of SEM. SS: Participated in the XRD, reviewing. AKB: Participated in the reviewing and editing of this manuscript. All authors have completely studied this manuscript and finally suggest the published version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors claim that the studies are authentic and that they don’t have any struggle with the hobby.
Ethical approval
This article does no longer incorporates any research on human beings or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sardar, R.H., Bera, A., Chattopadhyay, S. et al. Effect of dopants in the HTL layer on photovoltaic properties in hybrid perovskite solar cells. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2138 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11535-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11535-y