Abstract
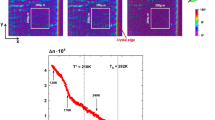
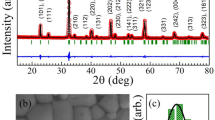
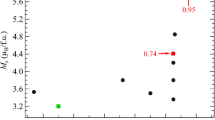
In the present article, we report the magnetic, dielectric, and structural properties of the perovskite Bi0.5La0.5Fe0.4Al0.1Mn0.5O3. The structural analysis shows that this system crystallizes in a disordered orthorhombic phase with the space group Pnma. We found two consecutive magnetic transitions at 42 K and 147 K which have been suggested to be associated with the spin-glass and long-range ordering transitions, respectively. Further, temperature-dependent Raman spectra shows that this system has a spin-phonon coupling. Moreover, the dielectric measurement suggests that this system has a large dielectric constant at ambient temperature. Additionally, the dielectric spectrum suggests an unusual frequency-dependent step-like trend and the presence of weak relaxor ferroelectricity in the system. Thus, the presence of such multiple interesting characteristics suggests that Bi0.5La0.5Fe0.4Al0.1Mn0.5O3 can be used as spintronic devices and high dielectric applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study’s findings are available within the article.
References
A. Kumar, S.D. Kaushik, V. Siruguri, D. Pandey, Evidence for two spin-glass transitions with magnetoelastic and magnetoelectric couplings in the multiferroic (Bi1−xBax)(Fe1−xTix)O3 system. Phys. Rev. B (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.104402
M.K. Singh, W. Prellier, M.P. Singh, R.S. Katiyar, J.F. Scott, Spin-glass transition in single-crystal BiFeO3. Phys. Rev. B 77, 144403 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.77.144403
W.-M. Zhu, H.-Y. Guo, Z.-G. Ye, Structural and magnetic characterization of multiferroic (BiFeO3)1–x(PbTiO3)x solid solutions. Phys. Rev. B 78, 014401 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.014401
S. Chillal, M. Thede, F.J. Litterst, S.N. Gvasaliya, T.A. Shaplygina, S.G. Lushnikov, A. Zheludev, Microscopic coexistence of antiferromagnetic and spin-glass states. Phys. Rev. B 87, 220403 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.87.220403
S.E. Musavi Ghahfarokhi, M.R. Larki, I. Kazeminezhad, The effect of Mn doped on the structural, magnetic, dielectric and optical properties of bismuth ferrite (BiFe1-xMnxO3) nanoparticles. Vacuum 173, 109143 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2019.109143
G. Catalan, Magnetocapacitance without magnetoelectric coupling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 102902 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2177543
S. Kumari, K. Anand, M. Alam, L. Ghosh, S. Ghosh, P. Gupta, R. Singh, A.K. Jain, S.M. Yusuf, A.K. Ghosh, A. Mohan, S. Chatterjee, Spontaneous exchange bias and large dielectric constant in Bi0.8Tb0.2Fe0.8Mn0.2O3 multiferroic. J. Appl. Phys. 132, 183909 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0106110
S. Dong, Y. Yao, Y. Hou, Y. Liu, Y. Tang, X. Li, Dynamic properties of spin cluster glass and the exchange bias effect in BiFeO3 nanocrystals. Nanotechnology 22, 385701 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/22/38/385701
S.M. Yakout, Spintronics: future technology for new data storage and communication devices. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn.Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 2557–2580 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05545-8
M. De, S.P. Patel, H.S. Tewari, Strain induced structural phase transition in NaNbO3 doped BiFeO3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 6928–6935 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6393-9
S.K. Abdel-Aal, A.S. Abdel-Rahman, Graphene influence on the structure, magnetic, and optical properties of rare-earth perovskite. J. Nanopart. Res.Nanopart. Res. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05001-7
S.K. Abdel-Aal, M.F. Kandeel, A.F. El-Sherif, A.S. Abdel-Rahman, Synthesis, characterization, and optical properties of new organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites [(NH3)2(CH2)3]CuCl4 and [(NH3)2(CH2)4]CuCl2Br2. Phys. Status Solid A (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.202100036
S.K. Abdel-Aal, A.I. Beskrovnyi, A.M. Ionov, R.N. Mozhchil, A.S. Abdel-Rahman, Structure investigation by neutron diffraction and X-ray diffraction of graphene nanocomposite CuO–rGO prepared by low-cost method. Phys. Status Solid A. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.202100138
A. Sabry, A. Rahman, A.S. Abdel-Rahman, An approach to the micro-strain distribution inside nanoparticle structure, (2023). https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2281463/v2.
R. Katoch, C.D. Sekhar, V. Adyam, J.F. Scott, R. Gupta, A. Garg, Spin phonon interactions and magnetodielectric effects in multiferroic BiFeO3–PbTiO3. J. Phys. Condens. MatterCondens. Matter. 28, 075901 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/28/7/075901
A. Sarkar, A.K. Singh, D. Sarkar, G.G. Khan, K. Mandal, Three-dimensional nanoarchitecture of BiFeO3 anchored TiO2 nanotube arrays for electrochemical energy storage and solar energy conversion. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 3, 2254–2263 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00519
Y. Li, M. Cao, D. Wang, J. Yuan, High-efficiency and dynamic stable electromagnetic wave attenuation for La doped bismuth ferrite at elevated temperature and gigahertz frequency. RSC Adv. 5, 77184–77191 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15458H
R. Tholkappiyan, K. Vishista, Combustion synthesis of Mg-Er ferrite nanoparticles: cation distribution and structural, optical, and magnetic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process.Semicond. Process. 40, 631–642 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.06.076
K. Anand, A. Pal, A.G. Joshi, P. Pal, R. Singh, P.T.-W. Yen, S.M. Huang, M. Alam, S. Kumari, V. Sathe, S. Chakravarty, A. Mohan, S. Chatterjee, Giant exchange bias in antiferromagnetic Pr2CoFe0.5Mn0.5O6: a structural and magnetic properties study. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 55, 365004 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac79da
M. Alam, L. Ghosh, S. Majumder, P. Singh, S.V. Kumar, S. Dixit, D. Kumar, K. Anand, S. Kumari, A.K. Ghosh, R.J. Choudhary, S. Chatterjee, Multifunctional behaviour in B-site disordered double perovskite EuPrCoMnO6. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 55, 255003 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac5fd4
M. Umar, N. Mahmood, S.U. Awan, S. Fatima, A. Mahmood, S. Rizwan, Rationally designed La and Se co-doped bismuth ferrites with controlled bandgap for visible light photocatalysis. RSC Adv. 9, 17148–17156 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RĂ4F
R. Kumar, P. Yanda, A. Sundaresan, Cluster-glass behavior in the two-dimensional triangular lattice Ising-spin compound Li2Mn3O7. Phys. Rev. B 103, 214427 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.103.214427
K. Binder, A.P. Young, Spin glasses: experimental facts, theoretical concepts, and open questions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 58, 801–976 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.58.801
K. Anand, M. Alam, A. Pal, P. Singh, S. Kumari, A.G. Joshi, A. Das, A. Mohan, S. Chatterjee, Existence of Griffiths phase and unusual spin dynamics in double perovskite Tb2CoMnO6. J. Magn. Magn. Mater.Magn. Magn. Mater. 528, 168–169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167697
M. Alam, P. Singh, K. Anand, A. Pal, S. Ghosh, A.K. Ghosh, R.K. Singh, A.G. Joshi, S. Chatterjee, Extraordinary magnetic properties of double perovskite Eu2CoMnO6 wide band gap semiconductor. J. Phys. Condens. MatterCondens. Matter. 32, 365802 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/ab8ecc
P. Bag, P.R. Baral, R. Nath, Cluster spin-glass behavior and memory effect in Cr0.5Fe0.5Ga. Phys. Rev. B 98, 144436 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.98.144436
K. Anand, A. Pal, A.G. Joshi, P. Pal, R. Singh, P.T.-W. Yen, S.M. Huang, M. Alam, S. Kumari, V. Sathe, S. Chakravarty, A. Mohan, S. Chatterjee, Giant exchange bias in antiferromagnetic Pr2 CoFe0.5 Mn05 O6: a structural and magnetic properties study. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 55, 365004 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac79da
K. Anand, A. Pal, M. Alam, S. Dan, S. Kumar, S. Ghosh, S. Kumari, A. Das, M. Sawada, A. Mohan, V.G. Sathe, Emergence of metamagnetic transition, re-entrant cluster glass and spin phonon coupling in Tb2CoMnO6. J. Phys. Condens. MatterCondens. Matter. 33, 275802 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/abfe94
A. Kumar, S.D. Kaushik, V. Siruguri, D. Pandey, Evidence for two spin-glass transitions with magnetoelastic and magnetoelectric couplings in the multiferroic (B i1–x Bax)(Fe1–x T IX) O3 system. Phys. Rev. B (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.104402
G.R. Haripriya, H.S. Nair, R. Pradheesh, S. Rayaprol, V. Siruguri, D. Singh, R. Venkatesh, V. Ganesan, K. Sethupathi, V. Sankaranarayanan, Spin reorientation and disordered rare earth magnetism in Ho2FeCoO6. J. Phys. Condens. MatterCondens. Matter 29, 475804 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/aa919e
P. Lunkenheimer, V. Bobnar, A.V. Pronin, A.I. Ritus, A.A. Volkov, A. Loidl, Origin of apparent colossal dielectric constants. Phys. Rev. B 66, 052105 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.66.052105
R. Singh, P.K. Gupta, S. Kumar, A.G. Joshi, A.K. Ghosh, S. Patil, S. Chatterjee, Enhancement in electrical and magnetic properties with Ti-doping inBi0.5La0.5Fe0.5Mn0.5O3. J. Appl. Phys.Appl Phys. 121, 154101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4981876
D.N. Dubey, G. Singh, S. Tripathi, Relaxor ferroelectricity driven by ‘A’ and ‘B’ site off-centered displacements in cubic phase with Pm 3− m space group. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 54, 365304 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac0bda
M. Alam, A. Pal, K. Anand, S. Ghosh, S. Tripathi, R.K. Singh, A.K. Ghosh, H.D. Yang, S. Chatterjee, Relaxor–super-paraelectric behaviour and crystal-field–driven spin-phonon coupling in pyrochlore Eu2Ti2O7. Europhys. Lett.. Lett. 137, 26003 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/ac2455
R. Kumar, A. Sundaresan, Multiferroicity in a quasi-one-dimensional magnet MnSb2Se4. Mater. Res. Bull. 145, 111569 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111569
P.K. Gupta, S. Ghosh, S. Kumari, A. Pal, S. Roy, R. Singh, P. Singh, R.K. Singh, A.K. Ghosh, S. Chatterjee, Spin phonon coupling and magneto-dielectric coupling in BiFeO3–TbMnO3 composite. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 086114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab2742
Acknowledgements
The authors express sincere gratitude to the Central Instrumentation Facility Centre, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) for their support of the magnetic measurement facility. Mohd Alam is thankful to the I-DAPT Hub Foundation, IIT (BHU) Varanasi for providing the Chanakya Post-doctoral Fellowship. The measurements were carried out using the Raman spectrometer (Model: In Via, Make-Renishaw, UK) available at the Department of Physics, the University of Calcutta (Procured under DST PURSE, Phase-2 Scheme).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK: conceptualization, data curation, methodology, investigation, software, analysis, and writing—original draft preparation; MA: analysis, software, data curation; SD: data curation, LG: data curation, SG: data curation, PKG: software, JR: sample preparation, KA: software, formal analysis, NR: data curation and SM: data curation, AM: editing, AB: resources and SC: supervision, writing—review & editing, conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to this article’s content.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, S., Alam, M., Dixit, S. et al. Spin-phonon coupling and giant dielectric constant in Bi0.5La0.5Fe0.4Al0.1Mn0.5O3. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2142 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11476-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11476-6