Abstract
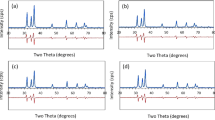
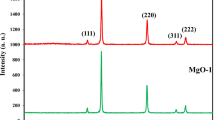
In this study, all \({\mathrm{Zn}}_{1-x}{{\mathrm{Cu}}_{0.05}\mathrm{Mn}}_{x}\mathrm{O}\) QUOTE \({\mathrm{Zn}}_{1-{x}}{{\mathrm{Cu}}_{0.05}\mathrm{Mn}}_{{x}}\mathrm{O}\) QUOTE polycrystalline nanoparticles were produced with various compositions \((0.01<x<0.05)\) QUOTE \((0.01<{x}<0.05)\) QUOTE by using sol–gel techniques. Zinc acetate dihydrate, manganese(II), and Cu(II) acetates were used as the precursors for the solutions. Methanol and acetylacetone were used as solvents while preparing the homogenous solutions. Halder–Wagner method (H–W), Williamson–Hall (W–H), and size–strain plot (SSP) were utilized in order to examine the crystal size and intrinsic strain by X-ray diffraction peak expansion analysis. In addition, different models were developed for the definition of microstructural and physical values including stress, strain, and energy density, in the W–H method. The average crystal sizes determined using W–H, SSP, and H–W methods were compared. The magnetic properties of Cu/Mn-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles were analyzed at room temperature. The highest saturation magnetization (Ms) value was found in the 5% wt Mn doping of ZnO and Ms increased with increasing the Mn doping due to the magnetic (paramagnetic) nature of manganese. In this study, XRD peak broadening analysis has been carried out by different models and X-ray peak profile analysis were used to estimate the physical parameters; different models are modified such as W–H plot, SSP method, and H–W method. D–S method, W–H plot, H–W plot, and SSP technique results were highly intercorrelated.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sharing is not applicable to this article asno datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Z.N. Kayani, T. Afzal, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, Optical and structural properties of thin films of ZnO at elevated temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 606, 177–181 (2014)
Z.N. Kayani, M. Iqbal, S. Riaz, R. Zia, S. Naseem, Fabrication and properties of zinc oxide thin film prepared by sol-gel dip coating method. Mater. Sci. Pol. 33, 515–520 (2015)
Z.N. Kayani, F. Saleemi, I. Batool, Effect of calcination temperature on the properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 119, 713–720 (2015)
K.C. Barick, S. Singh, M. Aslam, D. Bahadur, Porosity and photocatalytic studies of transition metal doped ZnO nanoclusters. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 134, 195 (2010)
K. Kaviyarasua, C.M. Magdalanec, K. Kanimozhie, J. Kennedya, B. Siddhardhag, E.S. Reddyh, N.K. Rottei, C.S. Sharmai, F.T. Themaa, D. Letsholathebej, G.T. Molak, M. Maaza, Elucidation of photocatalysis, photoluminescence and antibacterial studies of ZnO thin films by spin coating method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 173, 466–475 (2017)
F. Meng, J. Yin, Y.Q. Duan, Z.H. Yuan, L.J. Bie, Co-precipitation synthesis and gas-sensing properties of ZnO hollow sphere with porous shell. Sens. Actuators B 156, 703 (2011)
B. Sathyaseelan, E. Manikandan, K. Sivakumar, J. Kennedy, M. Maaza, Enhanced visible photoluminescent and structural properties of ZnO/KIT-6 nanoporous materials for white light emitting diode (w-LED) application. J. Alloys Compd. 651, 479–482 (2015)
J. Kennedy, P.P. Murmua, J. Leveneura, A. Markwitza, J. Futteraa, Controlling preferred orientation and electrical conductivity of zinc oxide thin films by post growth annealing treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 367, 52–58 (2016)
J. Kennedy, A. Markwitz, Z. Li, W. Gao, C. Kendrick, S.M. Durbin, R. Reeves, Modification of electrical conductivity in RF magnetron sputtered ZnO films by low-energy hydrogen ion implantation. Curr. Appl. Phys.. Appl. Phys. 6, 495–498 (2006)
J. Kennedy, P.P. Murmu, J. Leveneur, M.V. Williams, L.R. Moody, T. Maity, V.S. Chong, Enhanced power factor and increased conductivity of aluminum doped zinc oxide thin films for thermoelectric applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol.Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18, 1384–1387 (2018)
Z. Liu, C. Liu, J. Ya, E. Lei, Controlled synthesis of ZnO and TiO2 nanotubes by chemical method and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Renew. Energy 36, 1177 (2011)
Z. Jin, T. Fukumura, M. Kawasaki, K. Ando, H. Saito, T. Sekiguchi, Y. Yoo, M. Murakami, Y. Matsumoto, T. Hasegawa, High throughput fabrication of transition-metaldoped epitaxial ZnO thin films: A series of oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors and their properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 3824–3826 (2001)
F. Pan, C. Song, X. Liu, Y. Yang, F. Zeng, Ferromagnetism and possible application in spintronics of transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Reports 62, 1–35 (2008)
S. Singh, M.R. Rao, Optical and electrical resistivity studies of isovalent and aliovalent 3 d transition metal ion doped ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 80, 045210 (2009)
S. Singhal, J. Kaur, T. Namgyal, R. Sharma, Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles: synthesis, structural and electrical properties. Physica B 407, 1223–1226 (2012)
H. Liu, J. Yang, Y. Zhang, L. Yang, M. Wei, X. Ding, Structure and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO prepared by the sol–gel method. J. Phys. Condens. MatterCondens. Matter 21, 145803 (2009)
P.G. Undre, P.B. Kharat, R. Kathare, K. Jadhav, Ferromagnetism in Cu 2+ doped ZnO nanoparticles and their physical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 4014–4025 (2019)
D. Raoufi, Synthesis and microstructural properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by precipitation method. Renew. Energy 50, 932 (2013)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohamad, M.S. Takriff, K. Sopian, Optimization of process parameters using D-optimal design for synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via sol–gel technique. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19, 99 (2013)
T. Wangensteen, T. Dhakal, M. Merlak, P. Mukherjee, M.H. Phan, S. Chandra, H. Srikanth, S. Witanachchi, Growth of uniform ZnO nanoparticles by a microwave plasma process. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6859 (2011)
B. Woeichieng, Y.Y. Loo, Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by modified polyol method. Mater. Lett. 73, 78 (2012)
P. Rai, Y.-T. Yu, Citrate-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of single crystalline ZnO nanoparticles for gas sensor application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 173, 58 (2012)
M. Vaghayenegar, A. Kermanpur, M.H. Abbasi, Bulk synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by the one-step electromagnetic levitational gas condensation method. Ceram. Int. 38, 5871 (2012)
Y. Liu, Y. Yang, J. Yang, Q. Guan, H. Liu, L. Yang, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, M. Wei, X. Liu, L. Fei, X. Cheng, Intrinsic ferromagnetic properties in Cr-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Solid State Chem. 184, 1273 (2011)
R. Saleh, N.F. Djaja, S.P. Prakoso, The correlation between magnetic and structural properties of nanocrystalline transition metal-doped ZnO particles prepared by the co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 546, 48 (2012)
F. Ahmed, S. Kumar, N. Arshi, M.S. Anwar, B.H. Koo, C.G. Lee, Doping effects of Co2+ ions on structural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Microelectron. Eng.. Eng. 89, 129 (2012)
R. Narzary, B. Dey, S.N. Rout, A. Mondal, G. Bouzerar, M. Kar, S. Ravi, S.K. Srivastava, Influence of K/Mg co-doping in tuning room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, optical and transport properties of ZnO compounds for spintronics applications. J. Alloys Compd. 934, 167874 (2023)
B. Dey, R. Narzary, S.K. Panda, J. Mallick, A. Mondal, S. Ravi, M. Kar, S.K. Srivastava, Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, band-gap reduction, and high optical transparency in p-type K-doped ZnO compounds for spintronics applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. Process. 148, 106798 (2022)
B. Dey, R. Narzary, L. Chouhan, S. Bhattacharjee, B.N. Parida, A. Mondal, S. Ravi, S.K. Srivastava, Crystal structure, optical and dielectric properties of Ag:ZnO composite-like compounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 2855–2868 (2022)
L. Chouhan, G. Bouzerar, S.K. Srivastava, d0 ferromagnetism in Li-doped ZnO compounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 6389–6397 (2021)
B. Dey, S. N. Rout, M. Kar, S. K. Srivastava, Room Temperature d0 Ferromagnetism of Ag:ZnO Compounds, Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism 36, 657–663 (2023).
V.D. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B.N. Dole, Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theoret. Appl. Phys. 6, 6 (2012)
E. Emil, S. Gürmen, Estimation of yttrium oxide microstructural parameters using the Williamson-Hall analysis. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 1549–1557 (2018)
D. Nath, F. Singh, R. Das, X-ray diffraction analysis by Williamson-Hall, Halder-Wagner and size-strain plot methods of CdSe nanoparticles- a comparative study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 239, 122021 (2020)
S. Sarkar, R. Das, Determination of structural elements of synthesized silver nano-hexagon from X-ray diffraction analysis. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 56, 765–772 (2018)
S. Sarkar, R. Das, Shape effect on the elastic properties of Ag nanocrystals. Micro Nano Lett. 13, 312–315 (2018)
D. Balzar, H. Ledbetter, Voigt-function modeling in fourier analysis of size- and strain-broadened X-ray diffraction peaks. J. Appl. Crystallogr.Crystallogr. 26, 97–103 (1993)
A. Hepp, C. Baerlocher, Learned peak shape functions for powder diffraction data. Aust. J. Phys. 41, 229–236 (1988)
N.C. Halder, C.N.J. Wagner, Separation of particle size and lattice strain in integral breadth measurements. Acta Crystallogr. Crystallogr. 20, 312–331 (1966)
S. Gopinath, JohnPhilip, Preparation of metal oxide nanoparticles of different sizes and morphologies, their characterization using small angle X-ray scattering and study of thermal properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 145, 213–221 (2014)
A.C. Murrieta, D. Cavazos-Cavazos, P. Santos-Aguilar, J.L. Cholula-Díaz, F.F. Contreras-Torres, Microstructure of polycrystalline gold nanoparticles and thin-films from a comparative X-ray line profile analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 258, 123976 (2021)
M. Shobana, S.R. Meher, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of cobalt-doped ZnTe dilute magnetic semiconductors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 15140–15152 (2020)
Z.N. Kayani, A. Usman, H. Nazli, R. Sagheer, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, Dielectric and magnetic properties of dilute magnetic semiconductors Ag-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 126, 559 (2020)
H.B. Wang, H. Wang, C. Zhang, F.J. Yang, J.X. Duan, C.P. Yang, H.S. Gu, M.J. Zhou, Q. Li, Y. Jiang, Preparation and Characterization of Mn and (Mn, Cu) Co-Doped ZnO Nanostructures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol.Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 3308–3312 (2009)
A.A. Dakhel, Study of structural, optical and magnetic properties of hydrogenated Ni and (Ga, Zn) co-doped SnO2 nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 252, 123163 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Kastamonu University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Department under the Grant No. KÜ-BAP01/2020-75, KÜ-BAP01/2019-64 and Kastamonu University Research and Application Center for the supports.
Funding
Kastamonu Üniversitesi, KÜ-BAP01/2019–64, O. Ozturk, KÜ-BAP01/2020–75, Elif Asikuzun.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed sufficiently in the planning, execution, or analysis of this study to be included as authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
This material is the authors’ own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. The paper reflects the authors’ own research and analysis in a truthful and complete manner. The results are appropriately placed in the context of prior and existing research. All authors have been personally and actively involved in substantial work leading to the paper and will take public responsibility for its content.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tokeser, E.A., Ozturk, O. Estimation of microstructural parameters by Williamson–Hall, Halder–Wagner, and size–strain plot methods and magnetic properties of (Cu/Mn) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2075 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11402-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11402-w